Introduction
The security model based on the military classification of data and people with clearances is a crucial aspect of national security. This model classifies information and personnel based on their level of sensitivity and access to classified information. Understanding this model is essential for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and provision of sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access. This paper will offer an overview of the security model based on the military classification of data and people with clearances, its principles, and its importance in maintaining national security.
History Of Security Models
The history of security models dates back to the early days of military operations and intelligence gathering. In the early 20th century, the military began to use a classification system to protect sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. This system was based on the idea that certain information was more sensitive than others and required different levels of protection. As computers and technology became more prevalent in the second half of the 20th century, the need for a security model that could be applied to civilian use became apparent. This led to the development of various security models, such as the Bell-LaPadula and the Biba models, designed to protect information in civilian settings.
Security models are used in various settings today, including government agencies, corporations, and personal devices. These models have become essential in protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access.
Principles Of The Security Model
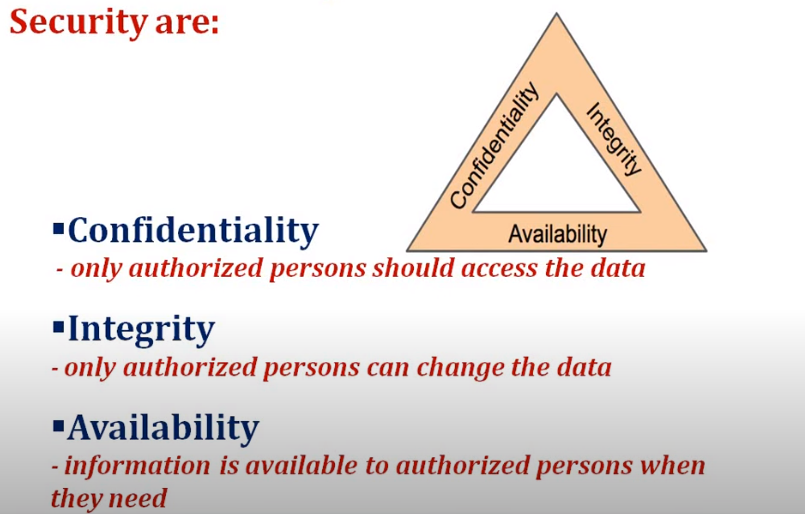
The security model is based on several principles designed to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. These principles include:
1. Confidentiality: This refers to protecting sensitive information from disclosure to unauthorized individuals or entities.
2. Integrity: This refers to protecting sensitive information from unauthorized modification or destruction.
3. Availability: This refers to ensuring that sensitive information is accessible to authorized individuals or entities when needed.
4. Authentication: This refers to verifying the recognition of an individual attempting to access sensitive information.
5. Authorization: This refers to granting or denying access to sensitive information based on an individual or entity’s level of clearance or permission.
6. Accountability: This refers to the ability to track and monitor access to sensitive information and to hold individuals or entities responsible for any unauthorized access or misuse.
Overview Of Security Models Used In The Military
There are several security models used in the military to protect sensitive information. These models include:
1. Mandatory Access Control (MAC): This model restricts access to sensitive information based on clearance levels. Access is granted based on the need-to-know principle, and individuals must have the appropriate clearance level to access the information.
2. Discretionary Access Control (DAC): This model allows the owner of the information to control access to it. The owner can decide who has access to the information and their access level.
3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This model assigns access based on the roles and responsibilities of individuals within an organization. Access is granted based on the user’s job function, and individuals are only granted access to information necessary to perform their duties.
4. Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): This model uses attributes to determine access to sensitive information. Attributes can include factors such as job title, location, and clearance level.
Understanding Military Security Classifications

Military security classifications are used to categorize sensitive information based on its level of confidentiality and potential impact on national security. The three main classifications are:
1. Confidential: This classification is used for information that, if revealed, could cause harm to national security. Examples include plans for future military operations and personnel records.
2. Secret: This classification is used for information that, if disclosed, could cause serious damage to national security. Examples include information about weapons systems and intelligence reports.
3. Top Secret: This classification is used for information that, if disclosed, could cause exceptionally grave damage to national security. Examples include information about ongoing military operations and nuclear weapons.
Access to information at each classification level is restricted to individuals with the appropriate security clearance level and a need-to-know basis. The military takes these classifications very seriously and has strict protocols to ensure that sensitive information is not compromised.
Impact Of Military Security Classifications On Information Security In The Civilian World
The impact of military security classifications on information security in the civilian world is significant. Many government contractors and private companies work closely with the military and must adhere to the same security protocols. This means that sensitive information is often shared between military and civilian organizations, and all parties involved must take the necessary precautions to protect that information. Additionally, the military’s strict security protocols serve as a model for information security in other industries. Many companies have adopted similar protocols to protect sensitive information, such as trade secrets or financial data.
