Introduction
Data security refers to protecting digital data and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It involves implementing measures such as encryption, access controls, backups and disaster recovery plans to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure of sensitive information. In today’s digital age where all types of organizations collect and store vast amounts of data from their customers or clients, ensuring data security is crucial.
In reality, everyone in an organization plays a role in maintaining data security. However, some individuals bear more responsibility than others. For example, IT professionals are typically responsible for implementing and maintaining security measures such as firewalls and encryption protocols. Managers and executives are responsible for setting policies around data access and ensuring that employees follow them.
Implementing comprehensive policies surrounding cybersecurity can help mitigate risks associated with cyber threats such as hacking or phishing attacks. The consequences of failing to secure sensitive information can be severe – including financial loss or damage to reputation – making it essential that businesses take necessary steps towards maintaining high levels of data protection.
The Role Of Organizations In Data Security
Legal Obligations For Data Security

Organizations have legal obligations when it comes to data security. For instance, various laws such as HIPAA require healthcare organizations handling personal health information (PHI) to secure this information from unauthorized access, use or disclosure. Similarly, companies that handle payment card information are required by the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) to implement measures such as encrypting cardholder data and restricting access to sensitive information.
The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) also holds organizations accountable for securing the personal data they collect and process. GDPR requires businesses handling EU citizens’ personal data to notify authorities within 72 hours in case of a breach. Organizations should therefore put in place measures such as regular vulnerability assessments, employee training on cybersecurity best practices, encryption of sensitive data among others, in order to comply with these legal requirements while ensuring they maintain customer trust through robust cybersecurity practices.
The Role Of IT Departments In Data Security
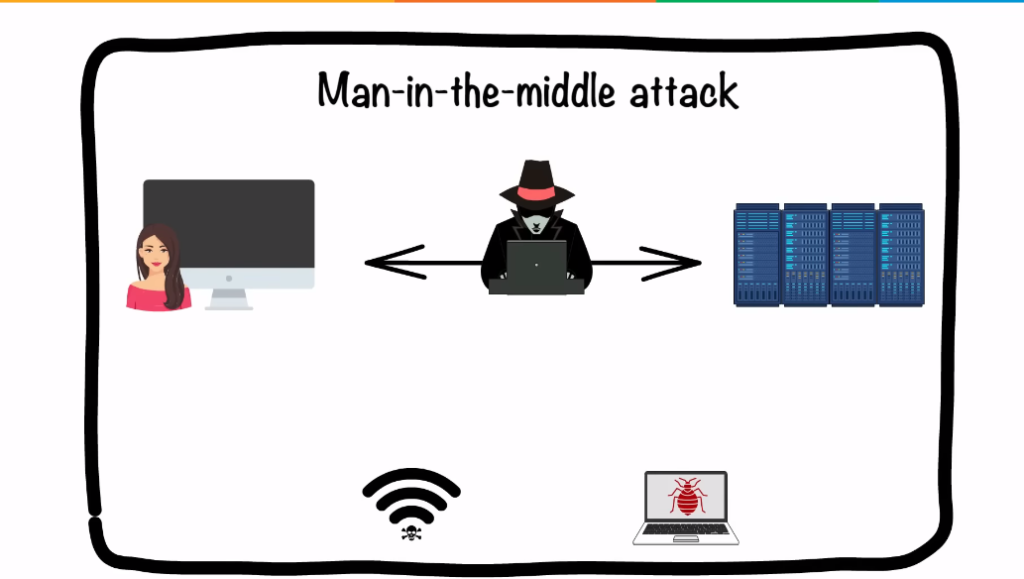
IT departments play a critical role in ensuring the security of an organization’s data. They are responsible for implementing and maintaining systems that protect against cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and phishing attacks. IT departments also ensure that employees are trained on best practices when it comes to data security, such as using strong passwords and avoiding suspicious emails or links.
In addition to protecting against external threats, IT departments must also monitor the internal use of company data. This includes tracking who has access to sensitive information and ensuring that proper protocols are followed when handling it. IT departments may also implement measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access controls to prevent unauthorized access to data.
The Role Of Managers In Data Security

Managers must also stay up-to-date on the latest data security threats and trends to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities within their organization. This requires ongoing training and education for themselves as well as their team members. Additionally, managers must ensure that all software and hardware used by employees meets industry standards for data encryption, firewalls, antivirus protection, and other security features.
