Introduction
Definition of Data Security Breaches
A data security breach refers to an occurrence where an unauthorized person or entity gains access to confidential information. Breaches can occur through various channels such as hacking, phishing, malware, ransomware and social engineering attacks. These breaches often result in the loss of sensitive personal or company data which is then used for identity theft, financial fraud and other malicious activities.
Importance of Data Security Breaches
It is essential to understand the importance of data security breaches as they can have a significant impact on businesses and individuals. Data breaches can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities for organizations. Businesses collect sensitive information from customers such as credit card details, personal identification numbers (PINs), and contact information. In the case of a data breach, this information can be exposed to cyber criminals who may use it for illicit purposes.
Moreover, data breaches can also affect individuals’ privacy rights by exposing their personal information to unauthorized parties. This breach of privacy can lead to identity theft or other fraudulent activities resulting in severe financial and emotional consequences. Therefore, both businesses and individuals must take necessary steps towards protecting their confidential data from potential security threats.
Types of Data Security Breaches
External Hacks
External hacks come from outside sources such as hackers or malicious software that infiltrate a company’s network to steal sensitive information or cause damage. The most popular methods for external hacks include phishing scams, ransomware attacks, brute force attacks, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
Malware Attacks

Malware is a type of software that is designed to infiltrate computer systems, steal sensitive information, and cause damage to the system. There are several types of malware, including viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware and spyware.
Viruses are programs that replicate themselves and spread throughout a computer system. They can cause damage by deleting files or corrupting data. Worms are similar to viruses but do not require any user interaction to spread. They often exploit vulnerabilities in operating systems or applications to gain access to a network.
Trojans are disguised as legitimate software but contain malicious code that can take control of a system or steal sensitive information such as passwords or credit card details. Ransomware is another type of malware that encrypts data on a victim’s device and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. Spyware is designed to monitor activity on a system without the user’s knowledge.
Ransomware Attacks
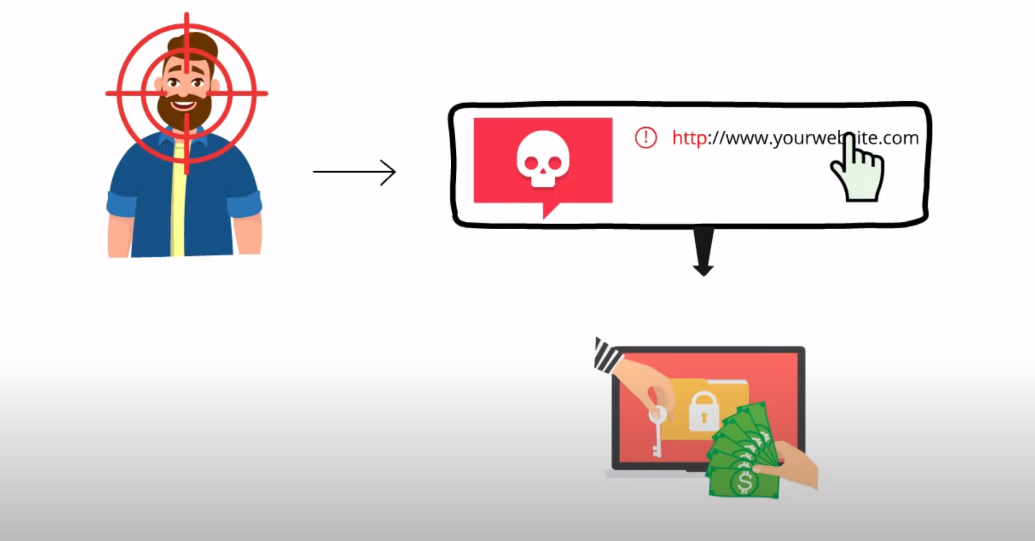
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files on a victim’s computer or network, rendering them inaccessible. The attacker then demands payment – usually in cryptocurrency – in exchange for the decryption key to unlock the files.
These attacks can occur through various means, such as phishing emails, exploiting vulnerabilities in software or operating systems, or even via social engineering tactics. Once infected with ransomware, victims may face not only financial costs but also reputational damage if sensitive information is leaked or lost due to data encryption.
