Introduction
Wireless network encryption is converting plain text data into a secret code to avoid unauthorized access to the network. This is done using encryption algorithms that scramble the data in a way that can only be deciphered with the right decryption key.
Wireless network encryption is a method of securing wireless networks by encoding the data transmitted over the network. This is done to prevent unauthorized access and eavesdropping on the network. Several encryption methods are used in wireless networks, including Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), and WPA2.WEP is the oldest and least secure encryption method, using a fixed key that hackers easily cracks. WPA and WPA2 are more secure, as they frequently use dynamic keys that change frequently and are harder to crack. WPA2 is the most secure encryption method recommended for all wireless networks.
Wireless Network Encryption Methods

Wireless networks have become an integral part of our daily lives, providing us with the convenience of connecting to the internet without the constraints of physical cables. However, with the increasing reliance on wireless connectivity, securing these networks has become a critical concern. Wireless network encryption plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive data transmitted over wireless networks, protecting it from unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
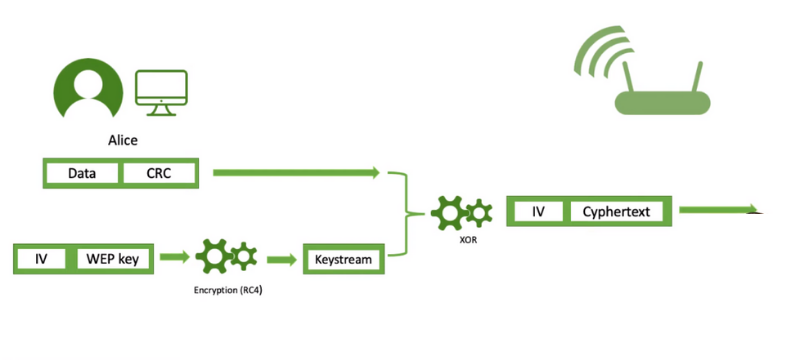
WEP, or Wired Equivalent Privacy, is an encryption method to secure wireless networks. It was introduced in 1999 to provide an equivalent level of security as a wired network. WEP uses a shared key authentication and encryption system, where the same key is used for both authentication and encryption of data. The key can be either 64-bit or 128-bit in length. However, WEP has been found to have several vulnerabilities, making it easy for attackers to crack the encryption and gain access to the network.
How Does WEP Work?
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is an older wireless network encryption protocol that is no longer recommended due to its vulnerabilities. WEP uses a shared key to encrypt data transmitted between devices on a wireless network. The key generates a stream of random data combined with plain text data to create the encrypted data. This encrypted data is then transmitted over the wireless network. However, WEP has been found to have significant security flaws that make it easy for attackers to intercept and decrypt the statistics being transmitted. As a result, it is highly suggested to use a more secure encryption protocol, such as WPA2 or WPA3, to protect your wireless network. These protocols use stronger encryption algorithms and provide better security features to prevent unauthorized access to your network.
Importance of Wireless Network Encryption
Wireless network encryption is the process of encoding data transmitted between devices within a wireless network, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals who might intercept the communication. It provides a secure environment for wireless data transmission and ensures that only authorized parties can access and decipher the information.
The importance of wireless network encryption cannot be overstated. It helps protect sensitive data from eavesdropping, unauthorized access, and data manipulation. Without encryption, wireless networks would be open to various security risks, including unauthorized users connecting to the network, intercepting data packets, and launching attacks such as man-in-the-middle attacks or packet sniffing.
Advantages of Using Wireless Network Encryption
Implementing wireless network encryption offers several advantages:
- Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that transmitted data remains confidential and only accessible to authorized recipients.
- Integrity: Encryption protects data from being modified or tampered with during transmission.
- Authentication: Encryption methods often incorporate authentication mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized users can access the network.
- Compliance: Many industries and regulatory standards require the implementation of wireless network encryption to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
- Peace of Mind: Wireless network encryption provides peace of mind, knowing that your wireless communications are secure and protected from unauthorized access.
