Introduction
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that describes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computer system. It is divided into seven layers, each with a specific function in the communication process. In this article, we will explore the layer of the OSI model used for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data. The Presentation Layer is crucial in ensuring data is transmitted securely and efficiently between devices. Let’s jump in and learn more about this important OSI model layer.
Overview Of OSI Model
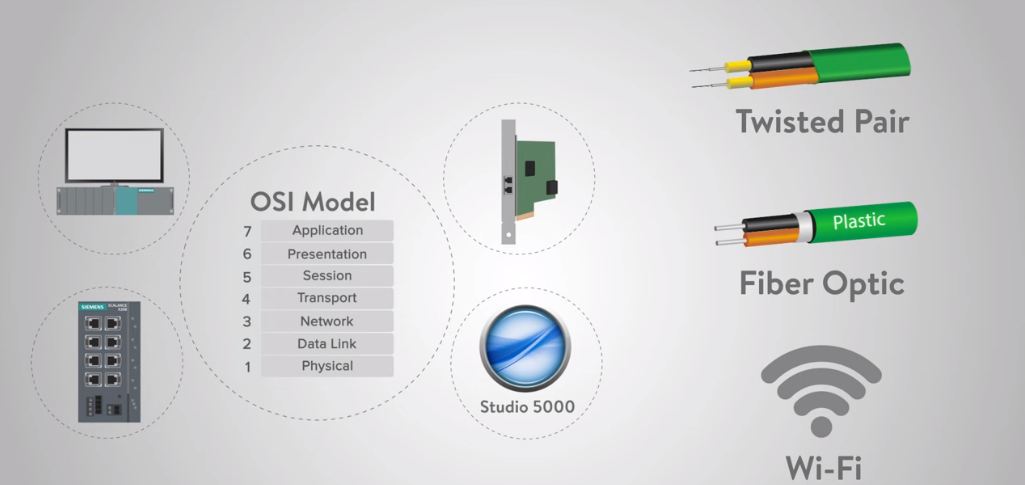
The OSI model is a theoretical agenda that standardizes communication between different computer systems. It was established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984 and consists of seven layers. Each layer is accountable for a specific function in the communication process, and they work together to confirm that data is transmitted accurately and securely.
Layers Of OSI Model
The seven layers of the OSI model are:
1. Physical Layer: This layer transmits raw data over a physical medium such as cables or airwaves.
2. Data Link Layer: This layer is responsible for reliable data transmission over a physical link.
3. Network Layer: This layer controls routing data between different networks.
4. Transport Layer: This layer is reliable data transmission between devices.
5. Session Layer: This layer manages and maintains communication sessions between devices.
6. Presentation Layer: This layer formats, compresses, and encrypts data.
7. Application Layer – This layer provides services to end-users, such as email, web browsing, and file sharing.
Which Layer In The OSI Model Is Required For Formatting, Compressing, And Encrypting Data?
The layer in the OSI model responsible for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data is the Presentation Layer.
Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer, the sixth layer in the OSI model, is responsible for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data. This layer ensures that data is presented in a format that can be known by the receiving device, regardless of the format in which it was sent. It also handles encryption and decryption of data to ensure secure transmission.
Comparison With Other Layers
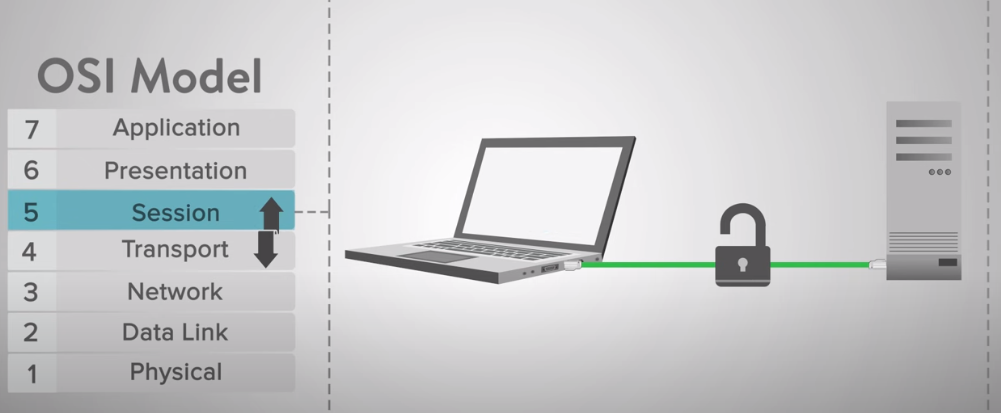
Session Layer
The Session Layer, the fifth layer in the OSI model, establishes, manages, and terminates sessions between devices. It provides authentication, authorization, and accounting services to ensure secure device communication. The Presentation Layer works closely with the Session Layer to ensure that data is presented in a format both devices can understand during the session.
