Understanding Data Encryption

Data encryption is the process of converting plaintext or readable data into an encoded format called ciphertext. This is done to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or interception. Encryption works by using an algorithm and a key to transform the original data into an unreadable format. The algorithm determines how the data is scrambled, while the key is a unique piece of information that is used to encrypt and decrypt the data.
Encryption Algorithms
Encryption algorithms are mathematical formulas or processes that determine how data is scrambled and transformed into ciphertext. There are various types of encryption algorithms, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some common encryption algorithms include:
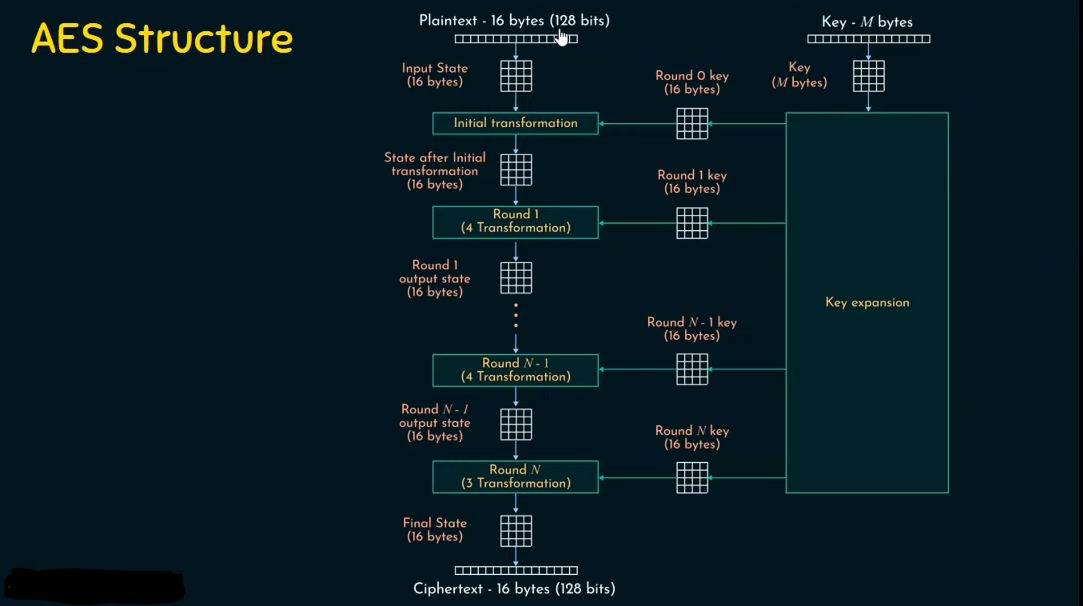
1. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): This symmetric encryption algorithm is widely used and considered secure. It supports key sizes of 128, 192, and 256 bits.
2. RSA: This asymmetric encryption algorithm is commonly used for secure communication and digital signatures.
Key Components of Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting data into ciphertext to ensure its confidentiality and security. It involves using encryption algorithms, such as AES and RSA, which have different methods of scrambling and transforming the data.1. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES):
– AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encryption and decryption.
– It operates on blocks of data and supports different key sizes, including 128, 192, and 256 bits.
Factors Influencing Data Encryption
- Sensitivity of the data
- Legal and regulatory requirements
- Industry best practices
- Cost and resources
- User experience considerations
Benefits of Data Encryption
- Protection against unauthorized access
- Mitigation of data breaches
- Compliance with data protection regulations
- Increased customer trust and reputation
Challenges and Limitations of Data Encryption
Challenges and Limitations of Data Encryption:
1. Performance Impact: Data encryption can introduce processing overhead, potentially slowing down data transfer and application performance.
2. Key Management: Effective encryption requires secure key management practices, including generating, storing, and distributing encryption keys. This can be complex and resource-intensive.
3. Compatibility Issues: Encrypting data can lead to compatibility issues, as encrypted data may not be readable by all systems or applications.
Key Management And Storage
Key management and storage are crucial aspects of data encryption. Effective encryption requires secure key management practices, including generating strong encryption keys, storing them securely, and distributing them to authorized parties. However, this process can be complex and resource-intensive, requiring careful planning and implementation. Compatibility issues can also arise when encrypting data. Encrypted data may not be readable by all systems or applications, especially if they do not support the same encryption algorithms or have the necessary decryption keys.
Performance Impact
When implementing secure key management practices, it is important to consider the potential performance impact. Encryption and decryption processes can introduce additional computational overhead, which may affect the overall system performance. The impact can vary depending on factors such as the encryption algorithms used, the size of the data being encrypted or decrypted, and the processing power of the system. To mitigate performance issues, it is advisable to carefully select efficient encryption algorithms and optimize the key management processes.
Compatibility And Interoperability
Encryption and decryption processes can also introduce compatibility and interoperability challenges. Different systems may use different encryption algorithms or have varying levels of support for encryption protocols. This can make it difficult to securely exchange encrypted data between different systems or ensure that encrypted data can be decrypted by the intended recipients. To address these challenges, it is important to establish clear encryption standards and protocols that are widely supported and compatible with the systems involved.
Encryption Vulnerabilities And Attacks
Encryption vulnerabilities and attacks pose a significant threat to the security of encrypted data. Cryptographic algorithms can be susceptible to vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited by attackers. For example, weaknesses in the algorithm itself or flaws in its implementation could lead to the encryption being broken.