The Role Of Employees In Data Security
Employees play a crucial role in ensuring data security within organizations. They are the first line of defence against cyber threats and must be aware of potential risks and their responsibilities in preventing data breaches. Employees should receive regular training on how to identify phishing emails, how to secure passwords, and how to use company devices safely.
In addition to being trained on best practices for data security, employees must also understand the importance of complying with organizational policies and procedures regarding data protection. For example, they should be aware of rules surrounding access controls, unauthorized disclosure or modification of sensitive information, and proper disposal of confidential documents.
The Role Of Customers In Data Security
Customer Education On Data Security
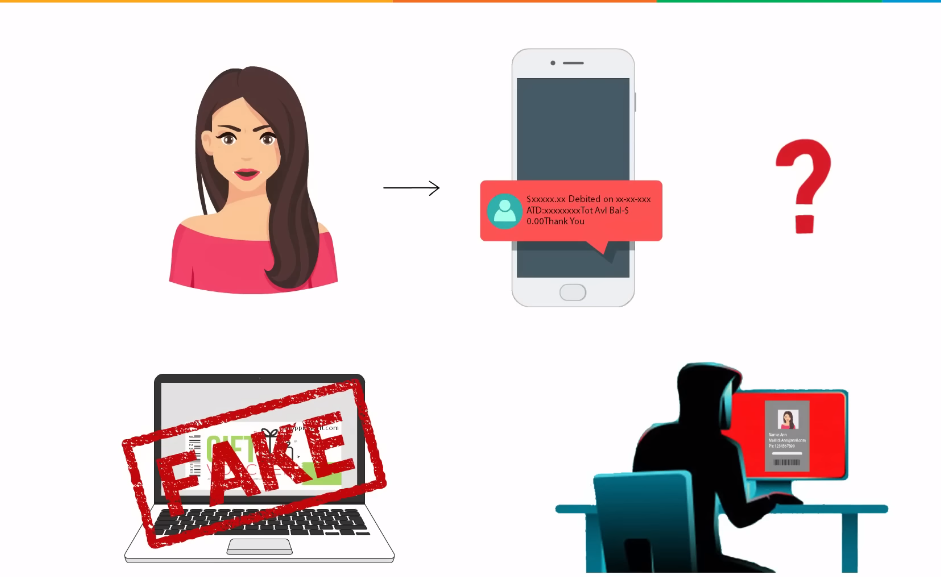
Customers also have a crucial role to play in ensuring their data remains secure. One way customers can take ownership of their data is by being vigilant when sharing personal information online. This includes avoiding public Wi-Fi networks when accessing sensitive accounts, creating strong passwords and changing them frequently, enabling two-factor authentication where possible, and keeping software up-to-date.
Additionally, customers should be aware of common scams such as phishing emails or fake websites designed to steal personal information. Companies can play a role in educating their customers on these risks and how to avoid them through regular communications and educational resources. Ultimately, maintaining strong data security requires a partnership between companies and their customers.
The Role Of Technology In Data Security
Technology has played a significant role in enhancing data security by providing various tools and techniques that can be used to protect sensitive information. For instance, encryption technology can be used to scramble the contents of files or messages so that they cannot be read by unauthorized parties. Additionally, firewalls and intrusion detection systems can help prevent unauthorized access to networks.
However, with every technological advancement comes new challenges and vulnerabilities that need to be addressed. As a result, individuals and organizations alike need to stay up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity trends and best practices. By doing so, we can ensure that our personal information remains safe and secure from potential cyber-attacks.
The Challenges Of Data Security:
Cyber Attacks And Data Breaches
Despite efforts made by individuals and businesses to strengthen data security, cyber attacks still occur frequently. These attacks can range from phishing scams that trick users into revealing their login credentials to ransomware that locks down entire computer systems until payment is made. Data breaches also pose a significant threat as they result in the exposure of personal information such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and other confidential data.
Human Error And Negligence
One of the biggest challenges in maintaining data security is human error and negligence. Despite having advanced technological tools and systems to protect sensitive information, a single mistake or careless action by an employee can compromise the entire network. Many businesses rely on employees to manage confidential data, which means that they must be educated about the risks associated with handling this type of information.
