Explanation of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to delivering computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the Internet. Instead of owning and maintaining physical servers, businesses can access these services on-demand from a cloud provider, paying only for what they use. Cloud computing allows businesses to scale their computing resources up or down quickly and easily, without investing in expensive hardware or infrastructure.
Importance of Data Security in Cloud Computing
Data security is crucial in cloud computing, as businesses entrust their sensitive information to third-party cloud providers. Cloud providers must ensure that their systems and networks are secure from cyber threats, such as hacking, data breaches, and malware attacks. They must also implement strict access controls, encryption, and other security measures to protect customer data. Businesses must also take steps to ensure the security of their data in the cloud.
Types of Attacks on Cloud Data
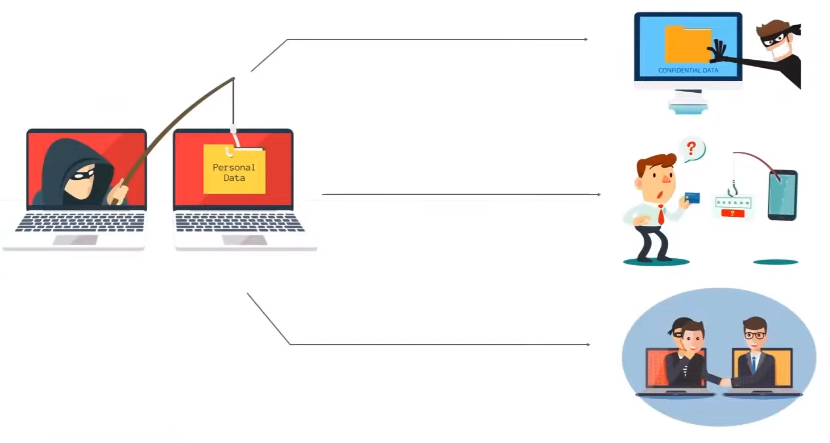
Several types of attacks can target cloud data, including:
1. Malware attacks: Malware is software designed to damage or disrupt computer systems. Malware attacks on cloud data can be particularly devastating, as they can spread quickly and affect multiple users.
2. Data breaches: A data breach occurs when an unauthorized person gains access to sensitive information. In cloud computing, data breaches can occur if a hacker gains access to the cloud provider’s systems.
Common Cloud Security Risks
In addition to the types of attacks mentioned above, there are several other common cloud security risks that organizations should be aware of. These include:
1. Insider threats: Employees or contractors with access to cloud data can intentionally or unintentionally cause harm to the organization’s data security.
2. Denial of Service (DoS) attacks: A DoS attack is designed to overwhelm a system with traffic, making it unavailable to users.
Examples of Cloud Data Breaches
There have been several high-profile cloud data breaches in recent years, including:
1. Capital One: In 2019, a hacker gained access to the personal information of over 100 million Capital One customers by exploiting a vulnerability in the company’s cloud infrastructure.
2. Dropbox: In 2012, Dropbox suffered a data breach that resulted in the theft of user email addresses and passwords. The breach was caused by a vulnerability in a third-party application used by Dropbox.
Understanding Cloud Security Architecture
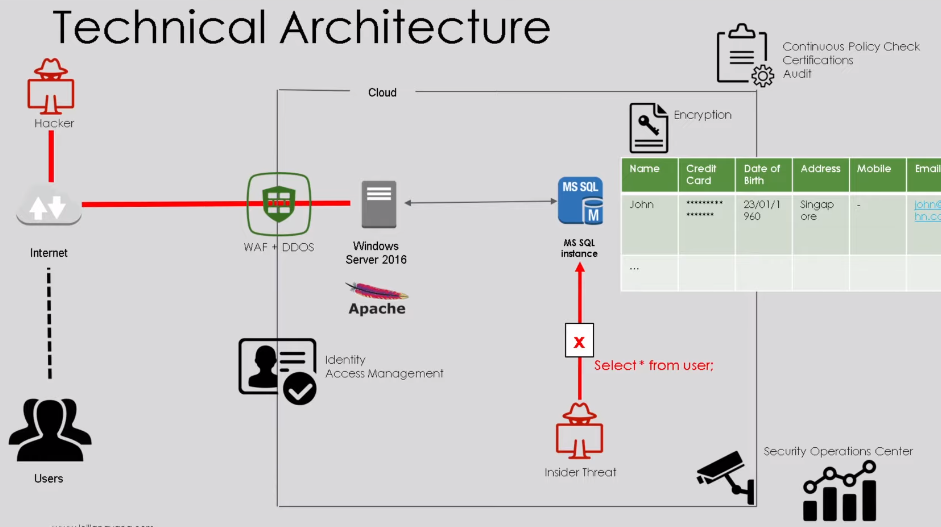
Cloud security architecture refers to the design and implementation of security measures in a cloud computing environment. This includes the use of firewalls, encryption, access controls, and other security technologies to protect data and applications stored in the cloud. To understand cloud security architecture, it is important to first understand the different types of cloud deployments. These include public clouds, private clouds, and hybrid clouds. Each type of deployment has its unique security considerations.
Cloud Computing Models
Cloud computing models refer to the different ways in which cloud services are delivered to users. There are three main cloud computing models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model has its security considerations that need to be addressed.IaaS involves the provision of computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking over the Internet.
