Overview of Data Security And The Importance of Restricting Access
Data security refers to the protection of digital information from unauthorized access, theft, or damage. It is essential to restrict access to sensitive data to prevent it from falling into the wrong hands. This includes limiting access to confidential information such as financial records, personal information, and trade secrets. Restricting access to data involves implementing security measures such as passwords, encryption, and firewalls. These measures help to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
Role of Security Concepts in Ensuring Data Confidentiality
Security concepts play a crucial role in ensuring data confidentiality. By implementing security measures such as passwords, encryption, and firewalls, organizations can restrict access to sensitive data and prevent it from falling into the wrong hands. Passwords, for example, can ensure that only authorized personnel can access confidential information. Encryption can protect data by converting it into code that can only be deciphered with a specific key. Firewalls can also be used to prevent unauthorized access to a network and protect against cyber attacks.
Authentication: The First Line of Defense
Authentication is an essential component of data security. It involves verifying the identity of users who are attempting to access sensitive information. By requiring users to provide a username and password, organizations can ensure that only authorized personnel can access confidential data. Two-factor authentication, which requires users to provide a second form of identification in addition to a password, can provide an extra layer of security.
Concept of Authentication And Its Role in Data Access Security
Authentication is a crucial component of data security that helps to verify the identity of users who are attempting to access sensitive information. The process involves requiring users to provide a username and password, which helps to ensure that only authorized personnel can access confidential data. Authentication helps to prevent unauthorized access to data, which can result in data breaches, identity theft, and other security threats. By requiring users to provide a password, organizations can ensure that only those who have been granted access can view or modify sensitive information.
Types of Authentication Methods
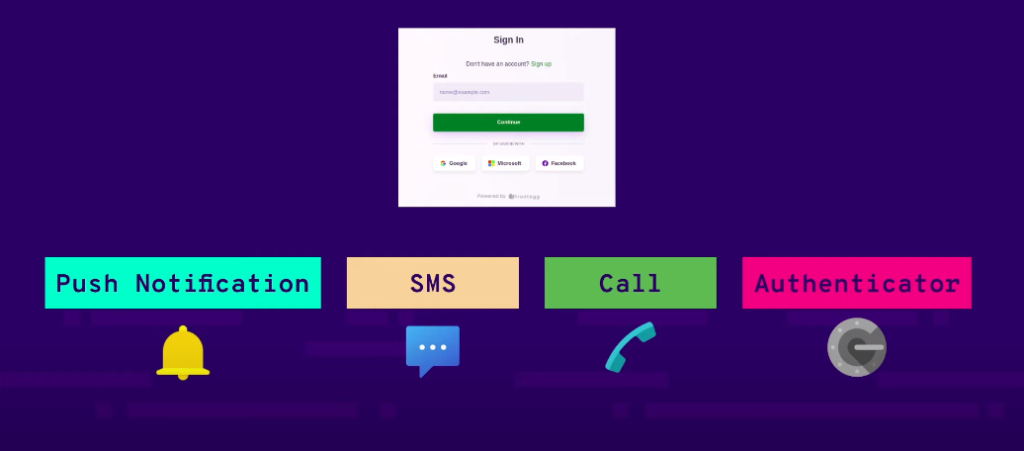
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device. There are several methods of authentication, including:
1. Passwords: This is the most common method of authentication, where users are required to enter a unique combination of characters (letters, numbers, and symbols) to access a system or application.
2. Biometrics: This method uses unique physical characteristics of a person, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, to verify their identity.
3. Two-factor authentication: This method requires users to provide two forms of identification, such as a password and a security token or biometric scan, to access a system or application.
Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and organizations may choose to use a combination of methods to provide the best possible security for their data and systems.
Authorization: Granting Permission
Authorization is the process of granting permission to a user or group of users to access specific resources or perform certain actions within a system or application. This is often done through the use of access controls, which can be implemented at various levels, such as network, application, or database. Authorization can be based on a variety of factors, such as user roles, job functions, or specific tasks.
