Introduction
The protection of HR data privacy is crucial for both employers and employees. With the increasing usage of technology in HR processes, there is a growing need to ensure that personal and sensitive information is kept confidential and secure. Failure is to the outcome in legal and financial consequences for the organization, as well as damage to the trust and morale of employees. This comprehensive guide will explore the numerous aspects of HR data privacy shields and provide practical tips for organizations to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Definition Of HR Data Privacy Shield
HR data privacy shield refers to the measures and practices put in place by organizations to protect the privacy and confidentiality of personal and sensitive information collected, processed, and stored within their HR systems and processes. This includes personal data such as names, addresses, and contact information, as well as sensitive information such as health records, bank account details, and social security numbers.
Objectives Of HR Data Privacy Shield

The primary objective of the HR data privacy shield is to protect employees’ personal and sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This includes employee names, addresses, social security numbers, medical records, and financial information. Another objective is to comply with privacy laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which require organizations to implement appropriate measures to protect personal data.
HR data privacy shield also aims to build a culture of trust and transparency between employees and the organization. Employees are more likely to realize they are valued and respected by their employers by ensuring data protection. This can lead to increased loyalty, job satisfaction, and productivity. To achieve these objectives, HR data privacy shield typically involves implementing various technical, administrative, and physical safeguards. These may include using encryption to protect sensitive data, restricting access to data on a need-to-know basis, and implementing policies and procedures for handling and disposing.
Role Of HR Data Privacy Shield In Protecting Employee Data

The role of the HR data privacy shield is crucial in protecting employee data. It ensures that sensitive information like personal and financial details, medical records, and employment history are kept confidential and secure. This is important for legal compliance and maintaining employee trust and confidence in the organization.HR data privacy shield helps to stop data breaches, identity theft, and other forms of cybercrime that could direct financial loss and reputational damage for both the employer and the employee.
Key Concepts In HR Data Privacy Shield
Personal Data
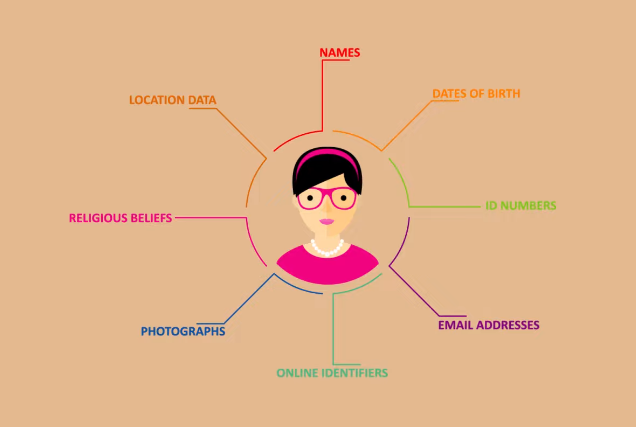
Personal data refers to any data that can recognize an individual, such as their name, address, email address, phone number, social security number, or any other unique identifier. HR departments often collect and process employees’ data for various purposes, such as payroll, benefits administration, and performance management. HR departments need to ensure that they are collecting and processing personal data in compliance with applicable data privacy regulations to protect the privacy and security of employees’ personal information. To ensure compliance with data privacy regulations, HR departments should implement appropriate data protection measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular data backups. They should also provide employees with clear and brief privacy notices that explain how their data will be collected, processed, and shared and their rights concerning their data.
Sensitive Personal Data
Sensitive personal data refers to any information that can reveal a person’s race or ethnicity, political views, religious or philosophical beliefs, trade union membership, genetic data, biometric data, health information, sexual orientation, or criminal records. This type of data requires even greater protection than other types of personal data due to the potential for discrimination or harm if it falls into the wrong hands. HR departments should take extra care to ensure that sensitive personal data is only collected and processed when necessary and that appropriate measures are in place to protect it. Additionally, HR departments should ensure compliance with relevant data protection laws and regulations. This may include obtaining consent from employees for collecting and processing their personal data, implementing appropriate security measures to thwart unauthorized access or disclosure, and ensuring that data is only stored for as long as necessary.