Cloud Security Best Practices
Cloud security best practices include:
1. Strong authentication: Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to your cloud accounts.
2. Encryption: Encrypt your data both in transit and at rest to prevent data breaches.
3. Regular backups: Regularly back up your data to avoid data loss in case of a security breach.
4. Access control: Implement access controls to limit access to sensitive data and resources to only authorized personnel.
Cloud Security Tools And Technologies
There are many cloud security tools and technologies available to help protect your data and resources. Some popular options include:
1. Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): These tools provide visibility and control over cloud applications and data, helping to prevent data breaches and ensure compliance.
2. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): CSPM tools help organizations identify and remediate security risks in their cloud environments.
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM solutions help manage user access to cloud resources.
Critical Factors for Securing Data in Cloud Computing
- Authentication and access control
- Data encryption
- Backup and disaster recovery
- Monitoring and logging
- Compliance and regulations
Cloud Security Measures for Specific Cloud Providers
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
Steps To Secure Your Cloud Infrastructure
Securing your cloud infrastructure is essential to protect your data and prevent unauthorized access. Here are some steps you can take to secure your cloud infrastructure:
1. Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to secure access to your cloud accounts.
2. Implement network security controls, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to monitor and prevent unauthorized access to your cloud resources.
3. Encrypt your data both in transit and at rest to protect it from interception and theft.
Managing Third-Party Risks in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become increasingly popular for businesses of all sizes, but it also comes with potential risks, particularly when it comes to third-party providers. Here are some steps you can take to manage third-party risks in cloud computing:
1. Conduct due diligence on potential cloud providers. This includes reviewing their security policies and procedures, as well as their track record for data breaches or other security incidents.
2. Clearly define your security requirements and expectations with your cloud provider. This should include details about access controls, data encryption, and incident response procedures.
3. Establish a strong service level agreement (SLA) with your cloud provider. This should outline the provider’s responsibilities for security, availability, and performance, as well as your recourse in the event of a breach or outage.
4. Regularly monitor your cloud provider’s security practices and performance. This can include conducting regular security audits and vulnerability assessments, as well as reviewing incident response plans.
By taking these steps, you can help mitigate the risks associated with third-party providers in cloud computing and ensure the security of your data and infrastructure.
Vendor Assessment And Selection
When selecting a vendor for cloud computing services, it’s important to conduct a thorough assessment to ensure they meet your security and performance requirements. Here are some steps you can take:
1. Define your requirements: Before you start evaluating vendors, define your specific requirements for security, performance, availability, and support. This will help you narrow down your options and ensure you choose a vendor that can meet your needs.
2. Research potential vendors: Research potential vendors to determine their reputation in the market.
3. Review service-level agreements (SLAs): Carefully review the SLAs of each vendor to ensure they meet your requirements for uptime, response times, and support.
4. Verify security measures: Verify that each vendor has adequate security measures in place to protect your data and systems. This may include encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
5. Test performance: Conduct performance tests to ensure that the vendor’s solution can handle your workload. This may include load testing and stress testing.
FAQs
What Are The Main Threats To Cloud Security?
The main threats to cloud security include data breaches, unauthorized access, insider threats, data loss or leakage, and insecure APIs. These threats can result in the compromise of sensitive data, financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal consequences. It is important to choose a cloud vendor that has robust security measures in place to mitigate these risks.
How Can I Secure My Data In The Cloud?
There are several ways to secure your data in the cloud, including:
1. Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Encrypt your data both in transit and at rest.
3. Regularly back up your data to prevent data loss.
4. Implement access controls to limit who can access your data.
5. Use a reputable cloud provider with a strong track record of security.
6. Regularly monitor your cloud environment for any suspicious activity.
What Are The Regulatory Requirements For Cloud Security?
The regulatory requirements for cloud security vary depending on the industry and location. Some common regulations include:
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – applies to all companies that handle EU citizen data.
2. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) – applies to healthcare organizations in the US.
3. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) – applies to companies that handle credit card information.
How Do I Manage Third-Party Risks In Cloud Computing?
Managing third-party risks in cloud computing can be challenging, but there are several steps you can take to mitigate these risks:
1. Conduct due diligence: Before partnering with a cloud provider, conduct a thorough evaluation of their security protocols and compliance with relevant regulations.
2. Establish clear expectations: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of the cloud provider and your organization in terms of security and data protection.
3. Implement strong contracts: Ensure that the contract with the cloud provider includes specific security requirements and provisions for breach.
What Emerging Trends Are There In Cloud Security?
There are several emerging trends in cloud security, including:
1. Multi-cloud security: As more organizations adopt a multi-cloud strategy, there is a growing need for security solutions that can manage and protect data across multiple cloud environments.
2. Cloud-native security: With the increasing use of cloud-native technologies like containers and serverless computing, security solutions are being developed specifically for these environments.
3. Zero-trust security: This approach to security assumes that all users and devices are potential threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the right vendor for your business is crucial for the success of your operations. By following these five steps, you can ensure that you choose a vendor that meets your requirements and provides the necessary support and security. Remember to thoroughly research each vendor, evaluate their experience and reputation, review their SLAs, verify their security measures, and test their performance. By doing so, you can make an informed decision and select a vendor that will help your business thrive.