The Need For Security Models In The Civilian World
The military’s emphasis on information security has highlighted the need for similar security models in the civilian world. As technology advances and more sensitive information is stored and transmitted electronically, the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks increases. Many companies and organizations have recognized information security’s importance and implemented their security protocols. However, more standardized and comprehensive security models must be applied across different industries and sectors.
Developing such models requires collaboration between government agencies, industry leaders, and cybersecurity experts. They can identify common threats and vulnerabilities and develop effective mitigation strategies by working together.
The Bell-LaPadula Security Model
The Bell-LaPadula Security Model is widely used in the field of information security. It was first introduced in 1973 by David Bell and Leonard LaPadula and has since been adopted by many organizations to ensure the confidentiality of their sensitive information. The Bell-LaPadula Security Model is based on the concept of a “security clearance” system, in which users are granted varying levels of access to information based on their security clearance level. The model is designed to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information by enforcing strict rules governing users’ read-and-write operations.
The model is based on three key principles: the Simple Security Property, the *-Property, and the Strong *-Property. The Simple Security Property states that users can only read the information at or below their security clearance level. The *-Property states that a user can only write information to a level at or above their security clearance level. The Strong *-Property states that a user can only perform a combination of read and write operations that maintain the security classification of the information.
The Biba Security Model
The Biba Security Model is another important security model used in information security. This model focuses on the integrity of information rather than its confidentiality. The Biba model is based on the principle of “no read-up, no write-down,” meaning that a user can only read the information at their integrity level or lower and can only write it at their integrity level or higher. The Biba model has two main properties: the Simple Integrity Property and the *-Integrity Property. The Simple Integrity Property states that a user can only write information to an object if the integrity level of the user is greater than or equal to the object’s integrity level. The *-Integrity Property states that a user can only read information from an object if the integrity level of the object is greater than or equal to the integrity level of the user.
The Clark-Wilson Security Model
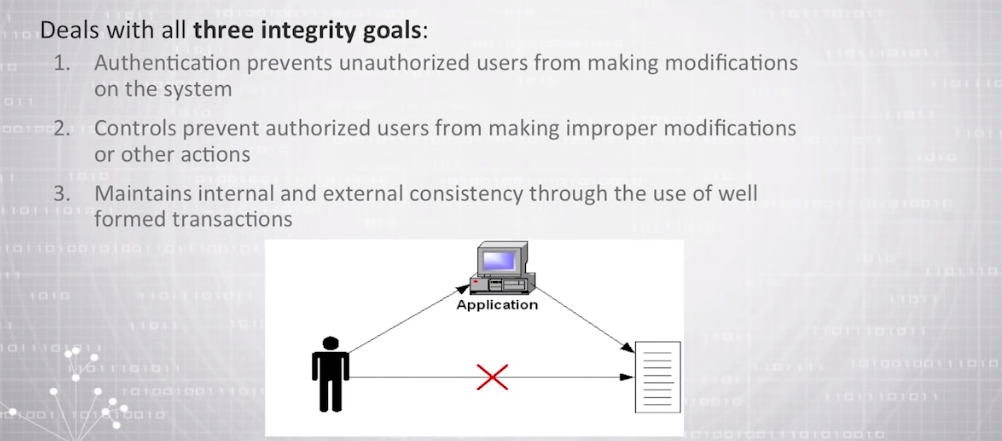
The Clark-Wilson Security Model is another popular security framework used to ensure the integrity of information. This model is based on the separation of duties, which means that different individuals or processes are responsible for different aspects of a system’s operation. The Clark-Wilson model defines three key elements: subjects, objects, and transformations. Subjects are users or processes that access objects, which are protected resources. Transformations are the operations that can be performed on objects, such as creating, modifying, or deleting them.
To ensure the integrity of information, the Clark-Wilson model enforces a set of rules that restrict the types of transformations that can be performed on objects. For example, a user may be allowed to create a new object but not modify an existing object without approval from a separate user or process.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Each Model
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of the Bell-LaPadula and Clark-Wilson security models:
Bell-LaPadula
Advantages
- -Provides strong confidentiality controls.
- -Easy to understand and implement.
- -Can be applied for a wide range of security needs.
Disadvantages
- Does not address integrity or availability concerns.
- It may not be suitable for organizations with complex security needs.
- Can be difficult to manage and maintain.
Clark-Wilson
Advantages
- Provides strong integrity controls.
- Separates duties to prevent unauthorized access.
- Can be customized to meet the exact needs of an organization.
Disadvantages:
- More complex to implement than Bell-LaPadula.
- May not be suitable for small organizations with limited resources.
- Requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure effectiveness.
