Introduction
Data encryption converts plain text or data into a coded form, which authorized individuals with the decryption key can only read. Encryption protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, or interception. It ensures that data remains confidential, secure, and protected from cyber threats.
Importance Of Data Security
Data security is crucial for any organization or individual handling sensitive information. Protecting data from unauthorized access, theft, or loss is essential to maintain the trust and confidence of customers, partners, and stakeholders. Encryption is vital in ensuring data security, making it difficult for hackers to access or steal data.
Encryption helps to protect data in transit, such as emails, online transactions, and data transfers, by making it problematic for cybercriminals to intercept and read the information. It also protects data at rest, such as stored files, by making it unreadable to anyone who does not have the decryption key.
Why Is It Important To Encrypt Files/Data?
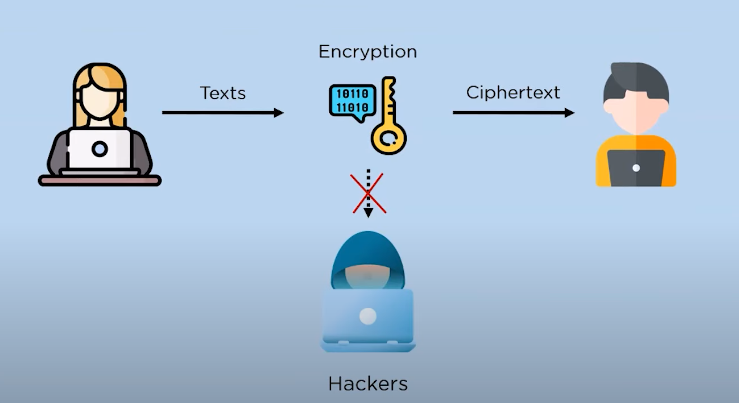
Encrypting files and data is important because it helps to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information. When data is encrypted, it becomes unreadable to unauthorized users or hackers, which helps to prevent data breaches and identity theft. Encryption also helps to protect information from being intercepted or tampered with during transmission, which is particularly important for sensitive data such as financial or medical records. Overall, encryption is a critical tool for maintaining the security and privacy of digital information.
Threats To Data Security
Data security is a serious concern for individuals and organizations alike. Several common threats to data security can compromise the privacy, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. Cyberattacks are one of the most common threats to data security. These attacks can take various forms, including malware, phishing, and ransomware. Malware is malicious software that can infect computers and other devices, allowing cybercriminals to steal sensitive data or take control of the device. Phishing is a social engineering attack that associates tricking individuals into providing sensitive data, such as passwords or credit card numbers. Ransomware is malware that encrypts data and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key.
Data breaches are another common threat to data security. A data breach occurs when illegal individuals access or steal sensitive information. This can happen for several reasons, including weak passwords, unsecured networks, or vulnerabilities in software or hardware.
Insider threats are also a significant concern for data security. These threats come from individuals within an organization who have authorized access to sensitive information. Insider threats can be intentional, like when an employee steals data for personal gain, or unintentional, like when an employee accidentally shares sensitive information.
Statistics On The Prevalence And Cost Of Data Breaches

According to an IBM Security and Ponemon Institute report, the average data breach cost in 2020 was $3.86 million. The report also originated that the average time to recognize and contain a data breach was 280 days, which can significantly increase the cost of the breach. In 2020, the healthcare industry had the highest cost per record breached at $7.13, followed by the financial sector at $5.85 per record breached. The report also found that malicious attacks were the most common reason for data breaches, accounting for 52% of all incidents.
Another report by Verizon found that 45% of data breaches in 2020 involved hacking, 22% involved phishing, and 17% involved malware. The report also found that cybercriminals increasingly targeted small businesses, with 28% of breaches involving organizations with fewer than 100 employees.
What Is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of converting plain text into a coded message, also known as cipher text, to protect the confidentiality and integrity of data. The purpose of data encryption is to ensure that sensitive information remains secure and unreadable to unauthorized users or hackers. Encryption algorithms use complex mathematical formulas to scramble data, making it unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. This helps to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft.
Explanation Of How Encryption Can Help Mitigate These Threats
Encryption can be a powerful tool in mitigating the threats of data breaches. By encrypting sensitive data, organizations can make it much more difficult for cybercriminals to access and use that data even if they manage to breach the organization’s defenses. Encryption works by converting the data into a code that can only be decoded with a specific key. This means that even if a hacker can access encrypted data, they won’t be able to read or use it without the key. In addition to encryption, organizations can also implement other security measures such as multi-factor authentication, regular employee training on cybersecurity best practices, and robust backup and recovery systems. By taking proactive access to data security, organizations can minimize the opportunities for data breaches and the potential financial and reputational damage resulting from such incidents.
