Introduction
Web application attacks refer to malicious activities that exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to gain unauthorized access or steal sensitive information. These attacks can occur for various reasons, including weak passwords, unpatched software, and social engineering tactics.
Common Web Application Attacks
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)

Cross-site scripting, or XSS, is a type of web application attack that involves injecting malicious code into a web page visited by other users. This code can steal sensitive information from unsuspecting users, such as login credentials or personal data.
SQL Injection
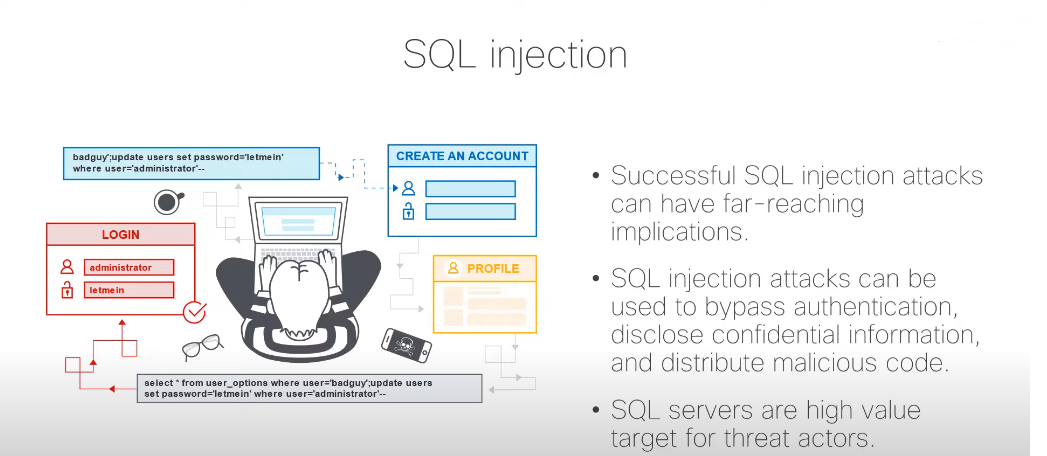
SQL injection is another web application attack that exploits vulnerabilities in a web application’s database to extract sensitive information. Attackers can use SQL injection to bypass authentication measures and gain access to sensitive data stored in the database.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
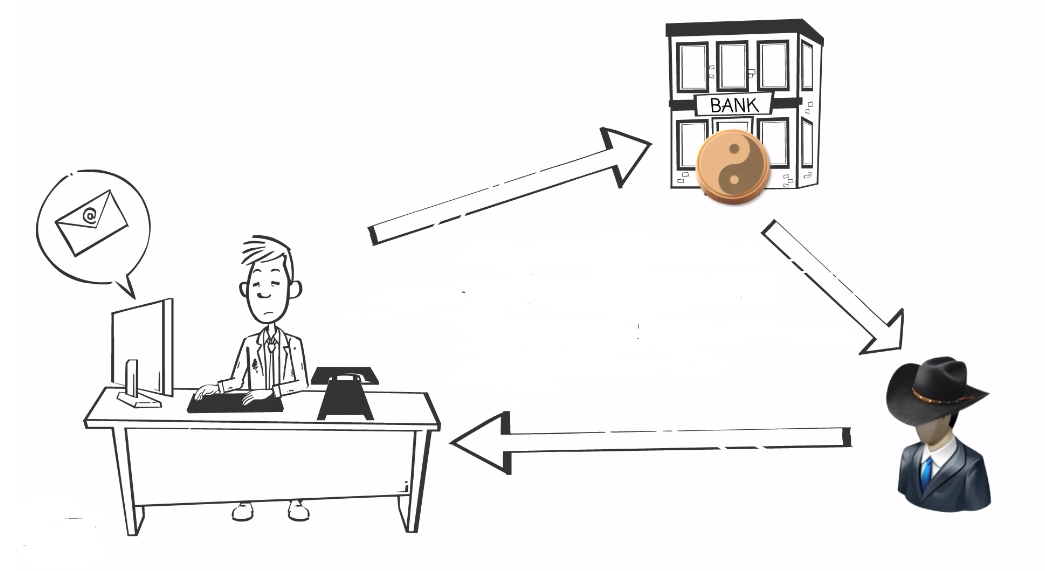
Cross-site request forgery, or CSRF, is an attack that tricks a user into acting on a web application without their knowledge or consent. This can include actions such as making a purchase or changing a password, which can result in the theft of sensitive information.
Factors Affecting The Likelihood Of Data Extraction
Vulnerability Of The Web Application
The vulnerability of a web application is a significant factor that can affect the likelihood of data extraction. If a web application has security vulnerabilities, attackers can exploit it to get unauthorized access to sensitive data. Common vulnerabilities include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure authentication mechanisms. Web developers need to ensure that their applications are secure and regularly updated to prevent the exploitation of vulnerabilities. Additionally, web application security testing can help identify and address liabilities before attackers can exploit them.
