Digital certificates, while not directly encrypting data themselves, facilitate and enable the encryption process by binding public keys to entities. They work in tandem with encryption algorithms to ensure data security during communication.
Digital certificates play a crucial role in ensuring the encryption of data in today’s interconnected world. Understanding the concept and function of digital certificates is essential in comprehending their significance in data security. Additionally, debunking common misconceptions and exploring emerging trends can shed light on the future of data encryption.
Understanding Digital Certificates
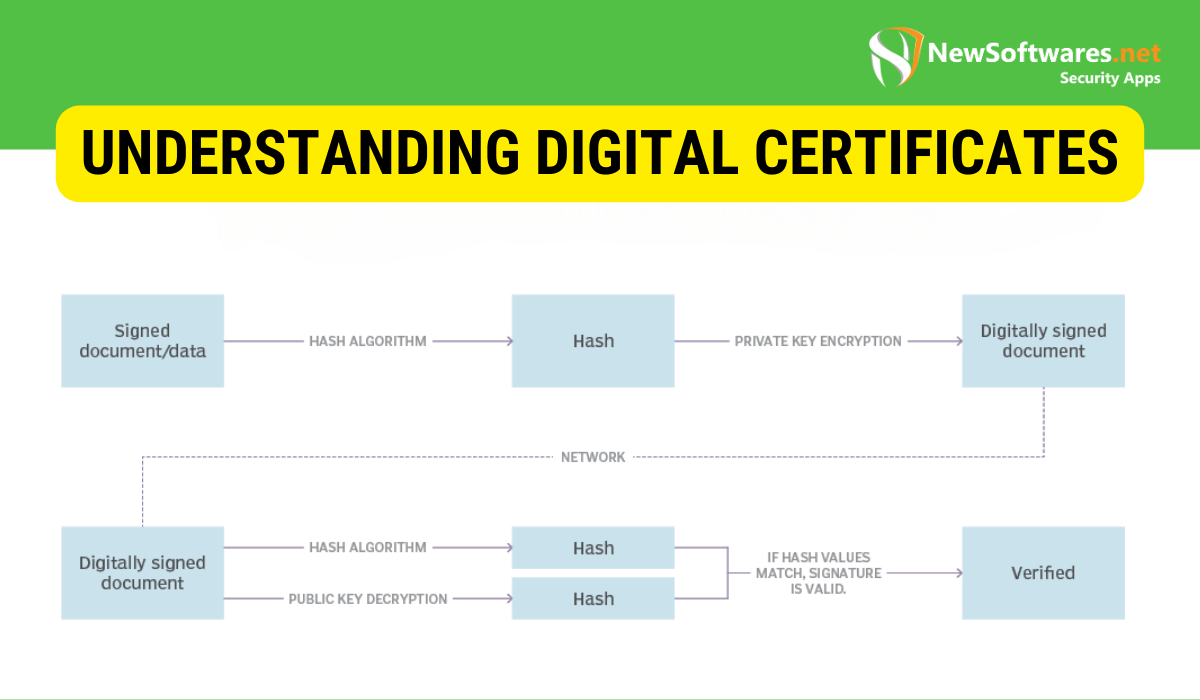
Definition and Function of Digital Certificates
A digital certificate is an electronic document that binds a public key to an entity, such as an organization or an individual. It contains information about the certificate holder and is typically issued by a trusted third party called a certificate authority (CA). The digital certificate serves as a digital identification card, verifying the authenticity and integrity of the certificate holder.
Let’s dive deeper into digital certificates and explore their components and functions.
A digital certificate consists of several key elements. Firstly, it includes the public key of the certificate holder. This public key is used for encryption and decryption, ensuring secure communication between parties. The certificate also contains information about the holder, such as their name, organization, and contact details. This information helps establish trust and credibility in online transactions.
The certificate authority (CA) is pivotal in the digital certificate framework. CAs undertake the task of validating the identity of certificate users and dispensing digital certificates. As reputable intermediaries, they confirm that the certificate’s data is authentic and trustworthy. To issue a certificate, CAs adhere to rigorous processes and standards to verify the identity of individuals or entities.