Benefits Of Data Encryption
Data encryption offers several benefits for organizations, including:
1. Protection of sensitive information: Encryption ensures that sensitive data such as financial records, personal information, and trade secrets are protected from unauthorized access.
2. Compliance with regulations: Many industries are subject to strict data safety regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare organizations and GDPR for businesses operating within the European Union. Encryption can help organizations comply with these regulations and avoid costly fines.
3. Increased customer trust: By implementing strong encryption measures, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to protecting their customers’ data, which can help build trust and loyalty.
4. Prevention of data breaches: Encryption makes it much more difficult for hackers to access and steal sensitive information, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Encryption Best Practices
Here are some best practices for implementing encryption in an organization:
1. Use strong encryption algorithms: Make sure to use encryption algorithms that are considered strong and secure, such as AES-256.
2. Implement encryption at all levels: Encrypt data at rest, in transit, and in use to ensure complete protection.
3. Use secure key management: Proper key management is essential to ensure the security of encrypted data. Keys should be stored securely and only accessible to authorized personnel.
4. Regularly update encryption protocols: Keep up-to-date with the latest encryption protocols and update them regularly to ensure maximum security.
5. Conduct regular security audits: Regularly audit your encryption practices to identify any vulnerabilities and ensure that encryption is implemented correctly.
By following these practices, organizations can protect their data from unauthorized access and theft.
Encryption Challenges And Limitations
While encryption is a powerful tool for protecting data, it has challenges and limitations. Here are a few:
1. Key management: Encryption relies on keys to encrypt data. Managing these keys can be complex, especially in large organizations with many users and devices.
2. Performance impact: Encryption can impact systems, especially when dealing with large amounts of data. This can be mitigated by using hardware-based encryption or optimizing software-based encryption.
3. Compatibility issues: Encryption protocols and algorithms can vary between systems and devices, which can cause compatibility issues when trying to share encrypted data.
4. Vulnerabilities: Encryption is not foolproof and can be vulnerable to brute force attacks, side-channel attacks, and others.
5. Legal and regulatory requirements: Depending on the industry and location, there may be legal and regulatory requirements for data encryption that organizations must comply with.
Despite these challenges and limitations, encryption remains an important tool for protecting sensitive data and ensuring privacy.
Encryption In Different Industries
Encryption is used in various industries to protect sensitive data and ensure privacy. Some industries that heavily rely on encryption include:
1. Healthcare: Healthcare organizations use encryption to protect patient data and comply with regulations like HIPAA.
2. Finance: Financial institutions use encryption to secure financial transactions, protect customer data, and comply with regulations such as PCI DSS.
3. Government: Government agencies use encryption to protect classified information, secure communications, and prevent cyber attacks.
4. Technology: Technology companies use encryption to protect intellectual property, secure user data, and prevent unauthorized access.
5. Legal: Law firms use encryption to protect sensitive client information and maintain client confidentiality.
The Future Of Encryption
The future of encryption looks promising as more and more industries recognize the importance of protecting sensitive data. Technological advancements have made encryption methods more sophisticated and harder to crack. However, there are also issues about the potential misuse of encryption by criminals and terrorists. Governments and tech companies are working to balance privacy and security while addressing these concerns. Encryption will likely continue to play a crucial role in protecting sensitive information and maintaining privacy in the future.
Myths And Misconceptions About Encryption
Encryption is a complex topic that is often misunderstood. Here are common myths and misconceptions about encryption:
1. Encryption Is Only For Criminals And Hackers
This is not true. Individuals, businesses, and governments use encryption to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. It is a crucial tool for maintaining privacy and security in the digital age.
2. Encryption Is Unbreakable
While encryption methods are becoming more sophisticated, they are not completely unbreakable. With enough time and resources, even the strongest encryption can be cracked. However, the goal of encryption is to make it difficult and time-consuming for attackers to access sensitive information.
3. Encryption Is Only Used For Online Communication
Encryption is not limited to online communication. It can also protect data stored on computers, smartphones, and USB drives.
4. Tech-Savvy Individuals Only Use Encryption
Encryption is becoming more widespread and user-friendly. Many popular messaging apps, such as WhatsApp and Signal, use end-to-end encryption by default. This means that even users who are not tech-savvy can benefit from encryption.
5. Encryption Is Illegal
Encryption is legal in most countries. However, some countries have laws restricting the use or export of encryption technology. It is important to check your country’s laws and regulations regarding encryption before using it. In general, encryption is widely accepted and encouraged as a way to protect sensitive data and communications.
