Introduction
Data security is a crucial aspect of any organization that deals with sensitive information. In today’s world, data breaches have become more common, and organizations must take the necessary measures to safeguard their data. Safeguarding data is a comprehensive process that involves implementing policies, procedures, and controls that protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, destruction or modification.
The purpose of this guide is to provide a comprehensive overview of data security policy and its importance in protecting critical information. The guide will cover different aspects of data security policy such as defining what constitutes sensitive information; the legal requirements for securing sensitive information; the risks associated with not having adequate data security policies; how to develop effective data security policies; and tips for implementing these policies within an organization.
Understanding Data Security
What Is Data Security?
Data security refers to the measures taken to protect digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, theft or damage. Data security involves protecting sensitive and confidential information such as financial records, personal details, credit card information, trade secrets or intellectual property. The goal of data security policies is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data. Confidentiality means that only authorized personnel can access the data; integrity ensures that the data is accurate and has not been tampered with; availability means that authorized users can access the data when needed.
Why is Data Security Important?

Data security helps prevent cyber-attacks and data breaches that can compromise sensitive information such as personal details, financial records, and intellectual property. These attacks can lead to serious consequences for individuals and organizations alike ranging from reputational damage to financial loss.
Adhering to data security policies also ensures compliance with legal regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which require companies to safeguard customer information adequately. This enhances customer trust in companies’ ability to handle their personal data responsibly.
Data security policies are crucial for ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of their responsibilities regarding data protection. These policies should outline guidelines for securing physical devices such as laptops and mobile phones as well as securing networks through firewalls and encryption methods.
Risks Associated With Data Security
In addition to the threat of external attacks, there are also inherent risks associated with internal data breaches.
One such risk is employee negligence, which can lead to unintentional disclosure or loss of sensitive data. This can happen through simple mistakes like leaving a device unattended or sending an email to the wrong recipient. Another risk is the use of weak passwords, which can be easily guessed or hacked by cybercriminals.
Organizations must also consider the risks associated with third-party vendors who may have access to their data. Depending on the nature of their relationship with these vendors and the type of information being shared, organizations may need to implement additional security measures such as contractual agreements and regular audits.
Components Of A Data Security Policy
Access Control
Access control is one of the most important aspects of data security policy. It refers to a set of measures implemented to ensure that only authorized users have access to confidential information. These measures can include password-protected accounts, encryption, biometric identification, and more. Access control is essential for preventing unauthorized disclosure or theft of sensitive data.
To implement an effective access control system, organizations need to conduct a thorough assessment of their data security needs. This includes identifying the types of information they store, who needs access to it, and what level of protection is necessary. Once these factors have been determined, organizations can then implement appropriate access controls to protect their data from unauthorized use or disclosure.
Authentication And Authorization
Authentication is the process of verifying a user’s identity before granting access to a system or application. This can be achieved through various methods such as passwords, biometrics, or smart cards. It ensures that only authorized users have access to sensitive information.
Authorization, on the other hand, involves granting specific permissions to authenticated users based on their roles and responsibilities within an organization. This helps to ensure that users have only the necessary access required to perform their job functions.
By implementing strong authentication and authorization protocols across all systems and applications that handle sensitive information, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect against data breaches.
Encryption
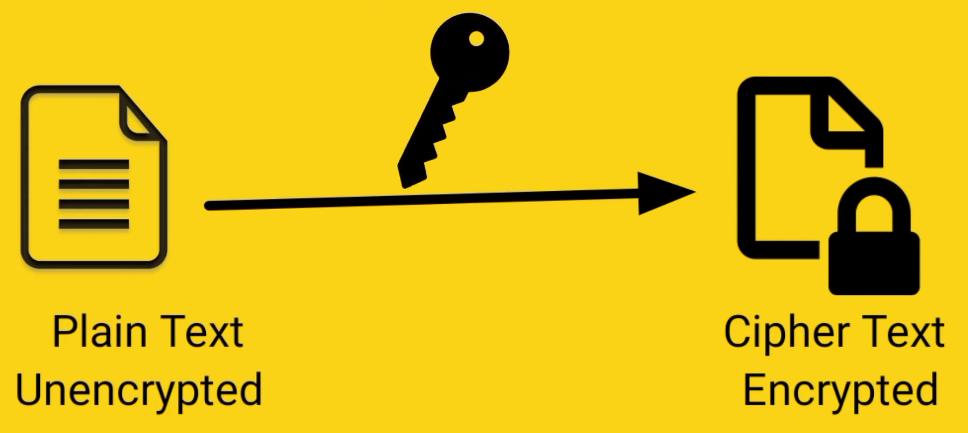
Encryption refers to the process of converting plaintext or readable information into an unintelligible form known as ciphertext, using an algorithm and encryption key. Encryption helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, tampering, or interception. Without encryption, anyone who intercepts your data can easily read and use it for malicious purposes.