Several vulnerabilities can increase the likelihood of data extraction from web applications. Some of the common ones include:
1. SQL injection: This vulnerability occurs when an attacker can inject malicious SQL statements into a web application’s database. This allows the attacker to extract sensitive data or modify the database.
2. Cross-site scripting (XSS): This vulnerability occurs when an attacker inserts malicious scripts into a web application, which unsuspecting users can execute. This can permit the attacker to steal sensitive data or even take control of the user’s browser.
3. Insecure authentication mechanisms: This vulnerability occurs when a web application uses weak or easily guessable passwords or does not properly validate user credentials. This can allow attackers to access sensitive data or even take control of user accounts.
4. Insecure file uploads: This vulnerability occurs when a web application allows users to upload files without proper validation or filtering. This can allow attackers to upload malicious files or scripts, which can then be executed on the server.
Web developers need to be aware of these vulnerabilities and take steps to mitigate them to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
How To Identify Vulnerabilities In A Web Application?

Identifying vulnerabilities in a web application can be a complex process, but several techniques can be used to help identify potential issues.
1. Manual Testing: One approach is to manually test the web application by attempting to exploit known vulnerabilities or performing a thorough analysis of the code and system architecture. This can be time-consuming and requires a deep understanding of web application security.
2. Automated Scanning: Another approach is to use automated scanning tools that can quickly identify vulnerabilities by scanning the web application for common issues such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and insecure file uploads. These tools are often more efficient than manual testing but may generate false positives or miss certain vulnerabilities.
3. Penetration Testing: A more comprehensive approach is to conduct a penetration test, which involves simulating an attack on the web application to identify vulnerabilities and assess the general security posture of the system. This approach requires specialized skills and tools but can provide valuable insights into the web application’s security.
Regardless of the approach used, it is important to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and likelihood of exploitation and to take appropriate steps to remediate any identified issues.
User Behavior
The Role of user behavior in data extraction
User behavior can significantly affect data extraction, particularly when sensitive information is accessed or shared. For example, suppose users are not properly trained to handle sensitive data. In that case, they may inadvertently expose it by emailing it to unauthorized recipients or storing it on unsecured devices.
Best Practices For Preventing Data Extraction Through User Behavior
Here are some best practices for preventing data extraction through user behavior:
1. Limit user access: Only grant access to sensitive data to those who need it to perform their duties. Implement access controls and permissions to ensure users can only access the data necessary for their work.
2. Monitor user activity: Use monitoring tools to track user activity and detect suspicious behavior, such as large data downloads or access to data outside of normal working hours.
3. Implement encryption: Encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access in case of a breach.
4. Use strong passwords: Require users to create strong passwords and implement policies for regular password changes.
5. Conduct regular training: Educate users on the importance of data security and provide regular training on best practices for handling sensitive data.
6. Implement multi-factor authentication: Require users to provide additional authentication factors, such as a fingerprint or a security token, to access sensitive data.
By implementing these practices, organizations can reduce the risk of data extraction through user behavior and protect their sensitive information from cyber threats.
Best Practices For Protecting Privacy Data Elements
Protecting private data elements is crucial for organizations that handle sensitive information. Here are some best practices to follow:
1. Implement data minimization: Collect only the minimum amount of data necessary for business purposes and dispose of it securely when it is no longer needed.
2. Use encryption: Encrypt sensitive data in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Implement access controls: Limit access to sensitive data to only those who need it to perform their duties.
4. Conduct regular audits: Review access logs and audit trails to identify unauthorized access attempts.
5. Train employees: Educate employees on the importance of protecting privacy data elements and provide regular training on best practices for handling sensitive data.
By following these practices, organizations can safeguard privacy data elements and prevent breaches that can cause irreparable harm to individuals and businesses.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is converting plain text or data into a coded language to protect it from unauthorized access or theft. This is done by using an algorithm to scramble the data, which can only be accessed and read by someone with the key to decrypt the information. Encryption is commonly used to secure sensitive data such as financial, personal, and confidential business data. It is an essential security measure for protecting data from cyber-attacks and unauthorized access.
Best Practices For Data Encryption
Here are some best practices for data encryption:
1. Use strong encryption algorithms: Use strong encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) or RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) to encrypt your data.
2. Use a secure key management system: A secure key management system is essential for protecting the encryption keys used to encrypt and decrypt your data. Use a system that provides strong key protection and access controls.
3. Encrypt data at rest and in transit: Encrypt data at rest (stored on a device or server) and in transit (sent over a network) to ensure maximum protection.
4. Implement multi-factor authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication to confirm that only authorized users can access the encrypted data.