How To Encrypt Data: A Step-By-Step Guide
Encrypting data can be a simple process with the right tools. Here is a step-by-step guide to encrypting your data:
1. Choose an encryption tool: There are many encryption tools available, such as VeraCrypt, BitLocker, and FileVault. Choose the tool that best suits your requirements and download it.
2. Install the encryption tool: Follow the installation instructions to install the encryption tool on your device.
3. Create an encrypted container: Open the encryption tool and create an encrypted container or volume. This is where you will store your encrypted data.
4. Choose a strong password: Choose a password that is problematic to guess and contains a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
5. Add data to the encrypted container: Add your sensitive data to it once the encrypted container is created.
6. Encrypt the data: Use the encryption tool to encrypt the data in the container. This process may take time, depending on how much data you encrypt.
7. Store the encrypted container: Once the data is encrypted, store the encrypted container in a safe location, like an attached hard drive or cloud storage service.
By following these steps, you can encrypt your sensitive data and protect it from unauthorized.
Encryption Vs Decryption
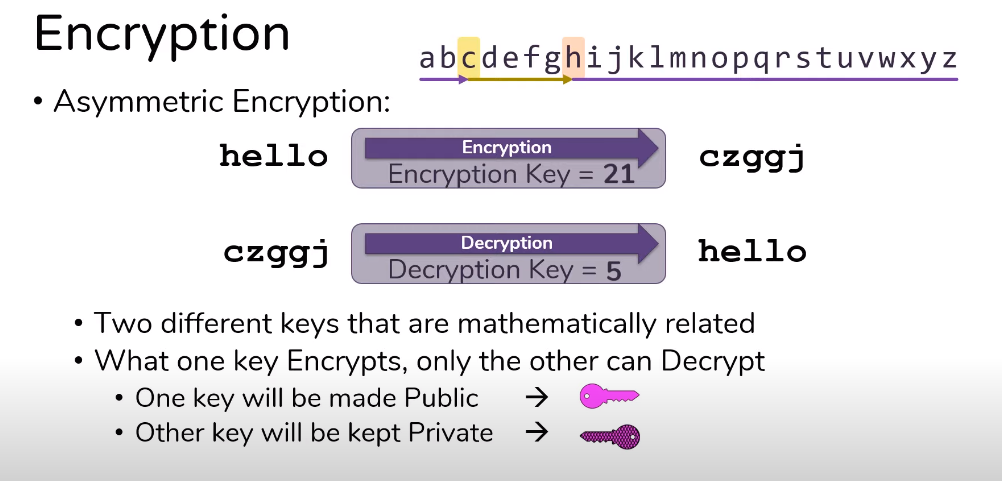
Encryption and decryption are two processes that are related to data security. Encryption converts plain text or data into an unreadable format, called ciphertext, using an encryption algorithm and a key. The purpose of encryption is to safeguard the privacy of the data by making it unreadable to unauthorized users. Decryption, conversely, is the process of converting the ciphertext back to its original form, called plaintext, using a decryption algorithm and the corresponding key. The purpose of decryption is to make the data readable again for authorized users. In summary, encryption is used to protect data confidentiality, while decryption is used to restore data readability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption uses an algorithm to scramble the original data, or plaintext, into an unreadable form called ciphertext. This is done using a key, a unique code used to encrypt and decrypt the data. The key is kept secret and is only known by the authorized parties who need to access the data. Deciphering the ciphertext and accessing the original data is virtually impossible without the key.
What Types Of Data Should Be Encrypted?
Sensitive or confidential data should be encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access or theft. This includes personal information such as social security numbers, financial information such as bank account numbers and credit card details, medical records, and any other data that could be used for identity theft or fraud. Additionally, any data subject to regulatory requirements or industry standards, such as payment card information under the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), should be encrypted.
Is Encryption 100% Secure?
Encryption is not 100% secure, as there is always a possibility that the encryption algorithm or key could be compromised. However, encryption protects sensitive data and significantly minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or theft. It is important to use strong encryption methods and regularly update encryption keys to ensure maximum security. Additionally, implementing other security measures, such as access controls and monitoring, can further enhance the protection of sensitive data.
Conclusion
Encryption is a powerful tool for defending sensitive information from unauthorized access or theft. While there is always a risk of compromise, using strong encryption methods and regularly updating encryption keys can greatly enhance security. It is also important to implement additional security measures, such as access controls and monitoring, to reduce the risk of data breaches.
As individuals and organizations continue to rely on digital data storage and communication, it is crucial to prioritize data security. One of the most effective methods to do this is through encryption. Using encryption methods to protect sensitive information can greatly minimize the risk of data breaches and theft. It is important to stay up-to-date on the latest encryption technologies and best practices and to review and update your security measures regularly. Let us all commit to prioritizing data security through encryption and take steps to protect our valuable information.