Phishing Attacks
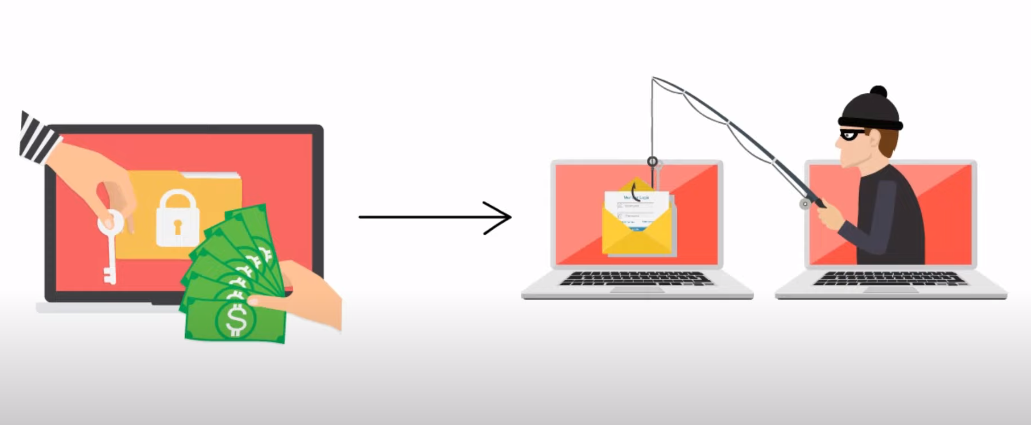
Phishing attacks involve tricking users into divulging sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and other personal data by posing as a legitimate entity like a bank or service provider. Typically, these attacks are carried out via email or social media channels using various tactics to deceive recipients.
One technique used in phishing is spear-phishing where attackers personalize their messages to appear more credible and trustworthy. This often involves using information gained from publicly available sources like social media profiles to craft a convincing message that appears to be from someone the recipient knows or trusts. In another form called whaling, high-level executives or employees are targeted with customized emails that seem urgent or important for them to respond to immediately.
Internal Threats
Internal threats are one of the primary causes of data security breaches in any organization. These threats can come from employees, contractors or even former employees who still have access to company networks and systems.
Insider Attacks
Insider attacks are security breaches caused by malicious or negligent actions of employees, contractors, or other authorized people within a company. According to research, insider attacks have been on the rise and constitute a significant threat to business data security. These types of cyber incidents can result in stolen sensitive information, financial losses, reputation damage and more.
Human Error
Human errors can take many forms, including misconfigured systems, weak passwords, accidental data leaks or loss of devices containing sensitive information.
One major factor contributing to human error is the lack of awareness and training for employees. Organizations need to invest time and resources in educating their employees on best practices for data security. This can include regular training sessions on password management, safe browsing habits and how to identify phishing attacks.
Causes of Data Security Breaches
Outdated Security Measures
Unfortunately, many companies continue to rely on outdated security measures that are no longer effective against modern threats.
One of the most common outdated security measures is relying solely on passwords for authentication. While passwords can be useful, they are no longer enough to protect sensitive data from determined hackers. Multifactor authentication is now seen as a baseline requirement for any organization serious about data security.
Another outdated measure is failing to encrypt all sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Encryption helps ensure that even if an attacker gains access to your system, they won’t be able to read or steal your data without also having access to the encryption keys. Encrypting all sensitive information should be standard practice across all industries.
Relying on legacy antivirus software alone is another mistake made by many businesses. Antivirus programs can only detect known malware and viruses but cannot protect against newer zero-day attacks or other advanced hacking techniques commonly used today.
Weak Passwords
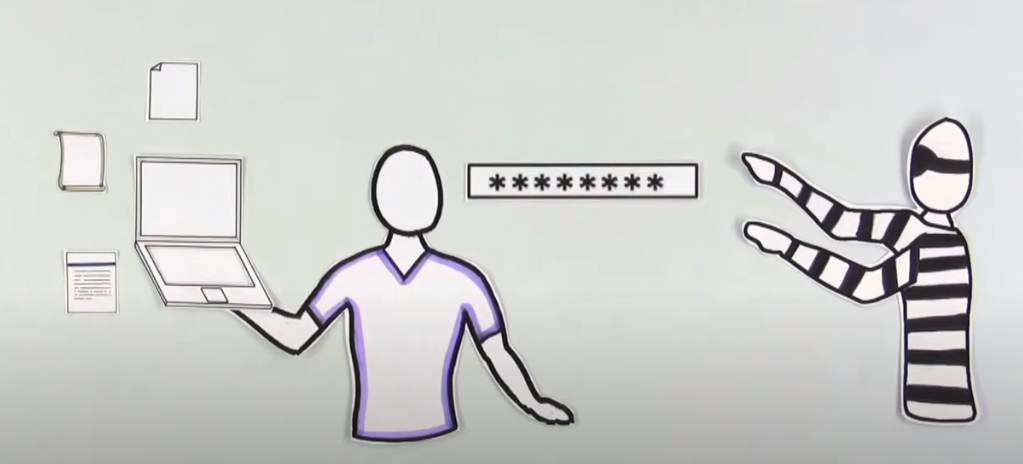
Weak passwords are one of the most common causes of data security breaches. They are easy to guess, leaving accounts and sensitive information vulnerable to cybercriminals. A weak password can be anything easy to guess or crack, such as “123456” or “password.” These two passwords have been among the top five most commonly used passwords for years.