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric-key encryption and public-key encryption. Symmetric-key encryption uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt messages between two parties while public-key encryption employs two different keys – one for encrypting messages and another for decrypting them. Both methods have their strengths and weaknesses depending on the needs of users.
Network Security
Network security refers to the measures implemented to protect a network from unauthorized access and cyber-attacks. This includes securing both hardware and software components of the network, such as firewalls, routers, switches, servers, and endpoints.
-
Physical Security
Physical security is an essential aspect of data security policy, as it concerns the protection of the physical infrastructure that houses sensitive data. An effective physical security system includes a range of measures such as access control systems, surveillance cameras, and biometric scanners. The primary objective is to prevent unauthorized access to areas where confidential data is stored or processed.
A data security policy should not neglect the importance of physical security measures in safeguarding confidential information. A well-designed physical security system helps to deter potential intruders and limit access to sensitive areas within a facility.
Incident Response And Business Continuity
Incident response and business continuity are critical components of any data security policy. Incident response plans to outline a framework for responding to cybersecurity incidents, including procedures for identifying, containing, analyzing, and eradicating threats. Effective incident response plans should also include measures for communicating with stakeholders during the incident’s duration and post-incident activities.
By establishing clear processes for dealing with cybersecurity incidents and maintaining essential functions during crises, businesses can ensure they are well-prepared to navigate unexpected challenges while protecting their sensitive information from potential harm.
Types of Data Security Policies
Information Security Policy
An information security policy outlines the measures that should be taken to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It also defines the roles and responsibilities of employees, contractors, and other stakeholders concerning data security.
The primary objective of an information security policy is to safeguard data against unauthorized access, modification or destruction. This includes protecting data from external threats such as hackers or malware as well as internal threats such as misconfiguration or accidental disclosure. The policy should also provide a framework for managing incidents when they occur.
Data Breach Response Policy
A data breach response policy should be in place in any organization that handles private and confidential data. This policy outlines the steps to be taken in case of a security incident, including how to identify the breach, contain it, and mitigate its effects.
The first step in a data breach response policy is identifying the source and extent of the breach. Once identified, all affected parties should be notified immediately about the incident. The next step involves containing the impact of the breach by preventing further access to sensitive information while addressing any vulnerabilities that contributed to it.
A clear communication strategy should also be outlined in a data breach response policy. This includes notifying customers, partners, and stakeholders about the incident while being transparent and honest about what happened and what actions are being taken to address it.
Incident Response Policy
An incident response policy should include measures for detecting, containing, and mitigating the effects of an attack. The goal is to minimize damage and restore normal operations as quickly as possible.
A well-designed incident response policy should be tailored to the specific needs of an organization. It should identify key personnel responsible for implementing the plan and outline their roles and responsibilities during an incident. It should also establish communication protocols, including who will be notified in case of a breach and how the information will be disseminated both internally and externally.
Best Practices For Developing A Data Security Policy
Conducting A Risk Assessment
The first step in conducting a risk assessment involves defining the scope of the process. This means identifying what assets need to be protected and who has access to them. Once this has been established, it’s important to conduct a threat analysis which involves identifying potential sources of harm such as hackers, malware or natural disasters. The final stage is assessing the likelihood and impact of each threat occurring.
Developing A Data Classification Policy
A comprehensive data classification policy should address issues such as who is responsible for classifying data, how frequently it should be reviewed, and what measures need to be taken in the event of a breach or loss. The policy must also outline training programs for employees on handling classified information, including guidelines for sharing or transferring sensitive data within and outside the company.
Developing a robust and effective data classification policy requires collaboration between various departments within an organization, including legal, IT, HR, and management.
Creating An Incident Response Plan
The first step in creating an incident response plan is to identify potential risks and threats to your organization’s data. This includes identifying internal and external threats such as cyber-attacks, unauthorized access, and natural disasters.
Once potential risks have been identified, the next step is to develop a response strategy for each scenario. This should include determining who will be responsible for handling the incident, what actions need to be taken immediately following the breach, and how communication will be handled with stakeholders including customers, employees, and regulatory agencies.
it’s important to test your incident response plan regularly to ensure its effectiveness. Conducting these tests can help identify areas for improvement so that you can refine your strategy over time.