Digital certificates chiefly exist to promote protected online communications. Leveraging asymmetric encryption techniques, these certificates facilitate the encoding and decoding data shared between entities. Such encryption guarantees data confidentiality and ensures it’s shielded from unauthorized access or modifications.
When two parties want to establish a secure connection, they exchange digital certificates. Each party verifies the authenticity of the other’s certificate using the CA’s public key. Once the certificates are validated, the parties can securely exchange encrypted data, confident that malicious actors cannot access it.
Importance of Digital Certificates in Data Security
Digital certificates are pivotal in data protection in fostering trust among interacting parties. Data encrypted with a public key can solely be decrypted by its paired private key. Thus, digital certificates shield confidential data from unwanted access and potential hazards.
Furthermore, digital certificates provide a mechanism for verifying the identity and integrity of the sender. By digitally signing data using their private key, the sender can guarantee that the information has not been altered during transmission. The recipient can verify this digital signature using the sender’s public key, ensuring the message’s authenticity and integrity.
Moreover, digital certificates help prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. These attacks involve an attacker intercepting communication between two parties and impersonating one or both. With digital certificates, the parties can verify each other’s identities, making it extremely difficult for attackers to deceive or manipulate the communication.
A notable benefit of digital certificates is website safety. Websites utilizing secure protocols, like HTTPS, depend on digital certificates to forge a safe link between the user’s browser and the website server. This guarantees that confidential data, including usernames and monetary information, is conveyed securely, minimizing the risk of unauthorized interception.
In summary, digital certificates are vital for guaranteeing safe communication and safeguarding information in the online realm. They associate public keys with specific users and offer methods for coding, decoding, and confirming identities, underscoring their significance in building confidence and upholding information safety.
The Role of Digital Certificates in Data Encryption
How Digital Certificates Contribute to Data Encryption?

Digital certificates serve as the foundation for establishing secure communication channels through encryption. When two parties want to connect securely, they exchange their digital certificates. Each party verifies the other’s certificate, ensuring its validity and authenticity.
Once the certificates are validated, the parties exchange their public keys securely. These public keys are then used to encrypt the data before transmission. Only the intended recipient, possessing the corresponding private key, can decrypt and access the information. This process protects the data from unauthorized access, providing encryption at the core of secure communication.
Additionally, digital certificates are vital in maintaining the encrypted data’s reliability. By confirming the validity of these certificates, both entities can be confident that the data remains untouched during its transfer. This confidence stems from digital signatures, formed using the sender’s unique key and authenticated with the related public key.
Moreover, digital certificates provide a mechanism for establishing a secure and reliable identification system. By associating a digital certificate with a specific entity, such as an individual or an organization, confirming the identity of the parties involved in the communication becomes possible. This is particularly important in scenarios where sensitive information is exchanged, as it helps prevent impersonation and certifies that only authorized individuals can access the data.
The Process of Data Encryption Using Digital Certificates
The process of data encryption using digital certificates involves multiple steps. Firstly, the sender generates a symmetric encryption key for the communication session. The symmetric key ensures efficient encryption and decryption of data, as it uses the same key for both processes.
The sender then encrypts the symmetric key using the recipient’s public key from their digital certificate. This encrypted symmetric key and the encrypted data are sent to the recipient. Upon receiving the encrypted data and symmetric key, the recipient decrypts the symmetric key using the private key associated with their digital certificate.
With the decrypted symmetric key, the recipient can decrypt the original data, ensuring secure and confidential communication. This process emphasizes the importance of digital certificates in facilitating the secure exchange of encryption keys, ensuring data remains protected throughout its journey.
It is worth noting that digital certificates are used for encryption in communication between two parties and in other scenarios where data security is paramount. For example, digital certificates are widely used in e-commerce transactions to secure online payments. By encrypting sensitive financial information using digital certificates, customers can confidently make purchases online, knowing their data is protected from prying eyes.
In addition, digital certificates are also essential in securing network communications. In large organizations, digital certificates authenticate and encrypt data exchanged between servers, ensuring that sensitive information, such as employee records or customer data, remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
Furthermore, digital certificates have become an integral part of securing cloud-based services. With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, digital certificates are crucial in launching trust between cloud service providers and their customers. By verifying the authenticity of the digital certificates, customers can be confident that their data is stored securely in the cloud and that only authorized parties have access to it.
