Definition of Data At Rest Encryption
Data at rest encryption refers to the practice of encrypting data that is stored or archived, as opposed to data that is in transit or being processed. This type of encryption helps to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or theft, as well as from accidental loss or corruption. Data at rest encryption can be applied to a variety of storage media, including hard drives, solid-state drives, backup tapes, and cloud storage platforms.
Importance of Data At Rest Encryption
The importance of data-at-rest encryption cannot be overstated. With the increasing amount of sensitive data being stored electronically, it is essential to have proper security measures in place to protect that data. Data breaches can result in significant financial losses, damage to a company’s reputation, and legal liability. By encrypting data at rest, organizations can ensure that even if their storage media is stolen or compromised, the data remains unreadable and unusable to unauthorized parties.
How Data At Rest Encryption Works?

Data at rest encryption works by converting plain text data into an unreadable format using an encryption algorithm. The encrypted data is then stored on a device or server, making it inaccessible to anyone without the proper decryption key. When data needs to be accessed, the decryption key is used to convert the encrypted data back into its original form. This process ensures that any unauthorized access attempts to the data will be unsuccessful, as the data is unreadable without the decryption key.
Encryption Algorithms Used For Data At Rest Encryption
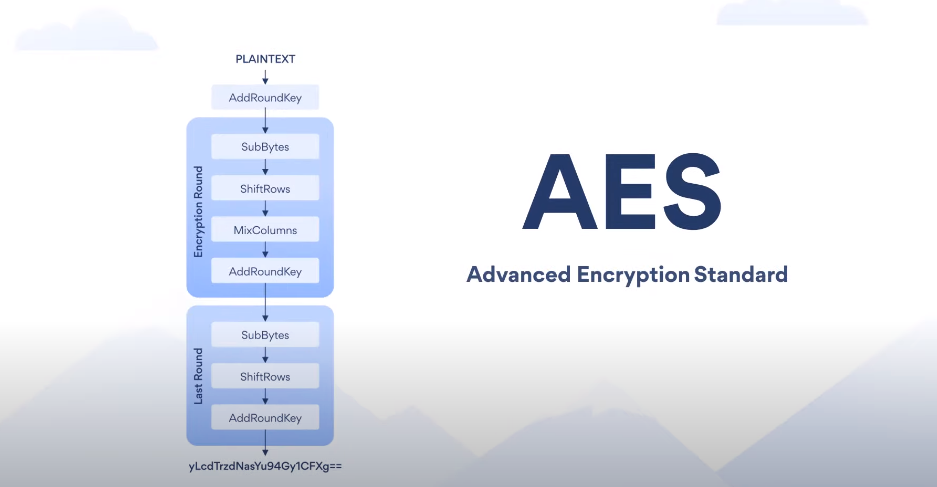
There are several types of encryption algorithms used for data-at-rest encryption, including:
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): This is a widely used symmetric encryption algorithm that is known for its high level of security and efficiency. It is used by many organizations to protect sensitive data.
- Blowfish: This is another symmetric encryption algorithm that is known for its speed and efficiency. It is often used in situations where fast encryption and decryption are required.
Benefits of Data at Rest Encryption
- Protection against unauthorized access
- Mitigation of data breaches
- Compliance with data protection regulations
- Improved trust and credibility
Risks of Not Using Data at Rest Encryption
- Exposure to cyber attacks
- Loss of sensitive data
- Reputation damage
- Legal implications
Implementing Data at Rest Encryption
When implementing data-at-rest encryption, there are a few important steps to follow:
- Identify what data needs to be encrypted: Determine which data is sensitive and needs to be protected.
- Choose an appropriate encryption algorithm: Select an encryption algorithm that is appropriate for the level of security needed and the performance requirements.
- Generate and manage encryption keys: Encryption keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data. It is important to securely generate and manage these keys to ensure the security of the encrypted data.
Identifying Data That Requires Encryption
To identify data that requires encryption, you should consider the sensitivity and confidentiality of the information. For example, financial information, personal identification information (such as social security numbers or driver’s license numbers), healthcare records, and intellectual property may require encryption to protect against unauthorized access or theft. It is important to conduct a risk assessment to identify the data that needs to be protected and to implement appropriate security measures, including encryption.
Choosing The Right Encryption Solution
Choosing the right encryption solution can be a complex process, as there are many factors to consider such as the level of security required, the type of data being protected, the cost of the solution, and the ease of use. It is important to research and compares different encryption solutions to find the one that best meets your specific needs. Some popular encryption solutions include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), and Blowfish.
Best Practices For Implementing Data At Rest Encryption
Implementing data-at-rest encryption is an important step in protecting sensitive information. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Identify the data that needs to be encrypted: Before implementing encryption, it’s important to identify the sensitive data that needs to be protected. This could include personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, or intellectual property.
- Choose the right encryption solution: As mentioned earlier, there are many encryption solutions available, so it’s important to choose the one that best meets your requirements.
Key Considerations for Data at Rest Encryption
- Performance impact
- Key management
- Compatibility with existing infrastructure
- Costs
Data at Rest Encryption for Cloud Storage
When it comes to data-at-rest encryption for cloud storage, there are a few additional considerations to keep in mind:
- Cloud provider encryption: Many cloud providers offer encryption solutions for data at rest. Make sure to understand the encryption options available from your cloud provider and ensure they meet your security needs.
- Client-side encryption: Consider using client-side encryption solutions that encrypt data before it is uploaded to the cloud. This can provide an additional layer of security and control over your data.
Differences Between On-Premises And Cloud Storage
On-premises storage refers to data storage solutions that are physically located within an organization’s premises or data center. This means that the organization has complete control over the storage infrastructure, including the hardware and software used for storage, security measures, and data access policies. Cloud storage, on the other hand, refers to data storage solutions that are provided by third-party service providers and accessed over the Internet. Cloud storage offers many benefits, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of access.
