Introduction
The Importance Of Data Security

Data security has become increasingly important as more businesses move their operations online. Cybercriminals are constantly developing new methods to infiltrate networks and steal sensitive information such as credit card numbers or personal identification details. A single data breach can have devastating consequences for both businesses and individuals alike.
To protect against these threats, it is essential to implement strong data security measures across all systems and devices used for business purposes. This includes using encryption protocols, regularly updating software and hardware systems, conducting regular security audits, and limiting employee access to sensitive data on a need-to-know basis, among other measures aimed at ensuring the three key principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability are maintained at all times.
The Rise Of Cyberattacks
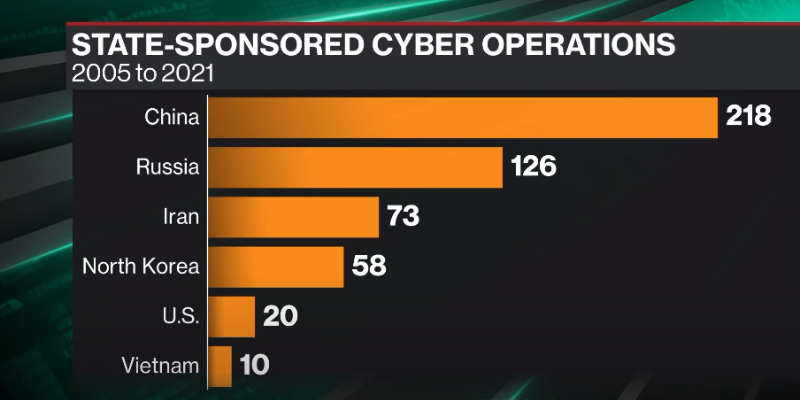
The rise of cyberattacks has become a significant concern for individuals and organizations worldwide. The recent surge in data breaches and hacking attacks highlights the need for robust measures to ensure data security.
The Three Key Principles Of Data Security
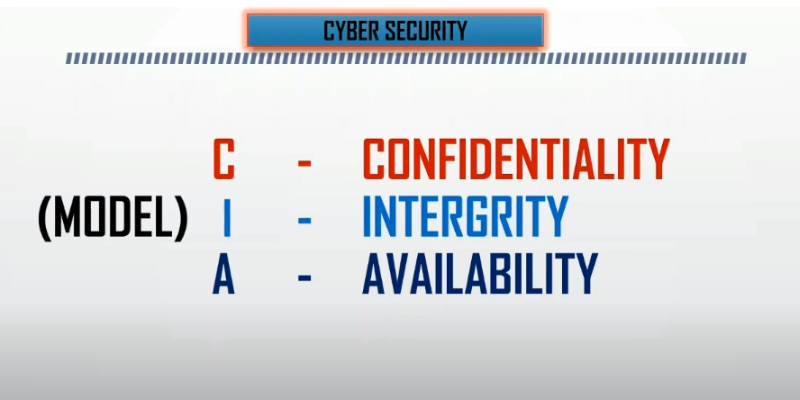
The three key principles of data security involve confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Confidentiality refers to the protection of sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. This means that personal information should only be shared with authorized personnel who have a legitimate reason for accessing it.
Integrity is the assurance that data has not been tampered with or modified without authorization. This principle ensures that data remains accurate and trustworthy over time. It also helps to prevent incidents where incorrect data is used to make important decisions.
The final principle is availability which refers to ensuring that data is accessible by authorized users when needed. Data must remain available at all times so that it can be used effectively and efficiently by those who need it most.
Principle 1: Confidentiality
Defining Confidentiality
Confidentiality refers to the protection of sensitive information against unauthorized access or disclosure. Confidentiality ensures that confidential information, such as trade secrets or personal information, is only accessible by authorized personnel who have a legitimate reason to access it.
To maintain confidentiality, organizations should implement strict access controls and user authentication measures. This includes password management policies, multi-factor authentication, and regular system audits to identify any potential vulnerabilities. Additionally, encryption technologies are essential in ensuring data confidentiality since they render data unreadable and unusable without the appropriate decryption key.
