Managing data breaches effectively requires a well-prepared and agile approach. In the event of a data breach, assembling a response team and having a clear response plan in place are paramount. Detecting breaches early through intrusion detection systems and user activity monitoring is crucial. Rapid containment and transparent communication with affected parties and authorities are essential steps in response. Post-breach, evaluating and improving security measures and providing support to affected individuals help in the recovery process. Proper data breach management not only minimizes financial and legal consequences but also safeguards your reputation and the trust of your stakeholders.
What is a Data Breach?
A data breach occurs when unauthorized individuals access sensitive or confidential information. This breach can take various forms, such as hacking, phishing, malware, or even physical theft of data storage devices. The consequences of a data breach can be devastating, including financial losses, legal penalties, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
The Cost of Data Breaches
Data breaches can be expensive, with the average cost of a data breach reaching millions of dollars. Beyond financial losses, businesses can also face regulatory fines and potential lawsuits. Moreover, the damage to customer trust and brand reputation can be irreparable.
What Causes a Breach of Data?
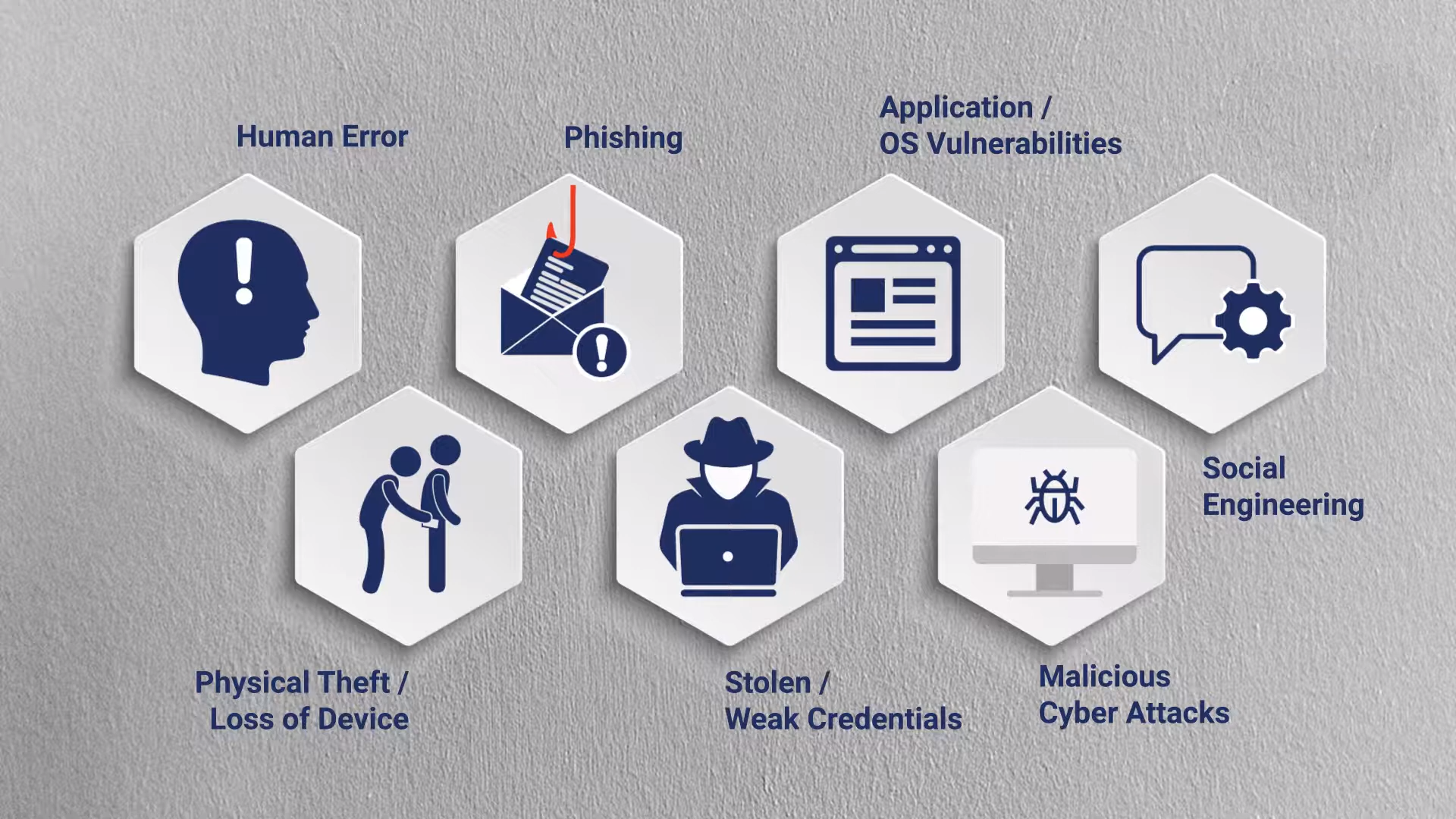
Data breaches are becoming increasingly common, and understanding their various causes is essential for effective prevention. In this section, we’ll explore the primary factors that lead to data breaches, ranging from human errors to malicious activities.
Human Error
One of the most common causes of data breaches is human error. Employees may accidentally expose sensitive information by sending emails to the wrong recipients, misplacing physical documents, or failing to update security settings properly.
