Understanding Research Data
Research data refers to the information collected during a research study. This data can be in the form of numbers, text, images, or other types of media. Understanding research data is important because it allows researchers to draw conclusions and make informed decisions based on the information gathered. To understand research data, it is important to first consider the research question or hypothesis being investigated. This will help to determine what data needs to be collected and how it should be analyzed.
Different Types of Research Data
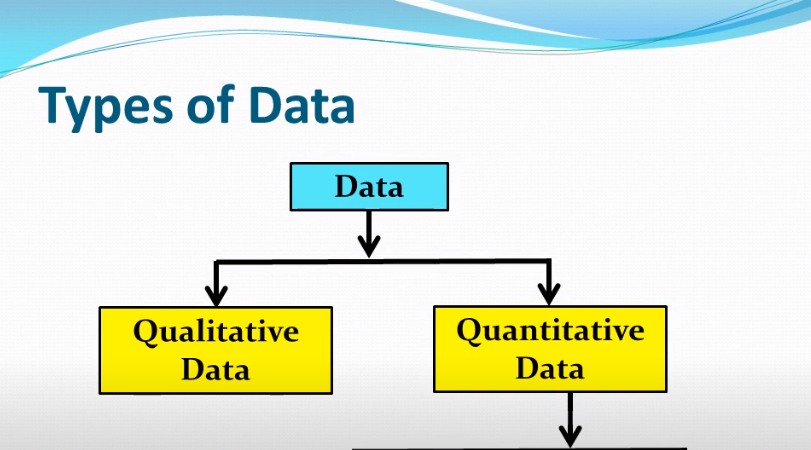
Several types of research data can be collected during a study. These include:
1. Quantitative data: This type of data is numerical and can be measured and analyzed using statistical methods. Examples include survey responses, test scores, and measurements of physical characteristics.
2. Qualitative data: This type of data is non-numerical and is collected through observation, interviews, and focus groups. Examples include transcripts of interviews, field notes, and audio or video recordings.
Sensitivity Levels And Classification
Sensitivity levels and classification refer to the degree of sensitivity or confidentiality of data and how it should be handled and protected. This can vary depending on the type of data being collected and its potential impact on individuals or organizations. For example, personal health information is considered highly sensitive and may require special security measures and strict confidentiality protocols. Other types of data, such as demographic information, may be less sensitive and require less stringent protection measures.
Identifying Vulnerabilities
To identify vulnerabilities in a system or organization, it is important to conduct a thorough risk assessment. This involves analyzing the potential threats and risks that could impact the system or organization, as well as the likelihood and potential impact of those threats. Vulnerabilities can include weaknesses in physical security, software or hardware vulnerabilities, and human error or negligence. Once vulnerabilities are identified, steps can be taken to mitigate or eliminate them by implementing security measures and protocols.
Common Threats to Research Data Security
1. Cyberattacks: These attacks can compromise the security of research data by exploiting vulnerabilities in the network, software, or hardware.
2. Insider threats: These threats come from individuals within the organization who have access to sensitive data and may misuse or steal it.
3. Physical theft or loss: This can occur when devices containing research data are lost or stolen.
Internal And External Risks

Internal risks to research data security include human error, lack of training, and unauthorized access by employees. External risks may include attacks from hackers, malware, and viruses. It is important to have a comprehensive security plan in place that addresses both internal and external risks to ensure the protection of research data. This plan should include regular security audits, employee training, and the implementation of strong passwords and encryption protocols.
Establishing a Secure Research Environment
Establishing a secure research environment is crucial to protecting research data. Here are some steps that can be taken to ensure a secure research environment:
1. Implement strong passwords and encryption protocols to protect data from unauthorized access.
2. Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
3. Provide training to employees on data security best practices to avoid human error.
4. Limit access to sensitive data to only those who need it.
5. Use firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems.
Implementing Strong Access Controls And User Authentication
It is also crucial in ensuring a secure research environment. This can include measures such as multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and permission levels. It is also important to regularly update software and systems to patch any security vulnerabilities and stay up-to-date with the latest security trends and threats. Additionally, having a disaster recovery plan in place can help ensure that data can be recovered in the event of a breach or other disaster.
Physical Security Measures For Data Storage Locations
Physical security measures for data storage locations are also important to ensure the safety of sensitive information. This can include measures such as secured access to the storage location, surveillance cameras, and alarms. It is also important to have backup systems and redundancy in place in case of any physical damage or destruction to the storage location. Regular maintenance and inspections can help identify any potential security risks and address them before they become a problem.