Common Challenges in Wireless Network Encryption
While wireless network encryption provides crucial security measures, it also presents some challenges. Understanding these challenges is essential for implementing effective encryption strategies:
Key Management
One of the primary challenges in wireless network encryption is effective key management. Encryption algorithms rely on encryption keys to encode and decode data. Maintaining secure and frequently updated encryption keys is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the encryption process.
Compatibility Issues
Different wireless devices and software may have varying levels of compatibility with encryption methods. It is important to ensure that encryption methods used in a network are supported by the devices and software being utilized to prevent connectivity issues and potential security vulnerabilities.
Performance Impact
Implementing encryption can introduce performance overhead, as the encryption and decryption processes require additional computational resources. Balancing security and performance is crucial to ensure optimal network performance without compromising security.
Best Practices for Implementing Wireless Network Encryption
To maximize the effectiveness of wireless network encryption, consider the following best practices:
Strong Passwords and Authentication
Utilize strong and unique passwords for wireless network access. Implement two-factor authentication mechanisms when possible to add an extra layer of security.
Regular Security Updates
Keep wireless devices and network infrastructure up to date with the latest security patches and firmware updates. Regularly updating the encryption keys and security protocols helps mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Network Segmentation
Segmenting the wireless network into different virtual LANs (VLANs) or subnets can enhance security. By isolating different user groups or devices, the impact of a security breach can be limited.
Monitoring and Intrusion Detection Systems
Implement network monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems to identify any suspicious activities or potential security breaches. Proactive monitoring enables prompt responses to security incidents.
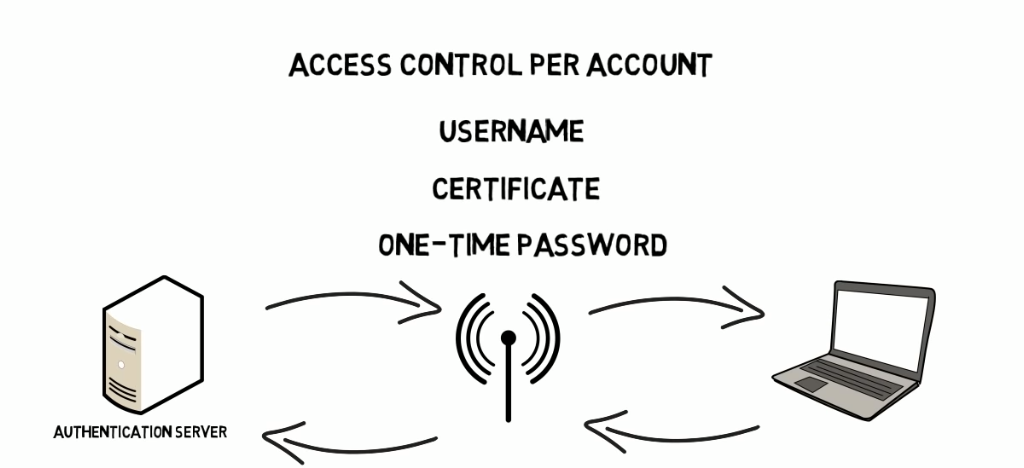
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol)
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is an authentication framework commonly used in enterprise wireless networks. EAP enables various authentication methods, such as username/password, digital certificates, or smart cards. By utilizing EAP, wireless networks can implement secure authentication mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized users can access the network.
Alternatives To WEP
Several alternatives to WEP provide stronger security for wireless networks. These include:
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA): WPA is a security protocol developed to replace WEP. It uses a stronger encryption algorithm and provides better protection against attacks. WPA also uses a unique encryption key for each user, which makes it more difficult for attackers to crack.
- WPA2: WPA2 is an updated version of WPA that provides even stronger security. It uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm, considered one of the most secure encryption methods. WPA2 includes additional security features, such as improved key management and message integrity checks.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs provide an additional layer of security by encrypting all network traffic between a user’s device and the network. This makes it much more problematic for attackers to intercept and read sensitive data.
- 802.1X: 802.1X is a network authentication protocol that requires users to authenticate themselves before being granted access to the network. This helps to prevent unauthorized access and can also be used in conjunction with other security protocols, such as WPA or WPA2.
- Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems (WIPS): WIPS are designed to detect and prevent unauthorized access to wireless networks. They use a combination of techniques, such as monitoring network traffic and detecting rogue access points, to identify potential security threats and take action to prevent them.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a security protocol for wireless networks. It was developed as an upgrade to the previous security protocol, WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), which was found to have several vulnerabilities. WPA uses stronger encryption algorithms and offers better security features than WEP. It also provides support for user authentication and key management. WPA is available in two versions, WPA and WPA2, with WPA2 being the more secure option.
WPA has several strengths that make it a reliable security protocol for wireless networks. Firstly, it uses a stronger encryption algorithm, Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is more secure than the encryption algorithm used in WEP. This makes it more problematic for attackers to intercept and decode wireless transmissions. Secondly, WPA supports user authentication, meaning only authorized users can access the network. This is done through a pre-shared key (PSK) or an advanced authentication protocol called Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). This ensures that only authorized users can connect to the network, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches. WPA also includes a Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) feature, which generates a unique encryption key for each data packet transmitted on the network. This augments an additional layer of security and makes it tough for attackers to intercept and decode wireless transmissions.
How Does WPA Work?
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a wireless security protocol designed to address the weaknesses of WEP. It uses a stronger encryption algorithm called TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) to encrypt the transmitted data over the wireless network. WPA also checks message integrity, which helps prevent attacks attempting to modify or inject data into the wireless network. Additionally, WPA uses a stronger authentication mechanism called 802.1X, which requires users to provide a username and password before connecting to the wireless network.
WPA2 is an improved version of WPA, which uses an even stronger encryption algorithm called AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). WPA3, the latest version of WPA, provides even stronger security features, such as individualized data encryption and protection against brute-force attacks.
What Are The Features Of WPA3?
The features of WPA3 include:
- Enhanced security: WPA3 uses a more secure key exchange protocol called Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) that provides better protection against password-guessing attacks.
- Protection against offline attacks: WPA3 protects against offline dictionary attacks using a stronger Dragonfly encryption algorithm.
- Improved public Wi-Fi security: WPA3 introduces a new feature called Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE), which provides encryption for open Wi-Fi networks without requiring a password.
- Better IoT device security: WPA3 includes a Device Provisioning Protocol (DPP) feature, simplifying securely adding IoT devices to a network.
Wi-Fi Protected Access II (WPA2)
WPA2 is a more secure version of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) introduced in 2004. It uses a stronger encryption algorithm called Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) to encrypt wireless network traffic. WPA2 also includes CCMP (Counter Cipher Mode with Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol), which provides stronger data encryption and integrity checks.WPA2 also includes pre-shared key (PSK) mode, which allows users to connect to a wireless network using a password or passphrase. This mode is commonly used in home and small business networks.
Advantages Of WPA2
- Stronger security: WPA2 provides stronger encryption and authentication than its predecessor, WPA. This makes it more problematic for hackers to break into wireless networks and steal sensitive information.
- Compatibility: WPA2 is widely supported by most modern wireless devices, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets. It can be used in various settings, from homes to businesses.
- Ease of use: WPA2 is easy to set up and configure and can be used with various authentication methods, including passwords, digital certificates, and smart cards.
- Flexibility: WPA2 offers a range of security options, including AES encryption, which is considered one of the most secure encryption methods available.
- Scalability: WPA2 can be used in large-scale wireless networks, making it a good choice for businesses and organizations that need to secure their wireless infrastructure.
Wi-Fi Protected Access III (WPA3)
WPA3 is the latest security protocol for Wi-Fi networks, designed to address the security vulnerabilities of its predecessor, WPA2. It was introduced by the Wi-Fi Alliance in 2018 and offers several new security features to enhance the protection of Wi-Fi networks. Some of the key features of WPA3 include:
- Improved encryption: WPA3 uses a stronger encryption algorithm called “Simultaneous Authentication of Equals” (SAE), which provides better protection against password-guessing attacks.
- Protection against offline dictionary attacks: WPA3 also includes a feature called “Dragonfly” that protects against offline dictionary attacks, where an attacker can use a pre-computed list of passwords to try and guess the network password.
- Enhanced public Wi-Fi security: WPA3 introduces a new feature called “Opportunistic Wireless Encryption” (OWE), which provides a higher level of security for public Wi-Fi networks that do not need a password.
