Understanding Data Classification
Data classification is the process of organizing and categorizing data into different groups or classes based on certain criteria. It is an important step in data management and analysis as it helps in organizing and structuring data in a meaningful way.
Types of Data Classification
Data classification is an essential process for organizing and categorizing data based on its sensitivity, confidentiality, and access levels. Here are some common types of data classification:
1). Confidential: This classification is used for highly sensitive data that should be accessible only to authorized individuals with a legitimate need. Examples include financial records, trade secrets, and personally identifiable information (PII).
2). Restricted: Restricted data classification is for information that is sensitive but may be accessed by a limited group of authorized individuals within an organization. It typically includes internal reports, intellectual property, and employee records.
3). Public: Public data classification is for information that is freely available to the general public. This may include press releases, public announcements, and information that does not contain any sensitive or confidential details.
The Role of Data Classification in Security
Data classification plays a crucial role in security by helping organizations identify and prioritize the protection of their data assets. Here are some key roles of data classification in security:
1). Risk Management: Data classification allows organizations to assess the level of risk associated with different types of data. By categorizing data based on its sensitivity, organizations can allocate appropriate security measures to protect high-risk data from unauthorized access or misuse.
2). Access Control: Data classification helps in implementing access controls based on the sensitivity of the data.
Identifying Different Types of Data
- Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
- Intellectual Property (IP)
- Financial Data
- Health Records
- Company Confidential Information
Need for Assigning Security Levels
Assigning security levels to different types of data is necessary for several reasons:
1). Protection of Sensitive Information: Certain types of data, such as Personal Identifiable Information (PII) and health records, contain sensitive information that needs to be protected from unauthorized access or misuse. By assigning a higher security level to these types of data, organizations can implement stronger security measures to ensure their confidentiality.
2). Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have specific regulations and compliance requirements for handling certain types of data.
Reason Different Types of Data Require Varying Security Levels
Different types of data require varying security levels due to the following reasons:
1). Sensitivity of Information: Some types of data, such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and health records, contain highly sensitive information that can be used for identity theft or other malicious purposes. To protect this sensitive information, a higher security level is required to ensure its confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
2). Legal and Regulatory Requirements: Different industries have specific regulations and compliance requirements for handling certain types of data
Assessing Data Sensitivity
Assessing data sensitivity is a crucial step in determining the appropriate security measures to protect the information. It involves evaluating the potential impact of unauthorized access or disclosure of the data and categorizing it based on its sensitivity level. This assessment helps in prioritizing security controls and allocating resources effectively to safeguard the data.
Methods to Evaluate Data Sensitivity
There are several methods to evaluate data sensitivity. Here are some commonly used approaches:
1). Data Classification: This involves categorizing data into different levels of sensitivity based on factors such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability requirements. For example, data may be classified as public, internal, confidential, or highly confidential.
2). Risk Assessment: Conducting a risk assessment helps identify potential threats and vulnerabilities associated with the data.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
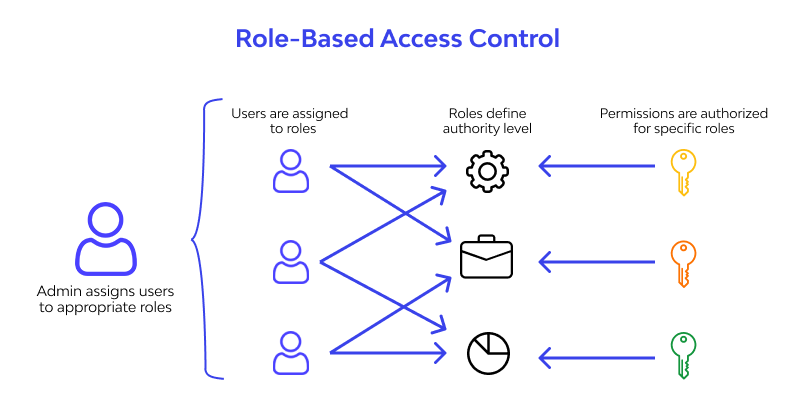
RBAC is a method of restricting data access based on the roles and responsibilities of users within an organization. It helps ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data helps protect it from unauthorized access. This involves converting the data into a format that can only be decrypted with a specific key.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions help prevent sensitive data from being leaked or lost.
Understanding RBAC and its Significance In Data Security
RBAC, or Role-Based Access Control, is a method of restricting data access based on the roles and responsibilities of users within an organization. It is an important aspect of data security as it helps ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. By assigning specific roles to users, organizations can control what data each user can access and what actions they can perform on that data. This helps minimize the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Implementing RBAC for Various Data Categories
Implementing RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) for various data categories is a recommended approach to enhance data security and control within an organization. RBAC allows organizations to assign specific roles to users, which determine their access privileges and actions they can perform on data. By categorizing data into different categories, organizations can apply RBAC principles to control access to each category. This involves defining roles and assigning them to users based on their responsibilities and job functions.