Encryption and Data Protection
Encryption and data protection are crucial in ensuring the security of sensitive information. Encryption involves the use of algorithms to convert data into a code that can only be deciphered with a key or password. This makes it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access and understand the information. Data protection involves implementing measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access, hacking, and data breaches.
Importance of Encryption In Safeguarding Data
Encryption is a critical tool for safeguarding data and protecting it from unauthorized access. By converting data into a code that can only be deciphered with a key or password, encryption makes it difficult for anyone without the proper authorization to access or understand the information. This is especially important for sensitive data such as financial information, personal identification information, and confidential business data. Without encryption, this information could be easily intercepted and used for malicious purposes such as identity theft or corporate espionage.
Encryption Methods And Best Practices
Several encryption methods can be used to secure data. Some of the most common encryption methods include:
1. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): This is a widely used symmetric encryption algorithm that is considered to be very secure.
2. RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman): This is an asymmetric encryption algorithm that uses two keys, one for encryption and one for decryption.
3. Blowfish: This is a symmetric encryption algorithm that is known for its speed and efficiency.
Network Security Measures
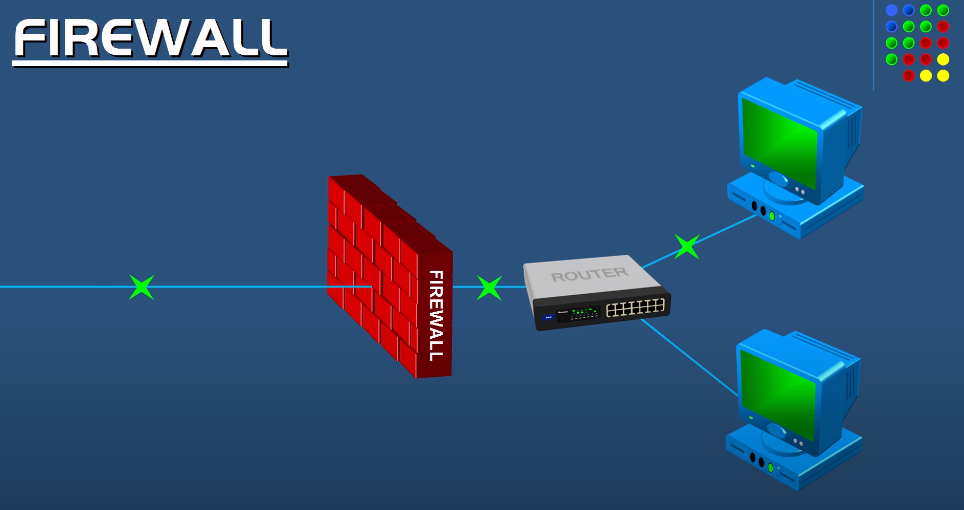
Several network security measures can be implemented to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. Some of the most common measures include:
1. Firewalls: These are hardware or software devices that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
2. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): These are secure connections that allow remote users to connect to a private network over the internet.
Securing Research Data During Transmission
To secure research data during transmission, you can implement the following measures:
1. Use encryption: Encrypting the data before transmitting it can prevent unauthorized access. There are various encryption methods available, such as SSL, TLS, and AES.
2. Use secure file transfer protocols: Use secure file transfer protocols like SFTP or FTPS to transfer the data. These protocols provide an additional layer of security by encrypting the data in transit.
Firewalls, VPNs, and Network Segmentation
To further secure research data during transmission, you can also implement firewalls, VPNs, and network segmentation. Firewalls can be used to block unauthorized access to your network, while VPNs can create a secure and encrypted connection between two devices over the internet. Network segmentation can also be used to separate sensitive data from other less sensitive data, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access to the sensitive data. Overall, implementing these measures can greatly enhance the security of your research data during transmission.
Data Backup and Recovery
Data backup and recovery is another important aspect of data security. It is crucial to regularly back up your research data to prevent loss in case of hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyber-attacks. You can choose to back up your data on external hard drives, cloud storage services, or both. It is important to ensure that your backups are encrypted and stored securely to prevent unauthorized access.
Secure Data Storage
Secure data storage is also a key component of data security. It is important to ensure that your research data is stored in a secure location that is only accessible to authorized personnel. This can be achieved by implementing access controls such as passwords, biometric authentication, and encryption. Additionally, you should ensure that your storage devices are physically secure and protected from theft, damage, or unauthorized access.
Choosing The Right Storage Solutions
Choosing the right storage solutions is crucial for ensuring the security of your research data. There are several options available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. One option is to use cloud storage services, such as Dropbox, Google Drive, or Microsoft OneDrive. These services provide convenient access to your data from anywhere with an internet connection, but it is important to ensure that the service provider has appropriate security measures in place to protect your data.
