Understanding Data Confidentiality
Data confidentiality refers to the protection of sensitive data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or use. This is important because sensitive data can include personal or financial information, trade secrets, or confidential business information that, if accessed by unauthorized parties, could result in significant harm to individuals or organizations. To ensure data confidentiality, there are several measures that can be taken, including implementing strong access controls, such as passwords, encryption, and multi-factor authentication.
Data Confidentiality in Maintaining Organizational Integrity
Data confidentiality plays a crucial role in maintaining organizational integrity. It ensures that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. By implementing measures to maintain data confidentiality, organizations can build trust with their customers, partners, and stakeholders. It also helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements related to data privacy and security. Failure to maintain data confidentiality can result in reputational damage, financial losses, and legal liabilities.
The Human Element: Insider Threats

Maintaining data confidentiality is crucial for any organization, and one of the biggest threats to data security comes from insider threats. These are individuals who have authorized access to sensitive information but may misuse it intentionally or unintentionally. This could include employees, contractors, or even third-party vendors who have access to the organization’s systems. To mitigate the risk of insider threats, organizations should implement strict access controls and limit access to sensitive information only to those who need it to perform their job duties.
Malicious Intent And Accidental Breaches
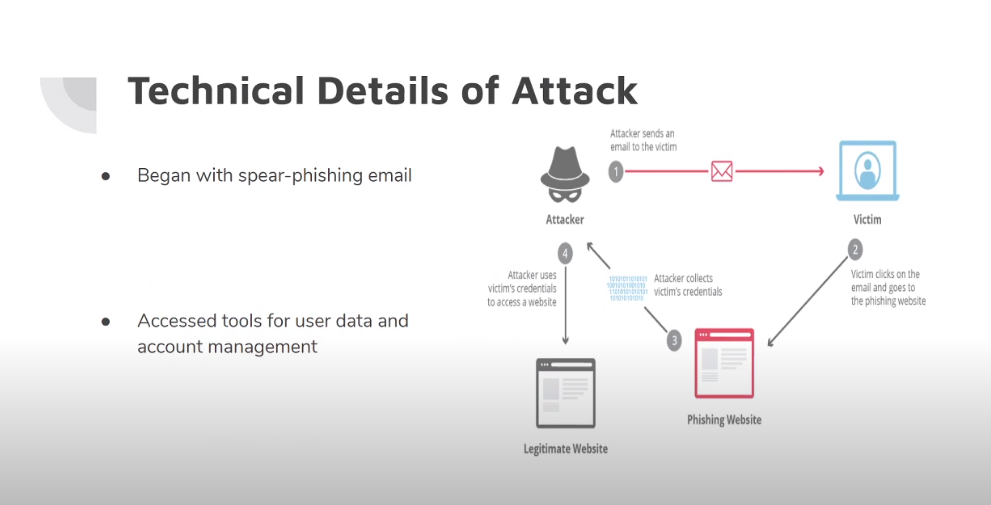
Insider threats can come in two forms: malicious intent and accidental breaches. Malicious intent involves individuals who intentionally misuse sensitive information for their own personal gain or to harm the organization. Accidental breaches, on the other hand, occur when individuals who have access to sensitive information inadvertently expose it through careless actions such as leaving their computer unlocked or sending an email to the wrong recipient.
Case Studies Highlighting Insider Threats
Sure, here are a few case studies that highlight insider threats:
1. Edward Snowden: In 2013, Edward Snowden, a contractor for the National Security Agency (NSA), leaked classified information to the media. He had access to sensitive information due to his job and intentionally leaked it to expose what he believed were illegal surveillance practices by the government.
2. Equifax: In 2017, Equifax suffered a massive data breach that exposed the personal information of over 143 million people.
Cyber Attacks: External Intrusions
Here are some examples of cyber-attacks that highlight external intrusions:
1. Target: In 2013, Target experienced a data breach that compromised the personal information of 110 million customers. The attackers gained access to Target’s network through a third-party vendor that had access to the retailer’s systems.
2. Yahoo: In 2013 and 2014, Yahoo suffered two separate data breaches that compromised the personal information of all 3 billion of its user accounts.