Implementing Access Control
Effective access control involves defining user roles and privileges, implementing authentication and authorization protocols, and monitoring user activity. User roles should be clearly defined based on job functions or responsibilities. Authorization protocols should be designed to grant or deny access based on these roles, while authentication should verify users before granting them access. Monitoring user activity can help identify potential security threats early on.
Establishing Data Retention Policies
To establish effective data retention policies, an organization must first identify what types of data it collects and why it does so. This will help determine which types of data are critical to retaining and which ones can be safely deleted after a set period. Additionally, organizations must consider both current and potential future regulations that may apply to their industry.
Once the necessary guidelines have been established, communicate them clearly to all employees who handle sensitive information. This ensures that everyone in the organization understands their responsibilities concerning data retention and helps prevent confusion or accidental violation of policies.
Compliance Regulations For Data Security Policy
Organizations need to comply with numerous laws and regulations to ensure the safety and confidentiality of their data. Compliance regulations can be categorized into two types: industry-specific and general regulations.
HIPAA
Industry-specific compliance regulations apply to organizations based on their industry, such as healthcare, finance, or government. For instance, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) applies to healthcare providers who must protect patients’ medical information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
GDPR
General compliance regulations cover all types of organizations regardless of their industry. These include laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which regulates how businesses collect, process, and store personal data belonging to European Union citizens.
PCI DSS
PCI DSS, or Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, is a set of standards developed by major credit card companies to ensure the secure handling of sensitive payment information. Compliance with PCI DSS is mandatory for all merchants that accept credit card payments. The standard includes requirements such as encryption of data at rest and in transit, regular vulnerability scanning, and strict access controls.
CCPA
Under CCPA, businesses are required to disclose what categories of personal information they collect from consumers and how they use it. They must also provide a clear and conspicuous link on their website titled “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” which allows users to opt out of the sale of their data. Additionally, companies need to ensure that any third-party vendors who receive consumer data comply with CCPA regulations.
Challenges To Data Security
Hackers: Cybercriminals use sophisticated methods such as social engineering, phishing scams, malware, and ransomware attacks to gain access to sensitive data. As technology advances and new vulnerabilities are discovered, it becomes increasingly important for businesses to regularly update their security systems.
The human factor: Data breaches often occur due to employee negligence or lack of awareness about cybersecurity best practices. This highlights the importance of educating employees on how to protect against cyber threats and ensuring that they follow established protocols regarding password protection and handling confidential information.
FAQs
Why Is Data Security Policy Important?
A comprehensive data security policy outlines the procedures and protocols for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, theft, or damage.
A well-defined data security policy can help organizations identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in their system before they become problematic. It also ensures that employees are aware of their responsibilities when it comes to handling sensitive information. By implementing strict guidelines for accessing and sharing confidential data, companies can minimize the risk of human error or intentional misuse.
A strong data security policy not only protects valuable information but also helps build trust between businesses and their customers. Clients want to know that their personal information is being handled with care and confidentiality at all times.
What Are The Components Of A Data Security Policy?
A data security policy outlines the rules and measures that an organization takes to protect its confidential information. The components of a data security policy generally include access control, encryption, network security, physical security, incident response, and employee training.
What Role Do Employees Play In Data Security?
Employees are the first line of defence against cyber threats and are responsible for safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. Employees who have access to confidential data should be trained on how to handle it securely and avoid any risks that might compromise its integrity.
Furthermore, employees must adhere to strict security policies, such as password protection protocols, encryption standards, and other best practices that help keep data safe. Moreover, they should report any suspicious activity immediately so that IT teams can take action promptly.
What Tools And Technologies Are Used For Data Security?
One of the most common tools used is encryption software, which converts information into code to prevent unauthorized access. Firewalls are another essential tool for data security, acting as a barrier between an organization’s internal network and the internet.
Other important technologies include intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), which monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can block attacks in real time. Access controls are also critical to data security, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive information. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is becoming increasingly popular as it requires multiple forms of identification before granting access, making it more difficult for hackers to gain entry.
Conclusion
Safeguarding data is a critical aspect of any organization’s security policy. Organizations must take the necessary steps to protect their data from unauthorized access, theft, or destruction. The implementation of a comprehensive data security policy that includes encryption, access controls, and regular backups can go a long way in ensuring data protection.
Additionally, organizations must train their employees on best practices for handling sensitive information and how to respond in case of a breach. Regular security audits and assessments can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with relevant regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
