Introduction
Definition Of Data Security Controls
Data security controls refer to the measures and strategies implemented by organizations to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. These controls are designed to safeguard an organization’s confidential information, such as customer data, employee records, financial statements, and other proprietary information.
Data security controls can be classified into three categories: administrative controls, physical controls, and technical controls. Administrative controls include policies and procedures that govern how employees should handle sensitive data. Physical controls refer to tangible measures like locks and surveillance cameras that secure an organization’s premises where sensitive data is stored. Technical controls encompass software tools like encryption programs that protect digital assets from cyber threats.
Importance Of Data Security Controls In Today’s World
In today’s world, data is everything. It drives business decisions, personal choices, and even government policies. With so much sensitive information being transmitted online every day, it’s crucial that we have strong data security controls in place to protect against unauthorized access and breaches.
Data security controls play an important role in safeguarding sensitive data by preventing unauthorized access or theft. Without these controls in place, businesses and individuals alike are at risk of losing their private information or suffering financial losses due to cybercrime.
Moreover, the importance of data security controls cannot be overstated given the increasing sophistication of cyber attacks today. Hackers are always searching for vulnerabilities to exploit in systems and networks around the world. By implementing strong data security controls backed by regular testing and updates, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and ensure that their most valuable asset – their data – remains safe from harm.
Types of Data Security Controls
Physical Security Controls
Physical security controls refer to the measures taken to ensure the physical safety and protection of company assets, such as equipment, data centers, and buildings. These controls are essential in preventing unauthorized access to critical facilities and information systems. Examples of physical security controls include surveillance cameras, fences, locks, biometric scanners, and electronic access control devices.
Organizations must have a comprehensive physical security plan that includes policies and procedures for managing access to their premises. The plan should be reviewed regularly to identify vulnerabilities and potential risks that may arise from changes in technology or business operations. Additionally, organizations should train their employees on how to enforce these policies effectively.
Technical Security Controls
Technical security controls refer to the measures taken to protect data and information systems through technology. These controls are essential in ensuring that data is not compromised and that unauthorized access is prevented. Technical security controls are often implemented at various levels, including the network, application, operating system, and database layers.
Some examples of technical security controls include firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), encryption technologies such as SSL/TLS, access control mechanisms like passwords and biometric authentication devices, and antivirus software. Firewalls serve as a barrier between an internal network and external networks or the internet; they can be hardware-based or software-based. IDS helps detect malicious activities before they become a threat.
Encryption technologies protect sensitive data by encoding it during transmission or storage. Access control mechanisms prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing data through various means such as biometric authentication devices or passwords. Antivirus software detects viruses and malware that can harm information systems.
Administrative Security Controls
Administrative security controls are the policies and procedures designed to manage and protect an organization’s information assets. These controls are implemented by management to ensure that the company’s information systems, data, and resources are protected against unauthorized access, theft, or misuse.
Administrative security controls can include measures such as background checks for employees who handle sensitive data, employee training programs on cybersecurity awareness and best practices, system auditing and monitoring protocols to detect security breaches or incidents in real-time, password policies that enforce complex passwords with frequent updates and limited access privileges based on job duties.
In addition to these measures, administrative security controls also involve continuous risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in a company’s infrastructure. Effective administrative security controls help organizations mitigate risks associated with data breaches and other security threats by providing a framework for managing their IT environment securely.
Common Data Security Threats
Malware And Viruses
Malware and viruses are some of the most prevalent threats to data security. Malware refers to any malicious software that is designed to harm or exploit a computer system, network, or device. Viruses, on the other hand, are specific types of malware that attach themselves to executable files and replicate themselves when those files are opened.
There are several ways that malware and viruses can infiltrate a system, including through email attachments, downloads from untrusted websites, or by exploiting vulnerabilities in software applications. Once in the system, they can cause damage by stealing sensitive information such as passwords and financial details, locking users out of their own devices or networks, or even rendering them unusable.