Comparison Of Security Models
Comparing security models can be a complex task, as each model has its strengths and weaknesses depending on the specific security needs of an organization. However, general comparisons between the Clark-Wilson and other popular security models can be made. For example, the Bell-LaPadula model focuses on confidentiality and access control but does not address integrity or accountability. On the other hand, the Biba model emphasizes integrity but does not provide a clear separation of duties or address the issue of untrusted subjects.
The Clark-Wilson model, emphasizing integrity and separation of duties, provides a more comprehensive approach to security. However, implementing it may be more complex and unsuitable for all organizations.
Ultimately, the best security model will depend on the specific security needs of an organization, as well as the resources and expertise available for implementation and maintenance.
Applying Military Security Models In The Civilian World
Military security models have been used successfully in the civilian world to secure sensitive information and protect critical infrastructure. One example is using the Bell-LaPadula model in the financial industry to protect confidential financial data. Another example is the use of the Clark-Wilson model in healthcare organizations to ensure the privacy and integrity of patient medical records. However, it is significant to note that these models may need to be customized to fit civilian organizations’ specific needs and requirements.
What Are The Characteristics Of Security Clearance And Data Classification?
A security clearance is a level of authorization that allows individual access to classified information or restricted areas. It is granted based on a thorough background check and determination of trustworthiness. On the other hand, data classification is classifying data based on its sensitivity and importance. It helps determine the appropriate level of protection and handling procedures for the data. While security clearance is related to the individual’s access level, data classification is related to the level of protection required for the data.
The Future Of Security Models
The future of security models is constantly evolving as technology advances and new threats emerge. One trend that is expected to continue is the shift towards more proactive and predictive security measures, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence. These technologies can analyze massive data and detect patterns indicating a potential security threat. Additionally, there is an increasing focus on securing the Internet of Things (IoT) as more and more devices become connected to the internet. This presents new challenges for security models, as traditional approaches may not suit these devices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Are The Key Challenges In Implementing Security Models?
There are several key challenges in implementing security models, including:
1. Complexity: Security models can be complex and difficult to understand, making it challenging to implement them effectively.
2. Cost: Implementing security models can be expensive, particularly for small businesses or organizations with limited budgets.
3. Resistance to change: Employees may resist security policy and procedure changes, making implementing new security models difficult.
4. Lack of expertise: Implementing security models requires specialized knowledge and expertise, which may not be available within an organization.
5. Compatibility: Security models may not be compatible with existing systems and processes, making integrating them difficult.
How Can I Ensure Compliance With Security Models?
Ensuring compliance with security models requires a combination of measures, including:
1. Regular audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure that security models are followed and identify any areas of non-compliance.
2. Training and awareness: Provide ongoing training and awareness programs to teach employees and stakeholders the importance of security models and how to comply with them.
3. Monitoring and enforcement: Implement monitoring and enforcement mechanisms to identify and address any instances of non-compliance.
4. Accountability: Establish clear lines of accountability for adhering to security models, including assigning specific responsibilities to individuals or teams and holding them accountable for their actions.
5. Continuous improvement: Review and improve security models to adapt to changing threats and technologies.
6. Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT, security, and other departments to ensure that security models are integrated into all aspects of the organization.
7. Risk management: Incorporate risk management principles into security models to prioritize and address the most critical risks.
By implementing these measures, organizations can ensure that their security models are effective and take the necessary steps to protect their sensitive data and assets.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Security Models Based On Military Classification?
Using security models based on military classification can offer several benefits, such as:
1. Clear and structured approach: Military classification systems provide a clear and structured approach to classifying and protecting sensitive information. This allows organizations to identify and prioritize their most critical assets and data easily.
2. Proven effectiveness: Military classification systems have been used for decades and have proven effective in protecting sensitive information. By adopting these models, organizations can benefit from the experience and expertise of the military.
3. Consistency: Military classification systems provide a consistent approach to security across all departments and levels of an organization. This confirms that everyone is on the same page regarding protecting sensitive information.
4. Compliance: Many industries and government agencies require compliance with specific security standards. Using security models based on military classification can help organizations meet these necessities and avoid penalties or legal issues.
5. Flexibility: Military classification systems can be customized to fit an organization’s needs and requirements. This allows organizations to tailor their security models to their unique situations and environment.
Conclusion
This article discussed the benefits of using military classification systems in developing security models for organizations. These benefits include a clear and consistent framework, the ability to prioritize sensitive information, compliance with security standards, and flexibility to customize the system to fit specific needs. Organizations can expand their security posture by implementing a military classification system and avoid legal issues or penalties.
Security models are essential in information security, providing a structured approach to securing information assets. They help organizations identify potential threats and vulnerabilities and develop appropriate mitigation controls. Security models also enable organizations to comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards. By implementing a security model, organizations can protect their information resources from unauthorized access, disclosure, or destruction. Additionally, security models can help organizations to achieve their business objectives by ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets. Overall, security models are crucial in maintaining the security and resilience of an organization’s information assets.