Data Encryption in Different Contexts
Encryption in personal devices is crucial for protecting sensitive data such as personal information, financial details, and private communications. It ensures that if a device is lost, stolen, or accessed by unauthorized individuals, the data remains secure and inaccessible. Encryption in personal devices can be achieved through various methods, such as full-disk encryption, file-level encryption, or encryption of specific applications or data.
Encryption in Enterprise Environments
Encryption in enterprise environments is essential for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining data integrity. It helps protect valuable corporate data, intellectual property, and customer information from unauthorized access or theft. Encryption in enterprise environments can be implemented at various levels, including data transmission, storage, and application layers. By encrypting data at rest and in transit, organizations can mitigate the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with industry regulations and privacy laws.
Encryption In Cloud Storage
Encryption in cloud storage is a crucial security measure that enhances data protection. It involves the use of encryption algorithms to convert data into unreadable ciphertext before storing it in the cloud. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they will not be able to understand or use it without the proper decryption key. Cloud storage providers typically offer encryption options, such as server-side encryption and client-side encryption.
Deciding to Encrypt Data
Encrypting data in cloud storage is a crucial security measure that enhances data protection. It involves the use of encryption algorithms to convert data into unreadable ciphertext before storing it in the cloud. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they will not be able to understand or use it without the proper decryption key. Cloud storage providers typically offer encryption options, such as server-side encryption and client-side encryption.
Alternatives to Encryption
There are several alternatives to encryption for enhancing data protection in cloud storage:
1. Access Controls: Implementing strict access controls can help prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive data. This can include using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls.
2. Data Redundancy: Storing multiple copies of data across different locations can help protect against data loss or corruption. This ensures that even if one copy of the data is compromised, there are still other copies available.
The Role of Encryption in Data Privacy
Encryption plays a crucial role in data privacy by ensuring that sensitive information remains secure and unreadable to unauthorized individuals. It involves the process of encoding data using an encryption algorithm, which can only be decrypted with the use of a unique decryption key. By encrypting data, organizations can protect it from being accessed or intercepted by unauthorized parties, even if the data is stolen or compromised.
Privacy Regulations And Encryption
Privacy regulations often require organizations to implement encryption as a security measure to protect personal and sensitive data. Encryption helps organizations comply with these regulations by ensuring that data is protected and unreadable, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Additionally, encryption can also help organizations maintain customer trust and protect their reputation by demonstrating a commitment to data privacy and security.
Encryption As A Privacy-Enhancing Technology
Encryption is widely recognized as a privacy-enhancing technology. It enhances privacy by transforming data into an unreadable format, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to access or understand the information. This is particularly important in today’s digital age where data breaches and cyberattacks are prevalent. By implementing encryption, organizations can safeguard sensitive information, such as customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unintelligible without the appropriate decryption key.
Conclusion
In conclusion, encryption plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and understanding. It provides a readable format that is difficult for unauthorized individuals to access, ensuring the security of data in today’s digital age. By implementing encryption, organizations can safeguard customer data, financial records, and intellectual property, preventing data breaches and cyberattacks. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unintelligible without the appropriate decryption key.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can encryption be cracked?

Encryption can be cracked, but it is extremely difficult and time-consuming. The strength of encryption depends on the algorithm used and the length of the encryption key. Currently, most encryption algorithms are considered secure if implemented correctly and if the encryption key is long enough. However, as technology advances, new encryption methods may be developed that can potentially crack current encryption algorithms. Organizations need to stay updated with the latest encryption standards and practices to ensure the security of their data.
Is data encryption foolproof?
Data encryption is not foolproof. While encryption can provide a high level of security for data, it is not immune to potential vulnerabilities or attacks. The security of an encryption system depends on various factors, such as the strength of the encryption algorithm, the length and complexity of the encryption key, and the implementation of the encryption process. If any of these factors are compromised, it can weaken the overall security of the encryption and potentially make it susceptible to attacks.
Does encryption impact data transfer speed?
Yes, encryption can impact data transfer speed. The process of encrypting and decrypting data requires computational resources, which can introduce additional latency and reduce the overall transfer speed. The impact on speed depends on various factors, such as the strength of the encryption algorithm used and the processing power of the devices involved in the transfer. However, modern encryption algorithms and hardware advancements have minimized the impact on speed, making it less noticeable in most cases.
What happens if I lose the encryption key?
If you lose the encryption key, you will no longer be able to decrypt the encrypted data. The encryption key is essential for the decryption process, as it is used to reverse the encryption and convert the ciphered data back into its original form. Without the key, the encrypted data will remain unreadable and inaccessible. It is important to keep the encryption key secure and make backups to avoid the risk of losing it.
Are there any legal requirements for encryption?
Yes, there are legal requirements for encryption in some jurisdictions. The specific requirements vary by country and can include regulations on the use, export, and import of encryption technologies. For example, some countries may require companies to provide access to encrypted data under certain circumstances, while others may restrict the use of strong encryption altogether. It is important to research and comply with the encryption laws and regulations applicable to your jurisdiction to ensure legal compliance. Consulting with legal professionals or authorities in your area can provide more specific guidance.
Can encrypted data be recovered without the key?
No, encrypted data cannot be recovered without the key. Encryption is designed to protect data by converting it into an unreadable format, and the key is required to decrypt the data and make it readable again. Without the key, it is extremely difficult, if not impossible, to recover the original data from the encrypted form.
