Introduction
Protecting healthcare data is a critical issue that has gained increased attention recently. With the rise of electronic health records and the increasing quantity of sensitive data being stored in digital form, it is crucial to understand the security acts that apply to healthcare data. This article will explore the key security acts that govern healthcare data and discuss their implications for healthcare providers and patients.
What Security Acts Apply To Healthcare Data?

Several security acts apply to healthcare data, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, and the Affordable Care Act (ACA). These acts aim to protect the privacy and security of patients’ health information and establish standards for the electronic transmission of health data. HIPAA, in particular, sets forth rules for using and disclosing protected health information (PHI) by covered entities, like healthcare providers and health plans. HITECH provides additional safeguards for PHI, including breach notification requirements and increased penalties for noncompliance. The ACA also includes provisions related to the security and privacy of health information, such as the requirement for health insurance exchanges to implement strong privacy and security protections for consumers.
HIPAA Security Rule
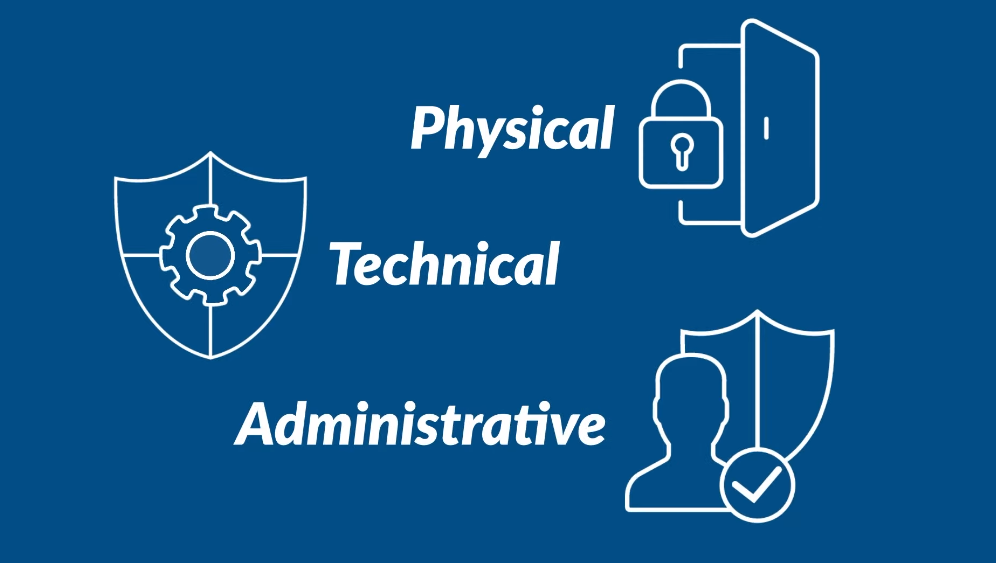
The HIPAA Security Rule is a combination of national standards that require covered entities to implement administrative, physical, and technical protections to confirm the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronically protected health information (ePHI). The Security Rule applies to all covered entities that create, receive, maintain, or transmit ePHI, including healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses. The Security Rule requires covered entities to conduct a risk analysis to identify potential vulnerabilities in their systems and implement security measures to address them. Covered entities must also implement policies and procedures to ensure that their workforce members are trained on the proper handling and safeguarding of ePHI. The Security Rule also requires covered entities to enter into contracts with their business associates, such as third-party service providers, to ensure that the business associates also comply with the Security Rule’s requirements.
HITECH Act
The HITECH Act, or Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, was enacted in 2009 as per the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. The HITECH Act expands HIPAA’s privacy and security requirements and incentivizes healthcare providers to adopt electronic health records (EHRs). Under the HITECH Act, covered entities and business associates must notify affected individuals and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) regarding a breach of unsecured ePHI. The HITECH Act also increased the forfeits for HIPAA violations, with fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per defilement, up to a maximum of $1.5 million per year.
In addition, the HITECH Act established the Office of National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) to promote the adoption and expressive use of EHRs. The ONC also developed standards and certification criteria for EHR technology to ensure it meets certain privacy and security requirements.
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) was executed by the European Union (EU) in 2018 to protect the privacy and personal information of EU citizens. It applies to all companies that process the personal data of EU citizens, regardless of where the company is located. The GDPR imposes strict requirements on companies, including obtaining explicit consent for data processing, providing individuals with access to their data, and reporting breaches within 72 hours. Non-compliance with the GDPR can result in significant fines and penalties.