Data Security Training and Awareness

Data security training and awareness is another important approach to enhancing data security and control within an organization. By providing training to employees on best practices for data security, organizations can ensure that their workforce is knowledgeable about potential risks and how to mitigate them. This includes educating employees on the importance of strong passwords, regular software updates, and recognizing and reporting phishing attempts or suspicious activities.
Importance of Employee Training in Data Security
Employee training in data security is crucial for several reasons:
1). Risk reduction: By educating employees about potential risks and how to mitigate them, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of data breaches and other security incidents. Employees who are trained in data security are more likely to follow best practices and take necessary precautions to protect sensitive information.
2). Increased awareness: Training helps employees become more aware of the importance of data security and the potential consequences of a breach.
Technology Solutions for Data Security
Implementing technology solutions is another crucial aspect of data security. Here are some technology solutions that organizations can utilize to enhance data security:
1). Encryption: Encryption is the process of converting data into a code that cannot be easily understood by unauthorized individuals. By implementing encryption techniques, organizations can protect sensitive information both at rest and in transit.
2). Firewalls: Firewalls act as a barrier between an organization’s internal network and external networks, monitoring incoming and outgoing network traffic.
3). Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools: DLP tools help organizations identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or accidental leakage. These tools can detect and prevent data breaches by monitoring data in use, data in motion, and data at rest.
4). Multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing sensitive data or systems. This can include something the user knows (like a password), something
Incident Response and Data Breach Management
Incident Response and Data Breach Management is a process that involves identifying and responding to security incidents and managing the aftermath of a data breach. It includes activities such as incident detection, containment, eradication, and recovery. The goal is to minimize the impact of a security incident and restore normal operations as quickly as possible.
Preparing An Incident Response Plan
Preparing an incident response plan involves creating a documented and structured approach to effectively respond to and manage security incidents. This plan includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing communication channels, outlining incident detection and response procedures, and identifying resources and tools needed for incident response. The plan should be regularly reviewed, updated, and tested to ensure its effectiveness in the event of a security incident.
Steps To Mitigate Data Breaches And Their Consequences
1). Develop a comprehensive security policy: Start by creating a security policy that outlines the organization’s commitment to protecting data and defines the acceptable use of technology resources. This policy should cover areas such as data classification, access control, encryption, and incident response.
2). Conduct a risk assessment: Identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to the organization’s data. This assessment should include an analysis of the organization’s infrastructure, systems, and processes. Use this information to prioritize risks and develop a plan to mitigate them.
Monitoring and Auditing Data Security
Monitoring and auditing data security is an essential part of maintaining a secure environment. Here are some steps to consider:
1). Implement a robust monitoring system: Set up tools and technologies to monitor and track data activity within the organization’s network. This includes monitoring access logs, network traffic, and system events. Regularly review and analyze these logs to identify any suspicious or unauthorized activities.
2). Conduct regular security audits: Perform periodic audits to assess the effectiveness of existing security controls and identify any gaps or vulnerabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the significance of data classification in data security?
Data classification is essential in data security because it helps organizations identify and prioritize the protection of sensitive information. By classifying data into different categories based on its sensitivity and criticality, organizations can apply appropriate security controls and allocate resources effectively. This ensures that sensitive data is adequately protected, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security incidents.
How can I determine the appropriate security level for different types of data?
To determine the appropriate security level for different types of data, you can consider the following factors:
1). Sensitivity: Assess the sensitivity of the data by evaluating its potential impact on individuals or the organization if it were compromised. For example, personally identifiable information (PII) or financial data may require a higher level of security compared to general business information.
2). Regulatory requirements: Determine if any legal or regulatory requirements dictate the security measures for specific types of data.
How can data encryption help in securing sensitive information?
Data encryption can help in securing sensitive information in several ways:
1. Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that only authorized individuals can access and understand the encrypted data. By converting the data into an unreadable format, encryption protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
2. Data Integrity: Encryption also helps in maintaining the integrity of the data. It ensures that the data remains unchanged during transmission or storage.
What measures can organizations take to prevent data breaches?
1). Strong Access Controls: Organizations should implement strong access controls to limit the number of individuals who can access sensitive data. This includes implementing strict user authentication processes, such as multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing and updating user access privileges.
2). Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits can help organizations identify vulnerabilities in their systems and address them promptly. This includes reviewing security policies and procedures, performing vulnerability assessments, and conducting penetration testing.
How often should data security audits be conducted?
Data security audits should be conducted regularly, typically at least once a year. However, the frequency of audits may vary depending on factors such as the size of the organization, industry regulations, and the sensitivity of the data being protected. It is important to establish a schedule for conducting audits and ensure that they are performed consistently to maintain a strong security posture.