Insiders with malicious intent, such as disgruntled employees or contractors, can deliberately compromise data security. They may steal data, leak confidential information, or introduce vulnerabilities into the system.
Phishing attacks involve cybercriminals impersonating legitimate entities to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information. Victims may unknowingly provide login credentials or personal data, allowing attackers access to systems.
Spear phishing is a targeted form of phishing where attackers tailor their messages to specific individuals or organizations. This approach increases the likelihood of success since the messages appear more convincing and legitimate.
Malware and Ransomware
Malware, including viruses, Trojans, and spyware, can infect systems and steal data. It can be introduced through malicious downloads, compromised websites, or infected email attachments.
Ransomware encrypts a victim’s data, making it inaccessible until a ransom is paid to the attackers. Data can be permanently lost or exposed if the ransom isn’t paid.
Weak Passwords and Authentication
Weak or easily guessable passwords provide a gateway for cybercriminals. When users use simple passwords or fail to update them regularly, it becomes easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Criminals may steal login credentials through various means, such as phishing or hacking. Once they possess valid credentials, they can access sensitive data and systems undetected.
Unpatched Software and Vulnerabilities
Failure to regularly update and patch software can leave systems vulnerable to exploitation. Attackers often target known vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain access to networks.
Third-Party Breaches
Third-party vendors and suppliers may have access to your data. A breach in the supply chain can expose your sensitive information. It’s essential to assess the security practices of your third-party partners.
Physical Theft or Loss
Physical theft of laptops, smartphones, or storage devices containing sensitive data can lead to a breach if the data is not adequately encrypted or protected.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks overload a network or website’s resources, making it inaccessible to legitimate users. While not a direct data breach, DDoS attacks can be distractions, allowing attackers to exploit vulnerabilities during the chaos.
Inadequate Security Practices
Lax security measures, such as inadequate encryption, lack of access controls, and insufficient monitoring, can create opportunities for data breaches.
Preparing for a Data Breach
Establish a Data Breach Response Team
To effectively manage a data breach, you must assemble a team of experts to handle the situation promptly and efficiently. This team should include IT professionals, legal counsel, public relations experts, and senior management.
Develop a Data Breach Response Plan
A well-documented response plan is essential for navigating a data breach. This plan should outline the steps to take when a breach is detected, including containment, notification, and recovery procedures. Regularly update and test this plan to ensure it remains effective.
Detecting a Data Breach
Implement Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems can help identify unauthorized access or suspicious activities within your network. These systems can provide early warnings and enable rapid response to potential breaches.
Monitor User Activities
Continuous monitoring of user activities can help you spot unusual behavior patterns. Unusual login times, multiple failed login attempts, or unusual data access can indicate a data breach in progress.
Responding to a Data Breach

Contain the Breach
Upon detecting a data breach, it is crucial to contain it promptly. Isolate affected systems, change passwords, and shut down compromised accounts to prevent further unauthorized access.
Notify Affected Parties
Transparency is key when managing a data breach. Notify affected individuals, customers, and relevant authorities as data protection laws require. Provide clear information about the breach, its impact, and the steps you are taking to rectify the situation.
Engage Legal Counsel
Involving legal counsel is essential to navigate the legal complexities surrounding data breaches. They can advise you on compliance with data protection regulations and potential liabilities.
Communicate Effectively
Maintain open and honest communication with affected parties and the public. Address concerns and provide regular updates on the progress of your breach resolution efforts. Building trust during a breach is crucial for preserving your reputation.
Recovering from a Data Breach
Evaluate and Improve Security Measures
After managing a data breach, thoroughly review your security protocols and systems. Identify weaknesses and implement improvements to prevent future breaches.
Provide Support for Affected Parties
Support individuals affected by the breach, such as credit monitoring services or identity theft protection. Demonstrating care for those affected can help rebuild trust.
Conclusion
Data breaches are a significant and evolving threat in the digital landscape. Properly managing them requires preparation, detection, and effective response strategies. By following the best practices outlined in this article, you can minimize the impact of a data breach on your organization and protect your valuable data and reputation.
FAQs:
How do I determine if a data breach has occurred?
Detecting a data breach can be challenging, but there are signs to watch for. Unusual system activities, unauthorized access, or reports of suspicious behavior from employees or users are red flags. Implementing intrusion detection systems and conducting regular system audits can help you identify breaches early.
What should I include in a data breach notification to affected parties?
A data breach notification should provide clear and concise information. Include details about the nature and scope of the breach, the type of data affected, potential risks to individuals, and steps you are taking to address the breach. Also, include contact information for individuals for more information or assistance.
How can I minimize the reputational damage from a data breach?
Reputation management is crucial after a data breach. Maintain transparent communication, acknowledging the breach and your commitment to resolving it. Support affected parties, such as credit monitoring or identity theft protection. Demonstrating care and responsibility can help rebuild trust.
What should I do if my business experiences a data breach while operating internationally?
If your business operates internationally, you should know data protection laws in various regions. In the event of a data breach, ensure compliance with the relevant laws and regulations of the affected countries. Notify authorities and individuals as required by the local data protection authorities.
How can I prevent insider threats from leading to data breaches?
Insider threats can be challenging to mitigate. Implement strong access controls and user monitoring systems to identify unusual behavior among employees or authorized users. Provide cybersecurity training to educate your staff about the risks and consequences of insider threats, emphasizing the importance of data security and privacy.