CCPA (The California Consumer Privacy Act)
CCPA is a privacy law that continue to effect on January 1, 2020, in California, USA. The CCPA gives California residents the right to identify what personal data is being collected about them by companies, the right to request that their personal information be removed, and the right to choose the sale of personal information. The CCPA enforces on companies that do business in California and meet certain revenue or data processing thresholds. Companies that violate the CCPA can face fines and legal action from the California Attorney General’s office or private individuals.
Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA)

This is a federal law enacted in the United States in 2015. Its purpose is to encourage and facilitate sharing of cybersecurity threat information between the government and private sector entities. The law provides liability protections for private sector entities that share cybersecurity information with the government and for government entities that share information with private sector entities. CISA aims to improve the overall cybersecurity posture of the United States by promoting information sharing and collaboration between government and private sector entities.
The Role Of The Office For Civil Rights (OCR)
The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) plays a critical role in ensuring that individuals’ civil rights are protected in the context of cybersecurity. Specifically, OCR is responsible for enforcing federal laws and regulations protecting individual privacy and security rights, for example, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA).OCR works closely with other federal agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security, to investigate and respond to cybersecurity incidents that impact individuals’ privacy and security rights. OCR provides guidance and resources to help organizations better understand and comply with federal cybersecurity requirements.
Best Practices For Healthcare Data Security
Here are some best practices for healthcare data security:
- Implement strong access controls: Limit access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel and ensure each person has a unique login ID and password.
- Use encryption: Encrypt all sensitive data in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Conduct regular risk assessments: Evaluate potential risks to your data and implement measures to mitigate those risks.
- Train employees on security best practices: Educate your staff on the importance of data security and provide regular training on best practices.
- Monitor for potential breaches: Implement monitoring tools to detect and respond quickly to incidents.
- Develop and test a disaster recovery plan: Have a plan to recover data in the event of a disaster, and test it regularly to ensure it works as intended.
By following these practices, healthcare organizations can help protect sensitive data and maintain compliance with federal regulations.
Emerging Technologies And Healthcare Data Security
As technology advances, healthcare organizations must stay up-to-date on emerging technologies and their potential impact on data security. Some of these technologies include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices like wearable health trackers and medical devices can collect and transmit sensitive data. Healthcare organizations must ensure that these devices are secure and that data is transmitted and stored safely.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can help healthcare organizations analyze large amounts of data quickly and present potential security risks. Organizations must ensure that AI algorithms are secure and that data is protected.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology can help secure healthcare data by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger. Healthcare organizations can use blockchain to store and share patient data securely.
By staying informed about emerging technologies and implementing appropriate security measures, healthcare organizations can continue to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance with federal regulations.
Training And Education
Training and education are crucial for healthcare organizations to ensure their employees know the latest security threats and best practices for protecting sensitive data. This includes regular training on password management, phishing scams, and data encryption. Healthcare organizations should also conduct regular security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure all employees follow established security protocols.
In addition, healthcare organizations should consider partnering with cybersecurity experts to provide specialized training and support. This can help ensure that the organization is up-to-date on the latest security trends and has access to the expertise needed to address any potential threats.
Physical Security Measures
Physical security measures are also important for healthcare organizations to protect sensitive information and ensure the safety of patients and staff. This can include access control systems, surveillance cameras, and secure storage for sensitive documents and equipment.
Organizations should also have emergency response plans in place in case of natural disasters or other emergencies that could compromise physical security. Regular drills and training sessions can help ensure all staff members are prepared to respond appropriately.
Data Breach Response
In addition to physical security, organizations must prioritize data security to protect sensitive information from breaches. This includes implementing strong passwords and encryption, regularly updating software and security systems, and limiting access to sensitive information only to those needing it.
However, even with these measures, data breaches can still occur. In the event of a breach, organizations should have a clear and comprehensive response plan that includes notifying affected individuals and authorities, investigating, and taking steps to prevent future breaches.
It is important for organizations to regularly review and update their security protocols to stay ahead of evolving threats and ensure the safety of their patients, staff, and sensitive data.