Phishing Attacks
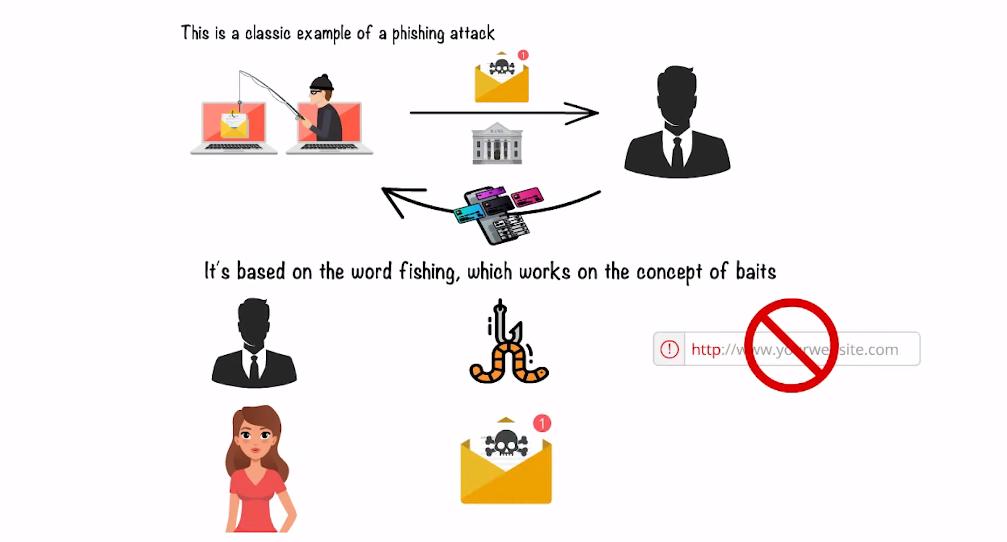
Phishing attacks are a type of social engineering attack that aims to trick users into sharing their sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and personal data. These attacks typically involve fraudulent emails, texts, or phone calls that appear to be from legitimate sources like banks, e-commerce sites, or government agencies. The ultimate goal of phishing attacks is to steal valuable information from unsuspecting victims which can then be used for financial gain.
Social Engineering
Social engineering can take many forms, such as impersonation, phishing emails or phone calls, and pretexting. Social engineers employ various tactics to trick people into sharing sensitive data or taking actions that could compromise their systems. They use psychological manipulation and social skills to get valuable information.
Insider Threats
Insider threats come from employees or contractors who have access to the company’s networks and systems and may intentionally or unintentionally cause harm. Insider threats can range from stealing confidential data to accidentally exposing sensitive information through a simple mistake.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are cyber-attacks that target specific organizations or individuals. APTs are different from typical malware attacks because they remain undetected for long periods, usually months or years. The goal of APTs is to steal data or intellectual property and cause significant damage to the target organization. They can infiltrate an organization through various means such as phishing emails, social engineering tactics, and using known vulnerabilities in software.
Key Components of Data Security Controls
Identification and Authentication
Identification and authentication are two crucial aspects of data security controls that help to ensure the privacy and integrity of sensitive information. Identification is the process of establishing a user’s identity, while authentication is the process of verifying that identity. This ensures that only authorized users have access to sensitive information.
There are several methods for identification and authentication, including passwords, biometric scans, and smart cards. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and it’s essential to choose the right method based on your organization’s needs. For example, biometric scans are more secure than passwords but can be costly to implement.
Effective identification and authentication practices can help prevent data breaches by ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. It also helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR which require companies handling sensitive data to have adequate security measures in place.
Access Controls
Access controls are designed to limit access to sensitive information, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify it. Access controls utilize various techniques such as authentication, authorization, and encryption to ensure that data is secure from unauthorized access.
Authentication involves verifying the identity of a user before granting access to sensitive information. This process is typically done using passwords or biometric identifiers like fingerprints or facial recognition software. Authorization, on the other hand, determines what level of access a user should have once they have been authenticated. This can range from read-only access to full administrative privileges.
Encryption
Encryption works by using complex algorithms to scramble the original text or data into unreadable codes. The encryption process converts the plaintext message into cipher text using a cryptographic key that is unique to each message. This means that even if hackers intercept the encrypted data, they cannot read it unless they have access to the decryption key.
Backups and Disaster Recovery
Backups refer to the process of making copies of data, applications, and systems in order to protect against accidental loss or corruption. In contrast, disaster recovery involves preparing for and responding to major disruptions that render an organization’s systems unusable.
Proper backup procedures can help prevent data loss due to human error, hardware failure, or cyberattacks. An effective backup system should include regular backups that are stored on different devices or locations as well as testing the backup system periodically to ensure it works when needed.