Advantages And Disadvantages of Cloud Storage
Advantages of cloud storage include:
- Scalability: Cloud storage allows organizations to easily scale their storage needs up or down as required, without having to invest in new hardware or software.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud storage is generally more cost-effective than traditional storage solutions, as organizations only pay for the storage space they need, rather than having to invest in expensive hardware and software.
- Ease of access: Cloud storage can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it easy for employees to access and share files from anywhere in the world.
Disadvantages of cloud storage include:
- Security concerns: Cloud storage is often perceived as less secure than traditional storage solutions, as data is stored on servers that are owned and managed by third-party service providers.
- Reliance on Internet connectivity: Cloud storage requires a reliable Internet connection to access and store data, which can be a problem in areas with poor connectivity.
- Limited control: Organizations have limited control over the storage infrastructure and security measures used by cloud storage providers, which can be a concern for organizations with strict data security policies.
Encryption Options For Cloud Storage
There are several encryption options available for cloud storage, including:
- Client-side encryption: This involves encrypting data on the client side before it is uploaded to the cloud storage provider. This ensures that the data is encrypted before it leaves the client’s device, making it more secure.
- Server-side encryption: This involves encrypting data on the cloud storage provider’s servers. The encryption keys are managed by the provider, but the data is still protected.
Common Data at Rest Encryption Technologies
- BitLocker
- VeraCrypt
- FileVault
- LUKS
Evaluating Data at Rest Encryption Solutions
When evaluating data-at-rest encryption solutions, it is important to consider factors such as the level of security provided, ease of use, compatibility with different operating systems and devices, and cost. It is also important to ensure that the encryption solution meets any regulatory or compliance requirements that may apply to your organization. Additionally, you may want to consider the reputation and track record of the encryption solution provider, as well as any customer reviews or testimonials available.
Criteria For Evaluating Encryption Solutions
When evaluating encryption solutions, there are several criteria that you should consider. These include:
- Level of security: The encryption solution should provide a high level of security to protect your sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Ease of use: The solution should be easy to use and integrate into your existing systems without requiring extensive technical knowledge.
- Compatibility: The solution should be compatible with different operating systems and devices to ensure that your data is secure across all platforms.
Maintaining Data at Rest Encryption
- Updating encryption keys
- Monitoring and auditing
- Responding to security incidents
Regulatory Requirements For Data At Rest Encryption
Data at rest encryption is an essential security measure that helps protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. This type of encryption involves encrypting data while it is stored in a database, file system, or other storage media. The encryption process uses complex algorithms to scramble the data, making it unreadable to anyone who does not have the decryption key. One of the main benefits of data-at-rest encryption is that it provides an additional layer of security to protect against data breaches.
Frameworks That Include The Data-At-Rest Encryption
It includes HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. These frameworks require organizations to implement encryption measures to protect sensitive data, such as personal information and payment card data, when it is stored on servers or other storage devices. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and damage to the organization’s reputation. Therefore, organizations need to prioritize data-at-rest encryption as part of their overall security strategy.
Best Practices For Complying With Data Protection Regulations
Here are some best practices that organizations can follow to comply with data protection regulations:
- Identify sensitive data: Organizations should identify sensitive data, such as personal information and payment card data, that needs to be protected and implement appropriate encryption measures.
- Choose the right encryption method: Organizations should choose the right encryption method based on the type of data they are protecting and the level of security required.
- Implement strong access controls: Access to encrypted data should be restricted to authorized personnel only.
Conclusion
Based on the above checks, you can determine whether your data at rest encryption is working. If encryption is enabled, files are marked as encrypted or have an encrypted file extension, and you are unable to access encrypted files, then your data at rest encryption is likely working as intended. However, if you are unsure or have concerns about the effectiveness of your encryption, it is recommended to consult with a security expert or IT professional for further guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between data-at-rest encryption and data-in-transit encryption?
Data at rest encryption refers to the encryption of data that is stored on a device or server, while data in transit encryption refers to the encryption of data that is being transmitted over a network or between devices. Both types of encryption are important for ensuring the security of sensitive data.
Can data at rest encryption be bypassed?
Data at rest encryption can be bypassed if the encryption keys are compromised or if there are vulnerabilities in the encryption software. It is important to regularly update and patch encryption software to prevent such vulnerabilities from being exploited. Additionally, it is important to implement strong access controls and security measures to prevent unauthorized access to encrypted data.
What happens if I lose my encryption key?
If you lose your encryption key, you may not be able to access the encrypted data anymore. This is because the encryption key is used to decrypt the data. It is important to keep your encryption key in a secure location and to make a backup copy in case it is lost or damaged. If you are unable to access your encrypted data due to a lost or damaged encryption key, you may need to contact a data recovery specialist for assistance.
Does data-at-rest encryption affect performance?
Yes, data-at-rest encryption can potentially affect performance. Encrypting and decrypting data takes additional processing power and can slow down read and write times. However, the impact on performance can vary depending on factors such as the encryption algorithm used, the hardware and software being used, and the amount of data being encrypted. It is important to carefully evaluate the performance impact of data-at-rest encryption before implementing it in a production environment.
How do I know if my data-at-rest encryption is working?
To ensure that your data at rest encryption is working, you can perform a few checks:
- Verify that the encryption is enabled: Check the settings of your storage system or software to confirm that encryption is enabled.
- Check for encrypted files: Look for files that have an encrypted file extension or that are marked as encrypted in the file properties.
- Attempt to access encrypted files: If you are unable to access files that should be encrypted.