Comparison WPA3 vs. WPA2
Compared to WPA2, WPA3 offers several improvements in terms of security. WPA3 uses Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) instead of the Pre-Shared Key (PSK) method used by WPA2. SAE provides stronger protection against password-guessing attacks, making it more problematic for attackers to crack the Wi-Fi password. In addition, WPA3 also offers protection against brute-force attacks by limiting the number of attempts an attacker can make to guess the password.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) is a security protocol used to enhance the security of wireless networks. It was developed as a replacement for the WEP protocol, which was found to have significant security flaws. TKIP is designed to provide stronger encryption and more robust key management than WEP.TKIP dynamically generates a new encryption key for each packet of data transmitted over the wireless network. This makes it much more problematic for an attacker to intercept and decrypt the data, as they would need to be able to crack each key to access the information.
In addition to its key management features, TKIP includes several other security enhancements, such as message integrity checks and replay protection. These features help to prevent attacks such as packet injection and replay attacks, which can be used to compromise the security of a wireless network.
Counter Mode With Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP)
It is the preferred security protocol for Wi-Fi networks that use the 802.11i standard. CCMP uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm for strong data encryption. It also uses a Message Authentication Code (MAC) to ensure the data’s integrity. The MAC is calculated using a secret key shared between the sender and receiver.
CCMP operates in two modes: Counter mode and Cipher Block Chaining mode. In Counter mode, a unique counter value encrypts each data block. In Cipher Block Chaining mode, the output of the encryption process for each block is combined with the input for the next block, creating a chain of encrypted blocks.
CCMP provides several security benefits over other wireless security protocols. It provides strong data encryption, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. It also provides message integrity, ensuring that data cannot be tampered with or modified in transit. Additionally, CCMP protects against replay attacks, which can be used to compromise the security of a wireless network.
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec)
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a protocol suite to secure Internet Protocol (IP) communications. It provides various security services, such as data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. IPSec encrypts and authenticates IP packets, ensuring they cannot be intercepted or modified in transit.IPSec can secure various communication types, including site-to-site VPNs, remote access VPNs, and secure communication between individual hosts. It is widely used in enterprise networks, as well as in government and military applications.
One of the key benefits of IPSec is that it operates at the network layer of the OSI model, providing security for all applications and protocols that use IP. It is also exceedingly configurable, allowing administrators to tailor the security settings to meet their organization’s needs.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
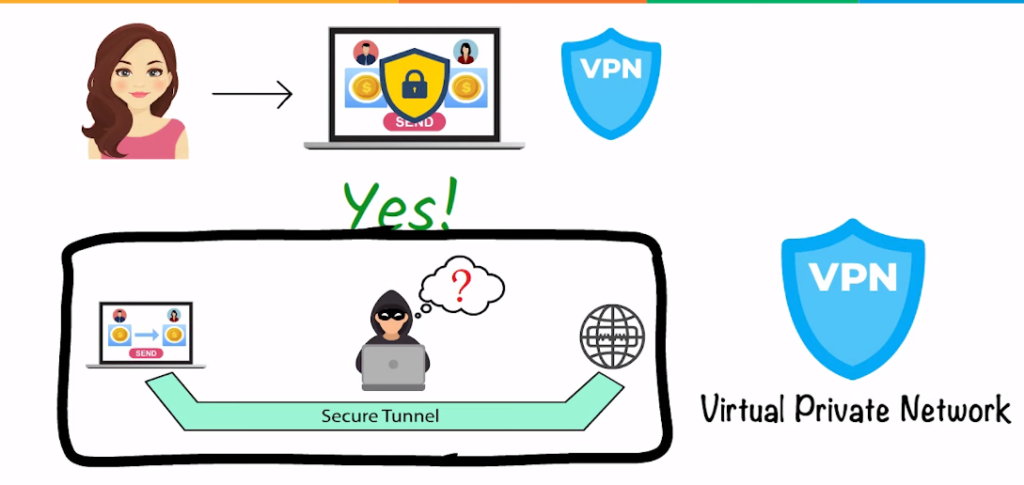
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are another important tool for securing online communication. A VPN is a private network that applies a public network, such as the internet, to connect remote sites or users. VPNs use encryption and additional security mechanisms to confirm that data transmitted over the public network is secure and private. One of the key benefits of VPNs is that they allow remote users to securely access resources on a private network, such as corporate intranets or file servers. VPNs can also bypass geographic restrictions, allowing users to access material that may be blocked in their location.