Confidentiality also extends beyond technological measures; it involves creating a culture of trust within an organization where employees understand the importance of keeping sensitive information private. Organizations should establish clear guidelines for handling confidential information and provide regular training for employees on how to handle this type of data appropriately. By prioritizing confidentiality as a core principle of data security, organizations can ensure that their sensitive information remains protected from potential threats both inside and outside the organization.
The Role of Encryption
Encryption plays a critical role in ensuring that confidential data remains private and protected from unauthorized access. It involves converting plain text into an unreadable form using complex algorithms, making it virtually impossible for anyone without proper authorization to decipher the information.
Data Masking And Anonymization
The concept of data masking involves obscuring sensitive information from unauthorized access. It is used to protect the confidentiality of valuable information while still allowing authorized users to use the data as needed. Data masking can be achieved by replacing sensitive information with fictitious, but realistic-looking values that do not reveal any personal or confidential data.
Anonymization, on the other hand, is a process that involves removing all identifying information from a dataset so that it cannot be traced back to an individual or entity. Anonymizing data ensures compliance with privacy regulations and helps reduce the risk of identity theft and other forms of cybercrime. With anonymization, personally identifiable information (PII) such as names, phone numbers, addresses, and social security numbers can be removed.
Access Controls
Access controls ensure that only authorized individuals are granted access to sensitive data, application systems, and network resources. Access controls can be implemented in various ways including physical security measures such as locks, biometric authentication methods like facial recognition or fingerprints, and software-based access control mechanisms such as login credentials or permissions-based roles.
Effective access controls must also include monitoring and logging mechanisms to detect any unauthorized attempts at accessing information. This is especially important for organizations that store sensitive customer data such as financial information or medical records. By implementing robust access controls, organizations ensure the protection of sensitive data.
Limiting Data Retention
This means that organizations should only collect and store data for as long as it is necessary to fulfill a specific purpose. Once that purpose has been fulfilled, the data should be securely deleted or destroyed.
Limiting data retention helps to reduce the risk of data breaches and other forms of unauthorized access to sensitive information. The longer an organization holds onto data, the greater the likelihood that it will be exposed to cyber threats or accidental disclosure.
In addition, limiting data retention is also good practice from a privacy perspective. By ensuring that personal information is not held beyond what is necessary, organizations can help to protect individual privacy rights and meet their legal obligations under privacy laws and regulations.
Principle 2: Integrity
Defining Integrity
The concept of integrity refers to maintaining the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of data over time. This means ensuring that data is not tampered with or altered in any way without authorization. Maintaining integrity is essential for ensuring trust in data, as inaccurate or incomplete information can lead to faulty decisions and outcomes.
There are several ways to maintain data integrity, including implementing access controls and encryption, regularly backing up data, and conducting regular audits to check for inconsistencies or errors. Additionally, organizations must establish clear policies and procedures around data handling to ensure that all employees understand their responsibilities when it comes to maintaining the integrity of sensitive information.
Data Validation And Verification
This process ensures that the data entered into a system or database is accurate, complete, and consistent with existing records. It involves checking for errors, inconsistencies, and missing information to avoid any potential threats to the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the data.
Data validation and verification can be achieved through various techniques such as manual inspection, automated tools, or external sources. The goal is to identify any anomalies in the data that may indicate fraudulent activities, human errors, or system malfunctions. By validating and verifying the accuracy of the data regularly and consistently, organizations can prevent security breaches that could be costly in terms of reputation damage or financial losses.
Maintaining Accuracy And Consistency
These principles ensure that the information stored within a system or database is reliable, trustworthy, and consistent across all platforms. Accurate data refers to information that is correct, up-to-date, and free from errors or discrepancies. Consistent data refers to ensuring the same information is available across all platforms and users.
One of the main reasons why maintaining accuracy and consistency is important in data security is because inaccurate or inconsistent information can lead to incorrect decisions being made by organizations. For example, if customer details are not updated correctly within a company’s database, this can lead to incorrect invoices being sent out or orders being delivered to the wrong address, leading to reputational damage for the organization.