In conclusion, digital certificates are a fundamental data encryption component, providing the necessary trust and security for secure communication. By verifying the authenticity of certificates, exchanging public keys, and encrypting data, digital certificates confirm that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access. Whether in online transactions, network communications, or cloud-based services, digital certificates are vital in safeguarding data in the digital age.
Types of Digital Certificates

SSL Certificates
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates are widely used to secure online transactions and protect sensitive info such as credit card details. Websites with SSL certificates ensure secure communication between the user’s browser and the server, encrypting data during transmission.
Code Signing Certificates
Code signing certificates are essential for software developers to guarantee their code’s authenticity and integrity. By digitally signing their code using a code signing certificate, developers secure their software against tampering and unauthorized modifications.
Email Certificates
Email certificates serve as a means of authenticating the sender of an email and ensuring the email’s integrity. By digitally signing the email using their email certificate, senders can prove their identity and protect the email’s contents from modification.
Misconceptions About Digital Certificates and Data Encryption
Common Misunderstandings
Despite the benefits and widespread usage of digital certificates, certain misconceptions persist. One common misunderstanding is that digital certificates provide encryption alone, without relying on other encryption mechanisms. However, digital certificates establish trust and facilitate encryption rather than directly performing encryption.
Clarifying the Truth
It is essential to understand that while digital certificates enable secure communication through encryption, they do not provide encryption on their own. Digital certificates use encryption algorithms to ensure data confidentiality, authenticity, and integrity. Without encryption algorithms, digital certificates alone cannot provide encryption.
The Future of Digital Certificates and Data Encryption
Emerging Trends
The future of digital certificates and data encryption holds exciting possibilities. One emerging trend is the adoption of quantum-resistant encryption algorithms. As quantum computing advancements continue, traditional encryption algorithms may become vulnerable. Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms aim to provide enhanced security and mitigate the risks of quantum computers.
Predictions for the Future of Data Encryption
Experts predict that data encryption will become even more crucial as technology advances. With the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), where numerous interconnected devices exchange sensitive data, robust encryption mechanisms will be essential to protect the massive amounts of information generated by these devices.
Additionally, integrating encryption into various aspects of daily life, such as smart homes and autonomous vehicles, will require innovative approaches to ensure data privacy and security. Emerging technologies like blockchain also hold promise in enhancing data encryption and authentication.
Key Takeaways
- Digital Certificates and Encryption: Digital certificates establish trust in the digital realm, enabling encryption to ensure data security during communication.
- Components of Digital Certificates: They contain the holder’s public key personal information and are issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- Protection Mechanism: Digital certificates safeguard sensitive information from interception and potential threats by facilitating encryption and authentication.
- Misconceptions: It’s essential to understand that while digital certificates play a role in the encryption process, they don’t directly encrypt data.
- Future Trends: With technological advancements, encryption and digital certificates’ significance is set to grow, especially with the rise of quantum computing and the proliferation of IoT.
FAQs
What is a digital certificate?
A digital certificate is an electronic document necessary for a public key to an entity, serving as a digital ID card that verifies the authenticity and integrity of the certificate holder.
How do digital certificates contribute to data security?
Digital certificates facilitate secure communication over the internet by providing the means for encryption and decryption of data, ensuring data remains confidential and is not tampered with during transit.
Do digital certificates directly encrypt data?
No, digital certificates themselves do not encrypt data. Instead, they provide the means to establish trust, facilitating the encryption process using associated keys.
What role do Certificate Authorities (CA) play?
CAs are trusted entities responsible for verifying the identity of certificate holders and issuing digital certificates, ensuring the information within the certificate is accurate and reliable.
What are the future trends for digital certificates and data encryption?
The future holds the adoption of quantum-resistant encryption algorithms, the significance of encryption in the Internet of Things (IoT), and integration into various aspects of daily life, like smart homes and autonomous vehicles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital certificates play a fundamental role in enabling the encryption of data, ensuring secure communication, and protecting sensitive information. Understanding the function and significance of digital certificates, debunking misconceptions, and staying updated on emerging trends can help navigate the ever-evolving landscape of data encryption and security.