Logging and Monitoring
Logging and monitoring allow organizations to track user activity, detect anomalies or security breaches, and ensure compliance with internal policies and external regulations. Logging involves the collection and storage of log data from various sources, such as servers, applications, network devices, and databases. Monitoring refers to the real-time analysis of this data for suspicious events or patterns.
Effective logging and monitoring require a well-defined strategy that considers the types of data to be collected, the storage capacity needed, the analysis tools required, and the response procedures in case of incidents. Organizations should establish clear guidelines for log retention periods based on legal requirements or business needs. They should also define roles and responsibilities for reviewing logs regularly and investigating any alerts generated by monitoring systems.
Incident Response
Incident Response involves taking appropriate measures to handle and respond to a security breach or threat. An incident can be anything from a malware attack, unauthorized access, phishing attack, or any other malicious activity that threatens information security.
The goal of Incident Response is not only to detect and contain the problem but also to minimize its impact on business operations and reputation. A proper Incident Response plan comprises several steps such as identification, containment, investigation, eradication, and recovery. Businesses should have a well-documented plan in place that outlines each step clearly along with the roles and responsibilities assigned.
Implementing Data Security Controls
Risk Assessment
The first step in developing an effective security policy is identifying the risks associated with your business processes. A thorough risk assessment will help identify potential vulnerabilities which can then be addressed through appropriate controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption techniques, access controls etc.
Security Policies and Procedures
Security procedures complement these policies by providing detailed instructions on how to implement them effectively. This includes guidance on handling sensitive information, incident management protocols, and disaster recovery plans that ensure minimal impact on operations in case of a breach or failure. Ultimately, having well-defined security policies and procedures not only helps protect sensitive information but also contributes to building trust among stakeholders who entrust organizations with their personal information.
Training and Awareness
Training should be comprehensive and ongoing, covering topics such as password management, email security, and the identification of suspicious activity. It should also include best practices for physical security measures such as locking computers when not in use or not leaving sensitive documents unattended.
Awareness campaigns can also increase employee vigilance about potential threats to data security. These campaigns can take various forms, such as posters or emails highlighting common phishing scams or reminding employees of the importance of strong passwords. They can also include simulations of social engineering attacks or other cybersecurity incidents to help employees understand how hackers operate and what signs they should look out for.
Compliance and Regulations
Compliance refers to the act of adhering to specific rules, regulations, or laws related to data security. Various compliance frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, PCI-DSS, and SOX outline requirements that organizations must follow to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
By implementing the right data security controls, companies can ensure they comply with these frameworks and avoid hefty fines or reputational damage due to non-compliance. These controls include access control measures such as password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and encryption techniques that help protect sensitive information.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Continuous monitoring helps organizations identify vulnerabilities or potential threats before they occur, allowing them to take proactive steps to prevent breaches. Another benefit of continuous improvement is its ability to enhance overall security posture. By regularly assessing and refining security processes, organizations can strengthen their defenses against emerging threats and evolving attack methods. Additionally, ongoing monitoring can help businesses remain compliant with regulatory requirements by ensuring that they are continuously meeting current standards.
Challenges in Implementing Data Security Controls
Lack of Resources and Budget Constraints
Lack of resources and budget constraints can make it difficult to implement comprehensive security controls to protect sensitive information. For instance, smaller businesses may not have access to the same level of resources as larger enterprises, which means they might need to rely on low-cost or free tools instead.
However, even if an organization has limited resources and budgetary restrictions, there are still steps it can take to improve its data security posture. One approach is to prioritize investments in critical areas such as firewalls or endpoint protection software that addresses multiple threats. Another strategy is to leverage cloud-based solutions that provide a cost-effective way of implementing robust security controls.
Complexity and Integration with Legacy Systems
Integrating new technologies into existing legacy systems can be a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Even with the best intentions, companies may encounter challenges as they try to integrate modern systems with older ones.
One of the biggest challenges associated with integration is data security. Legacy systems often lack the advanced security features needed to protect sensitive business data from cyber threats. As such, companies need to put in place robust security controls for both their older and newer systems to ensure that all data remains safe.
Furthermore, complexity is another issue that arises when trying to integrate modern computing environments with legacy systems. The more complex an IT environment becomes, the more difficult it becomes to manage risks effectively. This underscores the importance of having a comprehensive understanding of what one’s IT environment looks like before attempting any integration project.