Cloud-Based Storage Considerations
When considering cloud-based storage for research data, it is important to evaluate the security measures of the service provider. This includes encryption of data both in transit and at rest, as well as secure login credentials and multi-factor authentication options. Another consideration is the location of the data centre where your data will be stored. Some countries have stricter data privacy laws than others, so it is important to ensure that your data will be stored in a location that complies with your institution’s regulations.
Incident Response and Management
The security measures of a service provider should be thoroughly evaluated before entrusting them with sensitive data. It is important to ensure that the provider uses strong encryption methods for data both in transit and at rest. Secure login credentials and multi-factor authentication options should also be in place to prevent unauthorized access. The location of the data centre where the data will be stored should also be considered, as some countries have stricter data privacy laws than others.
Developing An Incident Response Plan
Developing an incident response plan is crucial for any organization that deals with sensitive data. An incident response plan outlines the steps that need to be taken in case of a data breach or any other security incident. The plan should include contact information for key personnel, procedures for containing the incident, and steps for notifying affected parties and regulatory authorities. It is important to test the incident response plan regularly to ensure that it is effective and up-to-date. This can be done through tabletop exercises or simulated drills.
Collaborative Research and Data Sharing
Collaborative research and data sharing can greatly benefit the scientific community by promoting the exchange of knowledge and ideas and accelerating the pace of discovery. However, it is important to ensure that any shared data is properly managed and protected to maintain its integrity and prevent unauthorized access. This can be achieved through the use of data-sharing agreements, which outline the terms and conditions of data sharing, including data ownership, permitted uses, confidentiality, and liability.
Secure Data-Sharing Practices
Secure data-sharing practices are essential for protecting sensitive information and maintaining the trust of data contributors. Some best practices for secure data sharing include:
1. Implementing strong access controls: Access to shared data should be restricted to authorized users only, with appropriate levels of access based on their roles and responsibilities.
2. Encrypting data in transit and at rest: Data should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access or interception, both while it is being transmitted and while it is stored.
Emerging Technologies and Data Security
In addition to best practices for secure data sharing, emerging technologies are also playing a key role in data security. For example, blockchain technology is being used to create secure and tamper-proof data storage and sharing systems. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used to detect and prevent cyber attacks, as well as to identify potential vulnerabilities in data systems. Cloud computing is also being used to provide secure and scalable data storage solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the consequences of a data breach in research?
The consequences of a data breach in research can be severe and far-reaching. It can lead to the loss of sensitive information, such as personal and financial data, intellectual property, and confidential research data. This can result in reputational damage, loss of trust, legal and regulatory penalties, and financial losses. In addition, a data breach can also impact research outcomes, compromise the validity of research data, and damage the integrity of the research process.
How can encryption help protect research data?
Encryption can help protect research data by converting the data into a code that can only be deciphered with a specific key or password. This means that even if the data is accessed by unauthorized individuals, they will not be able to read or use it without the key or password. Encryption can also help protect data during transmission, such as when it is being sent over the internet or through email.
What are the best practices for securing data storage?
There are several best practices for securing data storage, including:
1. Use strong passwords: Ensure that all passwords used to access data storage systems are strong and unique. Avoid using easily guessable passwords such as “password” or “123456”.
2. Limit access: Only grant access to data storage systems to those who need it. This can be done through user permissions and access controls.
How can researchers ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards?
Researchers can ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards by following these steps:
1. Familiarize themselves with relevant laws and regulations: Researchers should be aware of the laws and regulations that apply to their research, such as data protection laws and regulations governing the use of human subjects in research.
2. Obtain informed consent: Researchers should obtain informed consent from study participants before collecting any data. This means that participants should be fully informed about the study and its potential risks and benefits before they agree to participate.
What should be included in an incident response plan?
An incident response plan should include the following components:
1. Incident identification: A process for identifying and reporting incidents.
2. Incident analysis: A process for analyzing the incident to determine its cause and impact.
3. Incident response: A plan for responding to the incident, including steps to contain the incident and mitigate its impact.
4. Communication plan: A plan for communicating with stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and regulators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, secure data sharing is essential for businesses and organizations to protect sensitive information and maintain the trust of their customers. Best practices, such as encryption and access control, are important for securing data, and emerging technologies like blockchain, AI, and cloud computing are providing new and innovative ways to enhance data security. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and technologies, organizations can ensure that they are taking the necessary steps to protect their data and maintain the integrity of their business operations.