Unsecured Networks
When a network is unsecured, it means that anyone can access it without needing a password or any other form of authentication. This makes it easy for hackers to gain access to sensitive information, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and other personal data. Unsecured networks are often found in public places like coffee shops and airports.
Hackers gain access to unsecured networks by using a technique called “packet sniffing.” This involves intercepting data packets that are transmitted over the network and analyzing them for sensitive information. Hackers can also set up fake hotspots (known as “evil twins”) that mimic legitimate Wi-Fi networks to trick users into connecting to them.
Third-Party Services
Outsourcing certain tasks to third-party providers can help alleviate the workload of an internal team, as well as provide cost savings. However, it also means that sensitive information is being shared with another entity and there is potential for security vulnerabilities.
Social Engineering
Social engineering is a tactic used by hackers to manipulate people into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that benefit the attacker. This technique relies on human emotion, curiosity, and trust to deceive victims. Examples of social engineering tactics include phishing emails, pretexting, baiting, and quid pro quo.
Consequences of Data Security Breaches
Financial Losses
Data security breaches can cost companies and individuals substantial financial losses. The expenses incurred by a data breach include not only the direct costs of remediation but also the indirect costs associated with reputational damage and loss of trust from customers. Financial losses can occur in several forms such as fines, legal fees, customer compensation, credit monitoring services for affected customers, and lost revenue.
Legal Consequences
The legal fallout from a breach can be extensive and expensive. Companies that fail to protect their customers’ data may face lawsuits, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage. In some cases, a company’s failure to protect customer data may even result in criminal charges.
One of the most severe legal consequences of a data security breach is the potential for lawsuits. Customers whose personal information was compromised in a breach have the right to sue the company responsible for damages such as identity theft or financial losses resulting from fraudulent activity. Additionally, regulatory bodies such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) can bring action against companies that fail to comply with industry standards regarding data protection.
Reputation Damage
When a company’s sensitive information falls into the wrong hands, it can cause irreversible damage to its reputation, leading to a loss of trust among customers and clients. In today’s digital age, where privacy and security are paramount concerns for consumers, a breach can have far-reaching effects on an organization’s bottom line.
Prevention of Data Security Breaches
Robust Password Policies
A robust password policy involves creating strong passwords consisting of a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. In addition to creating strong passwords, it is important to enforce regular password changes. This practice ensures that even if a password is compromised, it will not remain vulnerable for an extended period. Password managers can also be used to create and store complex passwords securely.
It is equally important to educate employees on the importance of following these policies. Regular training sessions on data security best practices should be conducted for all employees in the organization so they understand the importance of maintaining strong passwords and adhering to established policies.
Up-to-date Security Measures
Install software and hardware firewalls that can monitor and filter both incoming and outgoing traffic. Use strong passwords with a combination of upper case letters, lower case letters, numbers, and special characters.
Apart from that, regular security updates are necessary to patch up vulnerabilities in current systems. This includes keeping all software updated on all devices used within an organization.
Training and Awareness Programs
Training and awareness programs provide employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to identify potential vulnerabilities and take appropriate measures to prevent hacks. Regular training sessions on topics such as password protection, phishing scams, and secure internet browsing can go a long way in reducing the risk of cyber attacks.
Apart from employee training, organizations can also conduct awareness campaigns aimed at educating customers and clients about potential risks associated with shared personal data. With increased public awareness, people are likely to be more cautious while sharing sensitive information online or offline.
Access Controls
Access controls refer to the mechanisms that regulate who is authorized to access sensitive information and how they can do so. Access control systems use various techniques such as passwords, biometric scans, or smart cards to ensure only authorized individuals can access confidential data.
One common type of access control system is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which assigns permissions based on an individual’s job function within an organization. Another technique, Mandatory Access Control (MAC), regulates access based on predefined security policies and uses labels that indicate the sensitivity level of each piece of data.
Regular Backups
Backing up data regularly means creating multiple copies of important files and storing them in different locations to prevent loss in case of a disaster. These backups should be kept updated as data changes over time.
There are several ways to back up data, including cloud-based solutions, external hard drives, or network-attached storage (NAS). It is important to choose a backup method that works best for your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Additionally, it is crucial to test the backup regularly to ensure that it can be restored without any issues.
Responding to a Data Security Breach
Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan is a documented process that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a security breach or cyber-attack. This plan should include the roles and responsibilities of all individuals involved, including executives, IT staff, legal counsel, and public relations representatives. It should also outline communication protocols with customers and stakeholders.