There are many types of VPNs, including site-to-site VPNs, remote access VPNs, and SSL VPNs. Each category has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of VPN will depend on the organization’s or individual’s needs.
Conclusion
Wireless network encryption is extremely important today, where data security is a major concern. Different types of wireless network encryption include WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3. WEP is the oldest and least secure encryption method, while WPA and WPA2 are more secure. WPA2 has several advantages over WPA, including stronger encryption and better security features. WPA3 is the latest encryption standard with several new features, such as stronger encryption and better protection against attacks. EAP is an authentication protocol used in wireless networks to ensure only authorized users can access the network. TKIP is a security protocol used in WPA to encrypt data and prevent unauthorized access. CCMP is a more advanced encryption protocol used in WPA2 to provide stronger security.
IPSec is a security protocol that creates a secure tunnel between two devices over the internet. It is commonly used in wireless networks to provide secure communication between devices. SSL/TLS is a security protocol that provides secure communication between web servers and clients. It is commonly used in wireless networks to provide secure access to web-based applications. Wireless network encryption is crucial for ensuring data security. There are different types of encryption, such as WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3, with WPA3 being the most secure. In addition to encryption, using secure protocols such as c and SSL/TLS can further enhance the security of wireless networks. Individuals and organizations must implement strong security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and cyber-attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is The Best Wireless Encryption Method?
Currently, WPA3 with individualized data encryption offers the highest level of security for wireless networks. It is recommended to use WPA3 when possible.
Can I Use Multiple Encryption Methods Simultaneously?
While it is possible to use multiple encryption methods, it can increase complexity and compatibility issues. It is generally recommended to use a single, robust encryption method.
How Often Should I Update My Encryption Keys?
It is good practice to update encryption keys regularly, ideally every few months or whenever there is a significant security event or breach.
Does Wireless Encryption Slow Down Network Performance?
Wireless encryption introduces some performance overhead due to the additional computational resources required for encryption and decryption. However, modern encryption methods have minimal impact on network performance.
Is Wireless Encryption Enough To Secure My Network?
While wireless encryption is an essential security measure, it should be complemented with other security practices such as strong passwords, regular updates, and network monitoring for comprehensive network security.
What Is TKIP, And How Is It Different From WEP?
TKIP stands for Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, a security protocol used for wireless networks. It was developed to improve the WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) protocol, which had several security weaknesses. TKIP is different from WEP in several ways. Firstly, TKIP uses a per-packet key instead of a static key like WEP, which makes it more difficult to crack. Secondly, TKIP includes a message integrity check to prevent tampering with packets. Finally, TKIP uses a longer initialization vector (IV) than WEP, which makes it more difficult for attackers to predict the key stream.
What Is CCMP, And How Is It Different From TKIP?
CCMP (Counter Cipher Mode with Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol) is an encryption protocol used in Wi-Fi networks that is more secure than TKIP. CCMP is part of the WPA2 protocol and is based on the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm, which is a more secure and efficient encryption algorithm than the RC4 algorithm used by TKIP.CCMP uses a unique encryption key for each data packet, making it more difficult for attackers to crack the encryption. It also includes a message integrity check to prevent packet tampering, similar to TKIP. However, CCMP uses a different encryption process called Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code (CBC-MAC), which provides stronger encryption and better protection against attacks.
What Is IPSec, And How Is It Used In Wireless Networks?
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) secures communications over IP networks. It provides security services, including encryption, authentication, and integrity, to protect data transmitted over the network. IPSec can be used in wireless networks to secure communication between wireless devices and access points. This is particularly important in public Wi-Fi networks, where attackers can intercept data. Wireless devices can establish a secure tunnel between each other using IPSec and encrypt all data transmitted over the network. This ensures that the data is protected from eavesdropping and tampering.