Cloud Computing And Healthcare Data Security
Cloud computing has become increasingly popular in the healthcare industry due to its cost-effectiveness and flexibility. However, it also presents unique security challenges, as healthcare data is highly sensitive and must always be protected. To ensure healthcare data security in the cloud, organizations should carefully select a cloud service provider that meets their specific security and privacy requirements. They should also implement strong access controls, encryption, and regular monitoring and auditing of cloud-based systems.
Healthcare organizations need to understand the shared responsibility model of cloud security, where the cloud service provider controls the security of the cloud infrastructure. In contrast, the organization secures its data and cloud applications.
Regular security assessments and testing should also be conducted to identify and address any vulnerabilities in the cloud environment. By taking these steps, healthcare organizations can leverage the benefits of cloud computing while ensuring the security and privacy of their sensitive data.
Business Associate Agreements
Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) are crucial to healthcare organization’s compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). BAAs are contracts between covered entities (such as healthcare providers) and their business associates (such as cloud service providers) that outline the expectations and responsibilities of each party concerning the handling of protected health information (PHI).BAAs should include provisions that require the business associate to implement appropriate safeguards to protect PHI, report any breaches or security incidents to the covered entity, and assist the covered entity in fulfilling its obligations under HIPAA. Additionally, BAAs should include provisions that specify the permitted uses and disclosures of PHI and the procedures for terminating the agreement.
It is important for healthcare organizations to carefully review and negotiate the terms of BAAs with their business associates to ensure that their PHI is adequately protected and that they are in compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Protecting Patient Privacy
To protect patient privacy, healthcare organizations must implement suitable administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure PHI’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability. This includes controlling access to PHI, encrypting electronic PHI, and properly disposing of PHI when it is no longer needed.
Healthcare organizations must also train their workforce on HIPAA privacy and security policies and procedures and regularly review and update them.
Healthcare organizations must take patient privacy seriously and ensure all staff know their responsibilities to protect PHI. Failure to do this can result in substantial fines and legal consequences.
Common Healthcare Data Security Threats
Common healthcare data security threats include phishing attacks, ransomware, insider threats, and physical theft or loss of PHI devices. Healthcare organizations should implement firewalls, encryption, and access controls to prevent unauthorized access to PHI. Regular security assessments and audits can also help identify vulnerabilities and areas for development in an organization’s security posture. Healthcare organizations need to stay vigilant and proactive in their efforts to protect patient data.
Disaster Recovery And Business Continuity Planning
Disaster recovery and business continuity planning are critical components of a healthcare organization’s security strategy. These plans help ensure that the organization can continue to provide essential services and protect patient data during a disaster or other disruptive event. Disaster recovery planning involves identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. This may include backing up data and systems, establishing alternative communication channels, and implementing emergency response protocols.
Business continuity planning focuses on maintaining essential operations during and after a disruptive event. This may involve identifying critical business functions and developing strategies to ensure they can continue operating during a disruption.
Both disaster recovery and business continuity planning require regular testing and updating to ensure they remain effective in changing threats and environments. Healthcare organizations should also have clear communication plans to inform patients and staff during a disruptive event.
Conclusion
Healthcare data security is paramount to protecting sensitive patient information and maintaining trust in the healthcare industry. HIPAA sets standards and requirements for healthcare organizations to implement safeguards to protect PHI. Still, it is also important for organizations to go above and beyond these requirements by implementing best practices such as regular risk assessments, strong access controls, and data encryption. As a writing assistant, I deliver accurate and informative content on this important topic.
Healthcare organizations must prioritize data security to protect patient health information (PHI) and comply with HIPAA regulations. Conducting regular risk assessments, implementing strong access controls, and encrypting data to prevent unauthorized access and breaches are crucial. Healthcare organizations can build patient trust by prioritizing data security and protecting their sensitive information. As a writing assistant, I encourage healthcare organizations to take proactive steps to safeguard PHI and prioritize data security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Healthcare Data Security?
Healthcare data security protects sensitive information related to patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare organizations from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or destruction.
Why Is Healthcare Data Security Important?
Healthcare data contains highly sensitive information such as personal health information (PHI), financial information, and other confidential data. Any unauthorized access or disclosure of this information can lead to grave consequences such as identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage.
What Are The Common Threats To Healthcare Data Security?
Common threats to healthcare data security include cyberattacks, data breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing scams, and employee negligence.