5. Regularly update encryption protocols: Keep your protocols up-to-date to ensure you use the latest and most secure encryption algorithms.
6. Conduct regular security audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify any vulnerabilities in your encryption system and take appropriate measures to address them.
By following these practices, you can ensure your data is well-protected and secure from cyber-attacks and unauthorized access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is A Web Application Attack?
A web application attack is a type of cyber attack that targets web-based applications such as online banking systems, e-commerce websites, and social media platforms. Such an attack aims to exploit vulnerabilities in the web application’s code or infrastructure to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or disrupt the application’s normal functioning. Some common web application attacks include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
What Are Privacy Data Elements?
Privacy data elements are pieces of personal information considered sensitive and private, requiring special protection and handling. These can include a person’s name, address, date of birth, social security number, financial information, medical records, and other personally identifiable information (PII). It is important to safeguard these privacy data elements to prevent identity theft, fraud, and other malicious activities that can harm individuals and organizations. Privacy laws and regulations, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), set standards for collecting, using, and disclosing personal information. Organizations must comply with these laws and implement appropriate security measures to protect privacy data. Failure to do so can result in authorized and financial consequences and damage the organization’s reputation. Therefore, it is important to handle privacy data with the utmost care and ensure that it is only accessed by authorized personnel with a legitimate need to know.
What Is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)?
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a security vulnerability that permits an attacker to inject malicious code into a web page viewed by other users. This occurs when the attacker can insert their own code into a web page viewed by other users, such as through a comment section or form submission. When users view the page with the injected code, the attacker can steal sensitive information, such as login credentials or personal data. XSS attacks can be prevented by implementing proper input validation and sanitization techniques on web applications.
What Is SQL Injection?
SQL injection is a cyber-attack where an attacker injects malicious SQL code into a web application’s input field, such as a login form or search bar. This allows the attacker to manipulate the database behind the web application and potentially gain access to sensitive information, modify or delete data, or perform other malicious actions. Implementing parameterized queries and input validation techniques in the web application’s code can prevent SQL injection attacks.
What Is Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)?
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is an attack where a malicious website or email tricks a user into acting on a different website without their knowledge or consent. For example, an attacker could send a user an email with a link to a website that the user trusts, but the link performs a covert action on a different website, such as transferring money or changing a password. CSRF attacks can be prohibited by implementing CSRF tokens and checking the referrer header in the web application’s code.
How Can Web Application Attacks Be Prevented?
Several measures can be implemented to prevent web application attacks. Here are a few examples:
1. Input validation: All user input should be validated and sanitized to ensure that it is safe to use within the application.
2. Authentication and authorization: Strong authentication and authorization mechanisms should be in place to stop unauthorized access to the application and its resources.
3. Encryption: Sensitive data should be encrypted in transit and at rest to prevent illegal access.
4. Access controls: Access controls should be implemented to ensure that only authorized clients can access the application and its resources.
5. Regular updates and patches: Web applications should be updated with the latest security patches and updates to avert known vulnerabilities from being exploited.
6. Security testing: Regular security testing should be performed to identify and remediate any vulnerabilities in the application.
By implementing these measures, web application attacks can be prevented, and the application can be kept secure from malicious actors.
What Is Data Encryption?
Data encryption converts plain text or data into a coded language to prevent unauthorized access. It involves using a cryptographic algorithm to transform the data into an unreadable format, which can only be decrypted using a specific key or password. Encryption is commonly used to protect sensitive information such as financial, personal, and confidential business data. It is an essential security measure that helps to confirm the privacy and integrity of data, making it more difficult for hackers to steal or misuse information.
How Often Should A Web Application Be Audited And Monitored?
The frequency of web application audits and monitoring depends on numerous factors, including the complexity of the application, the sensitivity of the data it handles, and the level of risk associated with potential security threats. Generally, it is recommended to audit and monitor web applications regularly, at least once a year, or more frequently if the application handles sensitive data or is subject to compliance regulations. Additionally, ongoing monitoring can help detect and prevent real-time security incidents, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Conclusion
Protecting private data is crucial for individuals and organizations. It helps to maintain trust, prevent legal liabilities, avoid financial losses, and protect sensitive information from theft and misuse. By implementing strong security measures and adhering to data protection laws, organizations can safeguard personal and confidential information and ensure their customers’ and employees’ safety and privacy.
Protecting privacy data elements is crucial for individuals and organizations to maintain trust, prevent legal liabilities, and avoid financial losses. Strong security measures and adherence to data protection laws are essential in safeguarding personal and confidential information. Organizations need to prioritize the safety and privacy of their customers and employees. As a writing assistant, I recommend that individuals and organizations regularly review and update their privacy policies and security measures to ensure they are up-to-date and effective in protecting sensitive information.