Digital Signatures And Certificates
A digital signature is a mathematical technique used to validate the authenticity of an electronic document or message. It uses public-key cryptography to encrypt the sender’s identity and ensure that the content of the message has not been tampered with during transmission. Digital certificates, on the other hand, are electronic documents that verify the identity of individuals or organizations involved in online transactions.
The use of digital signatures and certificates helps to enforce all three key principles that define data security: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Confidentiality ensures that only authorized persons have access to sensitive information while integrity ensures that data remains accurate and unmodified during transmission. Availability guarantees that users can access data whenever they need it.
Principle 3: Availability
Defining Availability
Availability refers to ensuring that authorized users have access to the necessary data and resources when they need them. This means that a system should be up and running, able to handle requests and provide timely responses at all times.
Achieving high availability requires proactive measures such as redundancy, failover systems, load balancing, and monitoring tools. Redundancy involves having multiple copies of critical components such as servers or storage devices so that if one fails, another can take over seamlessly. Failover systems automatically switch to a backup component when a primary one fails.
Load balancing distributes workloads across multiple servers so that no single server is overwhelmed with requests while others are idle. Monitoring tools continuously track the performance of network components and alert IT teams if any issues arise.
Redundancy And Backups
Redundancy refers to having multiple copies of data stored in different locations, while backups refer to creating regular copies of data for safekeeping. These two principles ensure that even if one copy or location of data is compromised, there are still other copies available for recovery.
Having redundancy and backups in place can also help prevent data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or human error. By having multiple copies of critical data stored in different locations, businesses can quickly recover from any unforeseen circumstances without losing valuable information.
Moreover, redundancy and backups play a vital role in ensuring business continuity by minimizing downtime during system failures or cyber-attacks. This helps businesses avoid costly loss of revenue or reputational damage that could result from extended periods of system outages.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster recovery planning refers to the process of creating a plan for how your organization will respond in the event of a catastrophic event, such as a natural disaster or cyber attack. This plan should outline steps for restoring critical systems and data, minimizing downtime, and preventing data loss.
The three key principles that define effective disaster recovery planning include preparation, communication, and testing. Preparation involves identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities to your organization’s systems and data, as well as establishing procedures for responding to these threats. Communication involves ensuring that all stakeholders are aware of the plan, including employees, customers, and vendors. Testing involves regularly reviewing and updating the plan based on changes in technology or business operations.
Service-Level Agreements (Slas)
Service-level agreements (SLAs) are contractual agreements between service providers and their clients that outline the level of service expected from the provider. In terms of data security, SLAs define the measures taken by service providers to protect their client’s sensitive information. These agreements often include provisions for regular security audits, penetration testing, and incident response plans to ensure that any breaches are promptly addressed.
Preventing Denial Of Service (Dos) Attacks
Preventing DoS attacks should be a crucial element in any organization’s overall data security strategy. One way organizations can prevent DoS attacks is by deploying firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems that can identify and filter out potential threats based on defined rulesets. Additionally, network administrators should monitor network activity regularly and proactively block suspicious IP addresses.
Organizations may also consider implementing rate-limiting policies to limit the number of requests from individual IP addresses or limit access to specific resources within their networks. These strategies can thwart attempts to flood systems with traffic and reduce an attacker’s ability to execute DoS attacks successfully.
Data Security Best Practices
Implementing A Layered Approach
A layered is based on the principle that relying solely on one security measure is not enough to protect against sophisticated cyber threats. By having multiple layers in place, any potential breach will be detected at different points of entry and mitigated before it can cause significant damage.
The first layer of security typically involves implementing strong access controls, such as requiring complex passwords or multi-factor authentication. The second layer may involve deploying firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor network traffic for unusual activity. The third layer could include encrypting data at rest or in transit to ensure that even if attackers gain access, they cannot read the information without the proper decryption keys.
Conducting Regular Security Audits
Regular audits can help companies stay ahead of evolving threats and ensure they are meeting regulatory compliance requirements. These assessments can also help organizations identify where their data resides, how it flows through various systems, and which users have access to it. By consistently performing these checks, businesses can proactively identify areas where they may be at risk before an attack occurs.