Application Layer
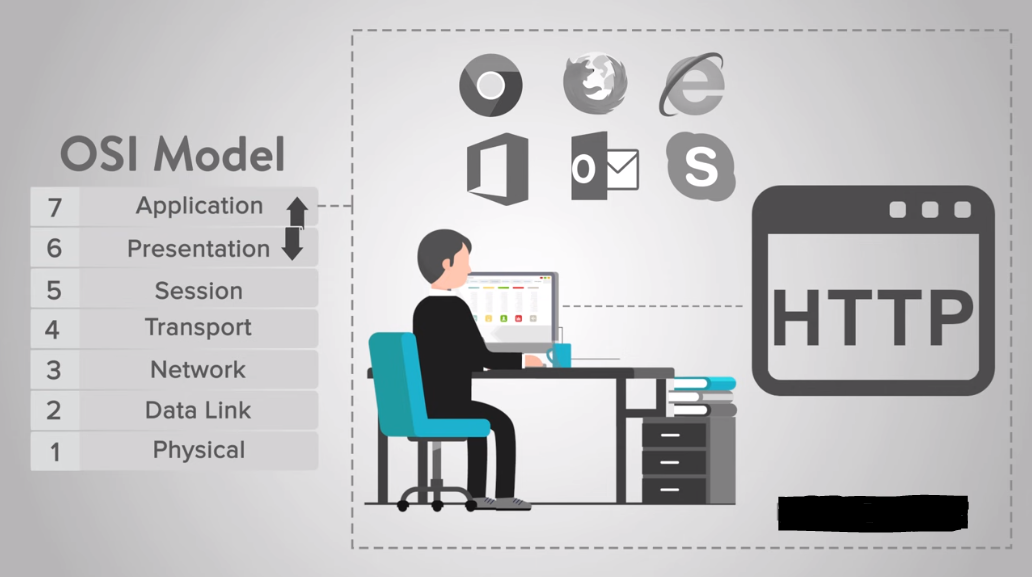
The Application Layer, the seventh and topmost layer in the OSI model, provides services to the end-user applications. The layer interacts directly with the user and provides file transfers, email, and web browsing services. The Application Layer also provides protocols that enable communication between applications running on different devices. Examples of protocols at this layer include HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS.
Function Of The Presentation Layer
The Presentation layer is the formatting, encrypting, and compressing of data transmitted across the network. It confirms that the data is in a format that can be understood by the receiving device, regardless of the format used by the sending device. It also handles data conversion between different character sets and data formats. In summary, the Presentation layer prepares the data for delivery and ensures that the receiving device can properly interpret it.
Some Protocols Operating At Presentation Layer
Some protocols that operate at the Presentation layer include:
1. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) – used for compressing and decompressing image files
2. MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group) – used for compressing and decompressing video files
3. American Standard Code for Information Interchange – ASCII is used for encoding text data
4. TLS (Transport Layer Security) – used for encrypting data during transmission
5. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) – used for encrypting data during transmission
6. GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) – used for compressing and decompressing image files
7. PNG (Portable Network Graphics) – used for compressing and decompressing image files
These are just a few examples of protocols that operate at the Presentation layer. Many others perform different functions depending on the type of data being transmitted.
Which Layer In The TCP/IP Model Is Used For Formatting, Compressing, And Encrypting Data?
In the TCP/IP model, the Presentation Layer is used for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data. This layer ensures that data is in a format the receiving application can understand. It also handles encryption and decryption of data, as well as compression and decompression of data. However, it is important to note that no protocols use only the Presentation Layer. Instead, protocols like SSL/TLS and MIME use the Presentation and Application Layers to provide secure communication and multimedia support.
Conclusion
The Presentation layer plays a crucial role in the OSI model by ensuring that data is properly formatted, encrypted, and compressed for transmission across different networks and systems. Without this layer, data transmission would be inefficient, unreliable, and vulnerable to security threats. By understanding the functions and protocols of the Presentation layer, network engineers and IT professionals can optimize their networks for better performance and security.
The Presentation layer is an essential component of the OSI model that plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and secure data transmission. Its functions and protocols are critical for optimizing network performance and protecting against security threats. As technology advances, network engineers and IT professionals must stay up-to-date on the latest developments in the Presentation layer and other OSI model layers to ensure their networks’ continued success and security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Does The Presentation Layer Format, Compress, And Encrypt Data?
The Presentation layer is responsible for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data before transmitting it across the network. It formats the data into a standard format that can be understood by the receiving device, regardless of the format used by the sending device. It also compresses the data to reduce the data that needs to be transmitted, improving network performance. Finally, it encrypts the data to ensure it is secure and cannot be intercepted or read by unauthorized parties. Overall, the Presentation layer is crucial in ensuring data is properly prepared for transmission and remains secure during transit.
How Does The Presentation Layer Format, Compress, And Encrypt Data?
The Presentation layer is responsible for formatting, compressing, and encrypting data before transmitting it across the network. It formats the data into a standard format that can be understood by the receiving device, regardless of the format used by the sending device. It also compresses the data to reduce the data that needs to be transmitted, improving network performance. Finally, it encrypts the data to ensure it is secure and cannot be intercepted or read by unauthorized parties. Overall, the Presentation layer is crucial in ensuring data is properly prepared for transmission and remains secure during transit.
What Are Some Commonly Used Encryption Algorithms In The Presentation Layer?
There are various encryption algorithms used in the presentation layer, including Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), and Rivest Cipher (RC4). These algorithms provide different levels of security and are widely employed to protect sensitive data during transmission.
Can The Presentation Layer Perform Data Encryption Without The Need For Encryption At Higher Layers?
Yes, the presentation layer can independently encrypt data without the need for encryption at higher layers. However, for robust security, it is recommended to implement encryption at multiple layers of the OSI model, including the presentation layer, transport layer, and application layer.