It is essential for organizations to establish protocols and guidelines for employees to follow when handling sensitive data. These protocols should detail how employees can access, store, transfer, or dispose of confidential information safely.
Insider Threats And Sabotage
Insider threats and sabotage are two of the biggest data security risks that companies face today. Employees, contractors, and other insiders have access to sensitive information and systems, making them potential sources of data breaches or other malicious activities.
Insider threats can take many forms, from accidental mistakes to intentional misconduct. For example, an employee might accidentally send sensitive information to the wrong person or leave a laptop containing confidential data in a public place. Alternatively, an insider might intentionally steal trade secrets or customer data for personal gain or to sell on the black market.
To prevent insider threats and sabotage, companies need to take a multi-pronged approach that includes education and awareness training for employees, as well as technical controls such as access controls and monitoring tools. It’s also important for organizations to establish clear policies around the acceptable use of company resources and the consequences for violating those policies.
Who Should Be Responsible For Data Security?
The responsibility of data security falls on everyone involved in the handling and processing of sensitive information. This includes employees, third-party vendors, and even customers to a certain extent. Organizations should have clear policies and procedures in place that outline the roles and responsibilities of each party in ensuring data security.
Employers must educate their employees about best practices for protecting sensitive data, such as regularly changing passwords, avoiding public Wi-Fi networks when accessing company systems, and being cautious with email attachments or links from unknown sources. Third-party vendors should also be held accountable for their role in safeguarding data by adhering to strict security protocols.
It is the responsibility of senior management to ensure that all parties involved are properly trained and equipped to handle sensitive information securely. This requires regular monitoring and auditing of systems and processes to identify potential weaknesses or vulnerabilities that could compromise the organization’s data security posture. By taking a proactive approach to data security, organizations can minimize risks associated with cyber threats while building trust with customers who entrust them with their personal information.
FAQs
Who Is Responsible For Data Privacy?
In most cases, companies that collect sensitive data from customers are responsible for keeping it safe. This includes everything from financial information and credit card numbers to email addresses and social security numbers.
However, there are also legal regulations in place that dictate how businesses must protect customer data. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires companies to obtain explicit consent before collecting any personal data and to implement strong security measures to prevent unauthorized access.
Why Is Data Security Important?
Data security is a critical aspect of any business, regardless of its size or industry. With the rise of technology and increased reliance on digital platforms, data breaches have become more common than ever before. A data breach can lead to severe consequences for businesses, including loss of revenue, legal ramifications, and damage to the company’s reputation. Therefore it is essential that companies prioritize data security.
What Are Some Common Challenges In Data Security?
One of the most common challenges in data security is human error. Employees may accidentally share sensitive information or fall for phishing scams, exposing company data to potential threats. To mitigate this risk, companies must train their employees on proper data handling procedures and establish protocols for reporting security breaches.
Another challenge is the increasing sophistication of cyber attacks. Hackers have become more skilled at breaching firewalls and other security measures, making it difficult for organizations to keep up with evolving threats. To address these challenges, businesses must invest in advanced cybersecurity technologies and regularly update their systems to stay ahead of potential attacks.
Regulatory compliance presents a significant challenge for companies that handle sensitive information. Businesses must comply with various laws and regulations around data privacy and protection, including HIPAA and GDPR. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in costly fines and legal repercussions, underscoring the importance of robust data security practices within any organization that handles sensitive information.
How Can Organizations And Individuals Improve Their Data Security?
In the case of organizations, they should implement strict security measures that include employee training and risk management strategies. They should also identify sensitive information and limit access only to authorized personnel. This can be done through encryption, secure networks, regular software updates, and firewalls.
On the other hand, individuals can also take steps to improve their own data security by practicing good online habits such as using strong passwords, avoiding public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions or communications, and being cautious about clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. They should also keep their software up-to-date with the latest security patches and regularly back up important data.
Conclusion
Data security is a shared responsibility between individuals, organizations, and governments. Individuals must take necessary precautions to protect their personal information, such as creating strong passwords and being cautious of phishing scams. Organizations must implement robust security measures to safeguard customer data and prevent breaches. This includes conducting regular security audits and providing employee training on cybersecurity best practices.