Having an incident response plan in place can minimize damages caused by a data breach or cyber-attack. The faster your organization can identify and contain the breach, the less likely it will spread or cause long-term damage to your organization’s reputation.
Containment
Containment refers to the process of isolating and limiting the spread of a breach to prevent further damage. Once a breach has been detected, containment measures should be immediately implemented to minimize its impact on the organization’s operations and reputation. This involves identifying affected systems, devices or networks and isolating them from others until they can be secured.
Effective containment measures ensure that the damage caused by a breach is limited, thus reducing the risk of financial loss and reputational damage. Containment efforts should also include informing relevant stakeholders of the breach so that they can take necessary precautions, such as changing their passwords or monitoring their accounts for suspicious activity. An effective containment plan should also consider how to restore normal operations once the threat has been neutralized.
Assessment
The first step in assessing a breach is to identify the type of information that has been compromised, such as personally identifiable information (PII) or confidential business data. This will help determine the level of risk involved and inform decisions on how to handle the situation.
Once the type of information at risk is identified, it’s important to determine how many individuals or entities have been affected. This can be done by analyzing server logs, system access records, and other relevant data sources. It’s also important to consider any legal obligations for notification or reporting, such as under GDPR.
FAQs
What Are The Regulatory Frameworks For Data Security Breaches?
In the United States, several federal and state laws have been enacted to regulate data security breaches. The most notable among these is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which mandates the protection of patient health information by healthcare providers, plans, and clearinghouses.
Another important regulation in the US is the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), which requires financial institutions to protect customer’s financial information. Under GLBA’s Safeguards Rule, covered entities must develop a written information security program that outlines how they will safeguard customer records and information.
In Europe, data protection regulations are governed by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This regulation provides strict guidelines for how companies should handle the personal data of EU citizens. GDPR mandates strict notification requirements in case of a breach affecting personal data, including notifying affected individuals within 72 hours of discovering a breach. Companies that fail to comply with GDPR risk facing significant fines for non-compliance.
What Are The Common Myths About Data Security Breaches?
Myth #1: Only big companies get hacked. This is a common misconception that smaller companies cannot be targeted by hackers. However, the reality is that small businesses are often easier targets because they often have weaker security measures in place.
Myth #2: Data breaches only happen as a result of external attacks. While external attacks such as hacking and phishing emails are a significant concern, internal threats from employees or contractors can lead to data breaches too. According to studies, insider threats make up about 60% of all data breaches.
Myth #3: Strong passwords are enough to protect against data breaches. While having strong passwords is an essential aspect of online security, it’s not always enough to prevent data breaches. Hackers use various techniques like social engineering and malware injections to bypass password protections and steal sensitive information.
When Should A Data Security Incident Be Reported?
In most cases, it’s essential to report data security breaches as soon as possible, within 72 hours in some jurisdictions. This is because the breach may cause significant harm to customers or individuals whose personal information was exposed.
What If The Policy Is Violated Related To Data Security?
If a company violates its policies regarding data security, it may face regulatory fines or penalties. These penalties can be significant depending on the scope of the breach and how much damage has been done. Additionally, if customers’ private information is compromised due to security violations, they may lose faith in the organization’s ability to protect their data in the future.
How Do You Spot A Data Security Breach?
One of the most common signs of a data security breach is when there is a sudden and unexplained increase in network activity. This may be an indication that hackers have infiltrated your system, as they will often use high amounts of bandwidth to transfer stolen data out of your network. Another red flag to watch out for is unexpected pop-ups or error messages, which could indicate the presence of malware on your computer.
Another important sign to look out for is unusual login activity, such as failed login attempts or logins from unfamiliar IP addresses. This could mean that someone has gained unauthorized access to your account or system.
What Constitutes A Breach Of Data Security?
A breach can occur when cybercriminals gain access to an organization’s network through a vulnerability in their system software or via a targeted spear-phishing email campaign. Once inside the network, hackers may use malware to infiltrate multiple systems and collect sensitive data on users’ online behavior, preferences and browsing history. Data breaches can have severe consequences for individuals affected by the attack. Personal information may be sold on the dark web resulting in identity theft or other fraudulent activities.
Conclusion
Data security breaches are becoming more common in today’s digital world. It is essential to take preventive measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access by implementing robust security protocols and educating employees on how to avoid potential vulnerabilities. Additionally, regular audits and assessments should be conducted to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities that could lead to a data breach.
In the event of a data breach, businesses must have an incident response plan in place that outlines the steps they need to take to mitigate the damage caused by the breach. This includes notifying customers who may have been impacted by the breach and taking steps to prevent further breaches from occurring. Businesses should also consider investing in cyber insurance policies as an extra layer of protection against potential losses resulting from a data breach.