Data Controller
A data controller is an individual or organization that governs the purposes and means of processing personal data. This can include collecting, storing, using, and sharing personal data. The data controller ensures that applicable data protection laws and regulations process personal data. They must also ensure that individuals are informed about processing their personal data and have the right to access, repair, or erase their data.
Data Processor
A data processor is an individual or organization that processes data on behalf of the data controller. This can include analyzing, organizing, storing, or transmitting personal data. Data controllers typically hire data processors to perform certain tasks or services that require the processing of personal data. Data processors must follow the data controller’s instructions and ensure personal data is processed securely and legally. They must also implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to defend personal data from unauthorized access.
Data Subject
A data subject is an individual whose data is collected, processed, stored, or transmitted by a data controller or processor. This can include customers, employees, patients, or anyone whose personal data is collected and processed. Data subjects have some rights under data protection laws, such as the right to access their personal data, the right to have their personal data corrected or deleted, and the right to object to processing their personal data. Data controllers or data processors are to ensure that they collect and process personal data obeying applicable data protection laws. This includes implementing apt technical and organizational measures to protect personal data against unauthorized or unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage and ensuring that data subjects are provided with clear and transparent information about how data is being used. Data controllers and processors need to stay up-to-date with changes in data protection laws and regularly review and update their data protection policies and procedures.
Consent
Consent is an important aspect of data protection, as it ensures that individuals have control over how their data is used. For data processing to be lawful, the individual must give their freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous consent for their data to be processed. This means that the individual must be provided with clear and understandable information about how their data will be used and must actively consent. Data controllers must ensure that consent is obtained clearly and transparently and that the individual is not pressured or coerced into giving consent. Additionally, the GDPR requires that data controllers have a lawful basis for processing personal data, including consent, contractual necessity, legal obligation, vital interests, public interest, or legitimate interests. Data controllers must demonstrate that they have a lawful basis for processing personal data and that they are only processing data for the specific purposes for which it was collected.
To Comply With The GDPR
It’s important to ensure that individuals clearly understand what personal data is being collected, why it is being composed, and how it will be used. This can be achieved through clear and concise privacy notices and consent forms. It’s also important to allow individuals to withdraw their consent at any time and to have their personal data erased if requested. Data controllers should also implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to confirm the security of personal data, such as encryption, access controls, and regular data backups. Additionally, data controllers should conduct regular risk assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in data processing activities. It’s also important for data controllers to only collect and process the minimum amount of private data necessary for their specific purposes. This means avoiding unnecessary data collection and ensuring that personal data is not saved longer than necessary.
Finally, data controllers should be transparent and accountable in their data processing activities. This includes keeping detailed records of their data processing activities, promptly responding to data subject requests, and implementing reasonable security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
Right To Be Forgotten
The right to be forgotten is a principle under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) that allows individuals to request the erasure of their data from the records of data controllers. This identifies that individuals have the right to delete their personal data if it is no longer necessary for the drive for which it was collected if they withdraw their consent for its processing, or if it was processed unlawfully.
Implementing HR Data Privacy Shield
Steps To Implement HR Data Privacy Shield
1. Conduct a Data Audit: The first step is thoroughly auditing all HR data your organization collects, processes, and stores. This includes employee data, applicant data, and any other HR-related data.
2. Identify Risks: Once you have identified all the HR data your organization collects, you must identify potential risks associated with storing and processing this data. This includes risks related to data breaches, unauthorized access, and non-compliance with GDPR.
3. Develop Policies and Procedures: Based on the identified risks, develop policies and procedures to ensure the security and compliance of HR data. This includes setting up access controls, implementing encryption, and establishing data retention and disposal guidelines.