Cyber Attacks Targeting Data Confidentiality

There are several types of cyber attacks that can target data confidentiality, including:
1. Malware: Malware is a type of software that is designed to gain unauthorized access to a computer system or network. Once installed, malware can steal sensitive data or allow attackers to gain control of the system.
2. Phishing: Phishing is a type of social engineering attack where attackers trick users into revealing sensitive information by posing as a trustworthy entity, such as a bank or email provider.
3. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are long-term, targeted attacks that are designed to gain access to sensitive data. They often involve multiple stages and can be difficult to detect and remove.
4. Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. It can cause significant damage to a company’s data and reputation.
Inadequate Encryption Practices
Inadequate encryption practices can also pose a significant threat to a company’s data security. Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. If a company’s encryption practices are inadequate, its sensitive data may be vulnerable to theft or exposure. This can lead to significant financial and reputational damage for the company. It’s important for companies to regularly review and update their encryption practices to ensure that their data remains secure.
Insider Trading and Espionage
Insider trading and espionage are also major threats to a company’s security. Insider trading occurs when an employee or someone with access to confidential information uses that information to make trades on the stock market. This can lead to significant financial losses for the company and legal consequences for the individual involved. Espionage involves the theft of sensitive information by a competitor or foreign entity. This can include trade secrets, intellectual property, and other confidential data.
The Impact of Confidential Information Leaks
Confidential information leaks can have a significant impact on a company, both financially and reputation-wise. When confidential information is leaked, it can result in financial losses due to insider trading, as well as damage the company’s reputation and customer trust. It can also lead to legal consequences, such as lawsuits or regulatory fines. Additionally, the theft of sensitive information through espionage can lead to a loss of competitive advantage, as competitors can use the stolen information to gain an edge in the market.
Notable Cases Involving Insider Trading And Espionage
There have been several high-profile cases involving insider trading and espionage. One notable case is the Martha Stewart insider trading scandal, where the businesswoman was convicted of insider trading and sentenced to five months in prison. Another example is the case of former Goldman Sachs employee, Rajat Gupta, who was convicted of insider trading and sentenced to two years in prison. In terms of espionage, one notable case is the theft of trade secrets from DuPont by a former employee who sold the information to a Chinese company.
Cloud Security Concerns
Cloud security concerns have become increasingly important as more companies move their data and applications to the cloud. One of the main concerns is the risk of data breaches, as cloud providers may be vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Additionally, there are concerns about the security of data in transit and at rest, as well as the potential for unauthorized access to sensitive information. To address these concerns, companies can implement strong security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Mobile Device Risks
Mobile devices have become an integral part of our lives, but they also pose a significant security risk. With the increasing use of mobile devices for work purposes, sensitive company information can be easily accessed and compromised if proper security measures are not in place. One of the main risks is the loss or theft of devices, which can lead to unauthorized access to company data. Another risk is the use of unsecured public Wi-Fi networks, which can expose devices to malware and other security threats.
Data Leakage, Unauthorized Access, And Mobile Malware
These are some of the major security risks associated with the use of mobile devices for work purposes. These risks can result in significant financial losses, damage to the company’s reputation, and legal issues. To mitigate these risks, it is important for companies to implement strong security measures such as encryption, password protection, and remote wiping of devices in case of loss or theft. Employees should also be trained on safe mobile device usage and encouraged to use secure networks and avoid downloading suspicious apps or opening emails from unknown sources.
Incidents Involving Mobile Device Breaches
It has become increasingly common in recent years, highlighting the importance of implementing effective security measures. These incidents can lead to significant financial losses, damage to a company’s reputation, and legal issues, making it essential for businesses to prioritize mobile device security. To minimize the risk of breaches, companies should consider implementing encryption and password protection on all mobile devices used for work purposes. In the event of loss or theft, remote wiping capabilities should also be enabled to ensure sensitive data does not fall into the wrong hands.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mobile device security is crucial for businesses that rely on technology to conduct their operations. With the increasing use of mobile devices in the workplace, the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks is higher than ever before. To protect sensitive information and prevent financial losses, companies should prioritize mobile device security by implementing encryption, password protection, and remote wiping capabilities. By taking these measures, businesses can ensure that their mobile devices are secure and that their data remains protected at all times.