Process of Granting Access Privileges to Authorized Parties
It is a crucial aspect of information security. It ensures that only those who have a legitimate need to access certain resources or perform certain actions are allowed to do so, and helps to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents. Several different types of authorization methods can be used, including role-based access control (RBAC), attribute-based access control (ABAC), and discretionary access control (DAC).
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
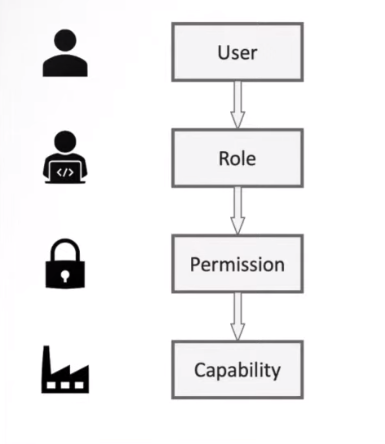
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a widely used authorization method in which access to resources is based on the roles that individuals or groups have within an organization. In RBAC, users are assigned roles based on their job responsibilities and permissions are granted based on those roles. For example, a user with the role of “manager” may have access to certain sensitive data, while a user with the role of “employee” may only have access to non-sensitive data.
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)

Discretionary Access Control (DAC) is another type of access control method that allows the owner of a resource to determine who can access it and what level of access they have. In DAC, the owner of a resource can grant or revoke access to other users or groups, and can also specify what actions those users or groups are allowed to perform on the resource. For example, a file owner may grant read access to some users and write access to others or may restrict access to certain users.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Mandatory Access Control (MAC) is a type of access control method that is typically used in high-security environments such as government agencies or military installations. In MAC, access to resources is determined by a set of rules or policies that are defined by a system administrator or security officer. These policies are based on the security clearance level of the user, the sensitivity of the resource, and other factors.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) is a type of access control method that uses attributes to determine whether a user should be granted access to a resource. These attributes can include user identity, role, location, time of day, and other factors. ABAC policies are typically defined using a rules engine, which evaluates the attributes of a user and the resource being accessed to determine whether access should be granted or denied.
Network Access Control (NAC)

Network Access Control (NAC) is a security solution that enforces policies to control access to a network. NAC solutions typically involve a combination of hardware and software components that work together to authenticate users and devices, check their compliance with security policies, and grant or deny access accordingly. NAC can be used to enforce policies such as requiring the use of up-to-date antivirus software, verifying the identity of users and devices, and restricting access to sensitive resources.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the primary goal of data access security?
The primary goal of data access security is to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction. This can be achieved through various security measures such as authentication, authorization, encryption, and monitoring. The ultimate aim is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data, and to prevent any breaches or data loss that could harm the organization or its clients.
How does authentication differ from authorization?
Authentication and authorization are two distinct but related concepts in data access security. Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or system attempting to access a resource. This is typically done through a login process where the user provides a username and password or other credentials to prove their identity. Authorization, on the other hand, is the process of determining whether a user or system has the necessary permissions and privileges to access a particular resource or perform a specific action.
What is the main difference between RBAC and DAC?
The main difference between Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Discretionary Access Control (DAC) is the way permissions are assigned and managed. In RBAC, access to resources is based on a user’s role within an organization. Permissions are assigned to roles, and users are assigned to those roles. (https://store.spaceylon.com) This makes it easier to manage permissions for large organizations with many users and resources, as permissions can be assigned at the role level rather than for each user.
How does a VPN contribute to secure data access?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, contributes to secure data access by encrypting all data that is transmitted between the user’s device and the VPN server. This means that any data that is intercepted by unauthorized parties will be unreadable and useless. Additionally, a VPN can provide an added layer of security by masking the user’s IP address, making it more difficult for hackers to target the user’s device.
What are the benefits of implementing Single Sign-On (SSO)?
Implementing Single Sign-On (SSO) has several benefits, including:
1. Improved User Experience: SSO allows users to access multiple applications and services with a single set of login credentials, eliminating the need to remember multiple usernames and passwords. This simplifies the login process and improves the overall user experience.
2. Increased Security: SSO reduces the risk of password-related security breaches by eliminating the need for users to remember and manage multiple login credentials.