4. Train Employees: It is crucial to train all employees who handle HR data on the policies and procedures to protect the data. This includes training on password management, phishing prevention, and data handling best practices.
5. Monitor and Review: Regularly review your HR data security policies and procedures to ensure they remain effective and current. This includes periodically conducting audits and risk assessments to identify new risks or vulnerabilities.
Challenges In HR Data Privacy Shield
There are several challenges that organizations may face when it comes to HR data privacy. Some of these challenges include:
1. Lack of awareness: Employees may not be aware of the importance of data privacy and the potential risks associated with mishandling HR data.
2. Complexity of regulations: Data privacy regulations can differ from region to region, making it hard for organizations to stay current with the latest requirements.
3. Insider threats: Employees may intentionally or unintentionally compromise HR data through negligence or malicious intent.
4. Cybersecurity threats: HR data is a valuable target for cybercriminals, and organizations must protect against data breaches and cyber-attacks.
5. Third-party risks: Organizations may need to share HR data with third-party vendors or service providers, increasing the risk of data breaches or unsanctioned access.
Overall, organizations must prioritize HR data privacy and take proactive steps to protect sensitive employee information. This includes implementing strong data privacy policies and practices, providing employee training and awareness programs, and monitoring and reviewing compliance regularly.
Future Of HR Data Privacy Shield
As technology advances and the data collected by HR departments grow, the future of HR data privacy will become increasingly important. New laws and regulations will likely be introduced to address emerging privacy concerns. One trend that is already emerging is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in HR processes. While these technologies can provide valuable insights and improve efficiency, they raise new privacy concerns. Organizations must ensure transparency about using AI and machine learning and take steps to protect employee privacy.
Another trend to watch is the growing importance of employee consent. Employees becoming more aware of their privacy rights may demand greater control over their personal data. Organizations will need to find ways to balance the requirement for data with the need to respect employee privacy preferences.
Conclusion
HR departments play a crucial role in protecting employee data privacy. They must implement policies and procedures to safeguard personal information, regularly review and update security measures, stay informed about emerging cyber threats, ensure compliant third-party service providers, and educate employees on data privacy. By taking these steps, HR departments can help prevent data breaches and protect the privacy of their employees.
Data privacy has become a critical issue for organizations in today’s digital age. HR departments, in particular, hold a vast amount of sensitive employee data, making them a prime target for cybercriminals. Therefore, HR departments need to take proactive measures to protect this information and ensure the privacy of their employees. By doing so, they comply with legal requirements and build trust and confidence among their workforce. A strong HR data privacy shield can help organizations avoid costly data breaches, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is An HR Data Privacy Shield?
Organizations need to ensure that they protect the privacy of their employee’s data, especially in the context of human resources. This may involve implementing appropriate security measures, obtaining employee consent to use their data, and being transparent about their data use.
What Are The Key Concepts In The HR Data Privacy Shield?
HR data privacy shield is a set of guidelines and best practices for protecting employee privacy in collecting, storing, and using HR data. The key concepts in HR data privacy shield include transparency, accountability, employee consent, and data security. Organizations that adopt these principles can build trust with employees and reduce the risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
What Are The Challenges In The HR Data Privacy Shield?
There are several challenges in HR data privacy shield, including:
1. Ensuring compliance with multiple data privacy regulations: HR departments must comply with various data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, which can be complex and challenging.
2. Balancing data privacy with business needs: HR departments must balance data privacy with the need to collect and use employee data to perform their job functions effectively.
3. Protecting against data breaches: HR departments must take steps to protect employee data from unauthorized access, theft, or loss, which can be difficult given the increasing sophistication of cyber threats.
4. Ensuring third-party service providers are compliant: HR departments must ensure that any third-party service providers who handle employee data have appropriate data privacy and security measures.
5. Educating employees on data privacy: HR departments must educate employees on privacy practices and policies to ensure they comprehend their rights and responsibilities regarding their personal data.