FAQs
What Is The Difference Between Data Security And Data Privacy?
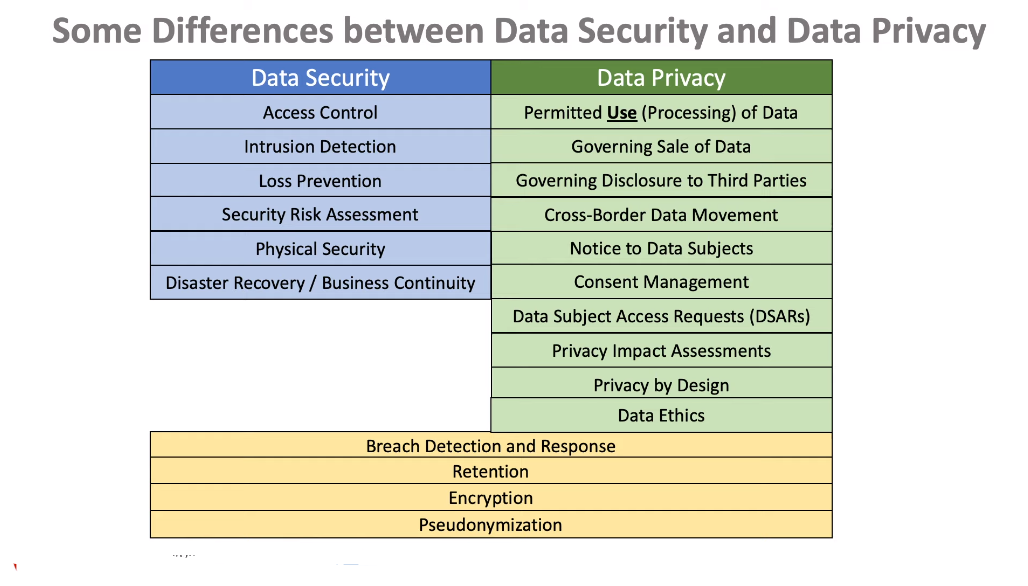
Data privacy refers to the protection of personal information, which includes sensitive data such as social security numbers, financial records, and medical records. It involves limiting access to this information and ensuring that it is not shared without the explicit consent of the owner.
On the other hand, data security is about protecting all types of data from unauthorized access or theft. This includes confidential business information and trade secrets in addition to personal information. Data security measures include encryption, firewalls, access controls, and regular system updates.
How Often Should Security Assessments Be Conducted?
The frequency of security assessments depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of an organization’s IT infrastructure, the type of data being processed, and the level of cyber threats that are present. For small to medium-sized businesses with limited IT resources, annual or bi-annual security assessments may be sufficient. However, for larger organizations dealing with sensitive information such as financial or health records, more frequent assessments may be required.
What Is The Best Way To Secure Sensitive Data?
The best way to secure sensitive data is to use multiple layers of security controls. The first line of defense is access control, which limits who can view or modify the data. This can be done through authentication methods such as passwords, biometric identification, and two-factor authentication. The second layer of defense is encryption, which transforms the data into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered with a key or password.
Another security control that organizations should implement is regular backups and disaster recovery plans. This ensures that even if the sensitive data is compromised or lost due to a natural disaster or cyber attack, it can still be recovered from a backup copy. Additionally, employees should receive regular training on how to identify and prevent common threats such as phishing scams and social engineering attacks.
What Are The Most Important Regulations For Data Security?

The most important regulations for data security include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which outlines the requirements for protecting the personal data of individuals within the European Union. Another key regulation is the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which sets guidelines for safeguarding credit card information.
Additionally, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) provides rules for protecting sensitive patient health information in healthcare settings, while the Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires public companies to implement controls to ensure financial reporting accuracy and integrity. It’s also important to note that many countries have their own specific data protection regulations that organizations must adhere to when operating within those regions.
Conclusion
Data security controls are an essential aspect of any organization that handles sensitive information. The implementation of these controls ensures that the data is protected against unauthorized access, use, disclosure, modification or destruction. As technology continues to advance and cyber threats become more sophisticated, it is crucial for businesses to remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to data security.
To achieve optimum data security, organizations should adopt a comprehensive approach that encompasses a range of measures such as physical security controls, technical controls, and administrative controls. These may include encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication systems, and employee training programs.