Moreover, conducting regular security audits provides valuable insight into how network infrastructure works as a whole. This helps companies develop better cybersecurity policies and procedures to maximize protection against external threats such as malware or cyberattacks.
Monitoring And Responding To Threats
Keep a close eye on your systems, networks, and devices to detect any suspicious activities that may compromise your data. Monitoring can be automated or conducted manually by trained personnel who are equipped with the necessary tools to identify potential risks.
Once a threat is detected, it is crucial to respond promptly and effectively. The response should be based on the nature of the threat and the level of risk it poses to your data. A well-defined incident response plan can help you take appropriate action quickly and minimize damage if an attack occurs.
Challenges and Emerging Trends
The Impact Of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has had a profound impact on how businesses approach data management and security. By implementing principles such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability, cloud providers have raised the bar for secure storage solutions while also providing greater accessibility and flexibility for users. As more businesses turn to cloud computing as a cost-effective solution for managing their growing volumes of digital assets, these principles will continue to play an increasingly important role in ensuring safe and reliable storage practices worldwide.
The Rise Of IoT Devices
As the Internet of Things (IoT) devices continue to rise, data security becomes a critical concern for organizations and individuals alike. IoT devices are connected to the internet, making them vulnerable to hacking and cyber threats.
The Challenges Of Big Data

As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow exponentially, so do the risks associated with storing, processing, and transmitting it. This has led to a heightened focus on data security and privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
Another challenge is managing the sheer amount of data generated by organizations. Without proper infrastructure, tools, and processes in place, companies risk drowning in an overwhelming sea of information that cannot be effectively analyzed or leveraged for insights.
Big data also presents a challenge when it comes to talent acquisition. The demand for skilled professionals who can manage and analyze large datasets far exceeds the supply. Companies may struggle to find qualified individuals who possess both the technical expertise and business acumen needed to extract value from their data assets.
The Growing Importance Of Data Privacy
With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, it is crucial for individuals and organizations to prioritize data security by adopting strict protocols that govern how they handle sensitive information. This includes implementing strong encryption technologies, regularly updating software systems to patch vulnerabilities, and training employees on safe online practices like avoiding phishing emails or using weak passwords.
Conclusion
Data security is imperative in today’s digital age. The three key principles that define data security are confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is only accessible by authorized users through secure channels. It helps to prevent cybercriminals from gaining access to your information.
Integrity ensures that data remains accurate and complete throughout its lifecycle. This principle guarantees the authenticity of the information by ensuring it hasn’t been tampered with or altered in any way. Finally, availability guarantees that authorized users can access the necessary data when they need it.
FAQs
Why is data security important?
The importance of data security cannot be overstated. For individuals, it means keeping personal information such as social security numbers and banking details safe from potential identity theft. For businesses, data security is crucial to safeguard sensitive company data, trade secrets, client information, and other proprietary material.
What are the consequences of a data breach?
A data breach can result in significant financial losses for an organization. Companies may face substantial fines and legal costs as a result of failing to comply with data protection regulations. Additionally, businesses may experience a decline in consumer trust and reputation damage, leading to lost revenue.
A data breach can also result in the exposure of sensitive information such as personal details or confidential business information. This can be particularly damaging to individuals whose personal information has been compromised, potentially leading to identity theft or fraud. For businesses, leaked confidential information could lead to the loss of trade secrets or intellectual property.
It can also have operational consequences for organizations. It may lead to system downtime and disruption of services which could impact productivity levels within the company.
How can I protect my personal data?
To protect your personal data, start by being vigilant about who you share your information with online. Avoid giving out sensitive details like your social security number or credit card information unless you trust the website or individual requesting it. Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication for all online accounts, as well as keeping software updated regularly.
Furthermore, be aware of phishing scams where cybercriminals attempt to trick you into revealing personal information through emails or fake websites that appear real but are designed to steal your login credentials. Finally, consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) when accessing public Wi-Fi networks since these connections may be unsecured and easily accessible by hackers looking for valuable data such as login credentials or financial details.
