Cellphone vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses in the security of mobile devices that can be exploited by malicious actors or software, posing risks to data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Common vulnerabilities include operating system flaws, outdated software, malware, insecure connections, social engineering attacks, weak passwords, lost or stolen devices, and more. Device encryption is a crucial security feature that converts cellphone data into an unreadable format, protecting personal information and preventing unauthorized access. It works by using encryption algorithms and a decryption key, ensuring data security even if the device is lost or stolen.
What Are Cell Phone Vulnerabilities?
Cellphone vulnerabilities refer to weaknesses, flaws, or susceptibilities in the security of mobile devices that can be exploited by malicious individuals or software to gain unauthorized access or compromise the device’s integrity. These vulnerabilities can pose significant risks to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data and functionality stored on or accessed through cell phones.
Common Cell phone Vulnerabilities:
- Operating System Vulnerabilities: Mobile operating systems like Android and iOS may have security flaws that can be exploited by hackers. These vulnerabilities can lead to various types of attacks, such as remote code execution or privilege escalation.
- Outdated Software: Failure to update the device’s operating system, applications, or firmware can leave it susceptible to known vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals often target devices with outdated software because they are easier to compromise.
- Malware and Spyware: Malicious software, including viruses, Trojans, and spyware, can infect cell phones, compromising their security and potentially stealing sensitive information or monitoring user activities.
- Insecure Connections: Inadequate encryption or the use of unsecured Wi-Fi networks can expose cellphone communications to eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle attacks, where attackers intercept and manipulate data.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Attackers often use social engineering techniques to trick users into divulging sensitive information or installing malicious software. Phishing attacks via email, text messages, or fake websites can target cellphone users.
- App Permissions: Some apps request excessive permissions, allowing them to access sensitive data or control various device functions. Granting these permissions without scrutiny can lead to privacy and security risks.
- Weak or Default Passwords: Many users use weak or default passwords for their devices or online accounts, making it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Lost or Stolen Devices: Physical theft or loss of a cellphone can expose the data stored on the device if it lacks adequate security measures like PINs, passwords, or biometric authentication.
- Inadequate Backup and Recovery Plans: Without proper backup and recovery solutions in place, users risk losing their data permanently in the event of device compromise or loss.
- Bluetooth and NFC Vulnerabilities: Wireless technologies like Bluetooth and Near Field Communication (NFC) can be exploited by attackers to initiate unauthorized connections or transfer malicious files.
- Third-Party App Stores: Downloading apps from unofficial sources outside of official app stores can expose users to the risk of downloading malicious or compromised applications.
- Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: These are undisclosed vulnerabilities that are not yet known to the software vendor or the public. Attackers may exploit zero-day vulnerabilities before patches or updates are available.
Understanding Device Encryption
Device encryption is a security feature that converts the data on your cellphone into an unreadable format for anyone who doesn’t have the decryption key. Essentially, it scrambles your data, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized users to access your personal information. It’s like having a secret code that only you possess to unlock the treasure chest of your phone’s data.
How Does Device Encryption Work?
Device encryption uses complex algorithms to transform your data into a jumble of characters that resemble gibberish without the decryption key. When you unlock your phone with your PIN, password, or biometric data (like fingerprints or facial recognition), it uses this key to decrypt your data on the fly, making it accessible to you but still safeguarded from prying eyes.
The Importance of Device Encryption
Protecting Your Personal Information
One of the primary reasons to use device encryption is to safeguard your personal information. Your cellphone contains a wealth of sensitive data, including text messages, photos, emails, and more. Without encryption, this information is vulnerable to theft, putting your privacy at risk.
Preventing Unauthorized Access
Imagine losing your cell phone or having it stolen. Without device encryption, anyone who gets their hands on your device can easily access your personal data. Device encryption acts as a barrier, ensuring that even if your phone falls into the wrong hands, your information remains secure.
How to Enable Device Encryption on Your Phone?
Check if Your Device Supports Encryption
Not all cell phones support device encryption, so the first step is to check if your device is compatible. Most modern smartphones do, but it’s essential to verify.
Set a Strong Lock Screen Password
Device encryption relies on your lock screen password, PIN, or biometric authentication to work. Ensure you have a strong, unique password that’s difficult for others to guess.
Enable Encryption in Your Settings
On most smartphones, you can enable encryption in the security settings. Simply navigate to your device’s settings, look for “Security” or “Privacy,” and find the option to enable encryption. Follow the on-screen instructions, and your phone will begin the encryption process.
Other Methods to secure Cell phones from vulnerabilities:
Keep Your Device Software Up-to-Date
Mobile operating system updates often include security patches to fix vulnerabilities. Make sure your device’s operating system (e.g., Android or iOS) is set to automatically update, or regularly check for updates manually.
Download Apps from Trusted Sources
Download apps only from official app stores like the Apple App Store or Google Play Store. These platforms have security measures in place to screen for potentially harmful apps.
Before installing an app, review the permissions it requests. If an app asks for unnecessary access to your data or device features, consider whether it’s worth installing. Deny permissions if they seem excessive.
Secure Your Device with Strong Authentication
Set a strong, unique password or passcode for your device. Avoid easily guessable codes like “1234” or “password.” Consider using a passphrase with a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
Whenever possible, use biometric authentication methods like fingerprint recognition or facial recognition. These provide an additional layer of security and convenience.
Be Cautious with Public Wi-Fi
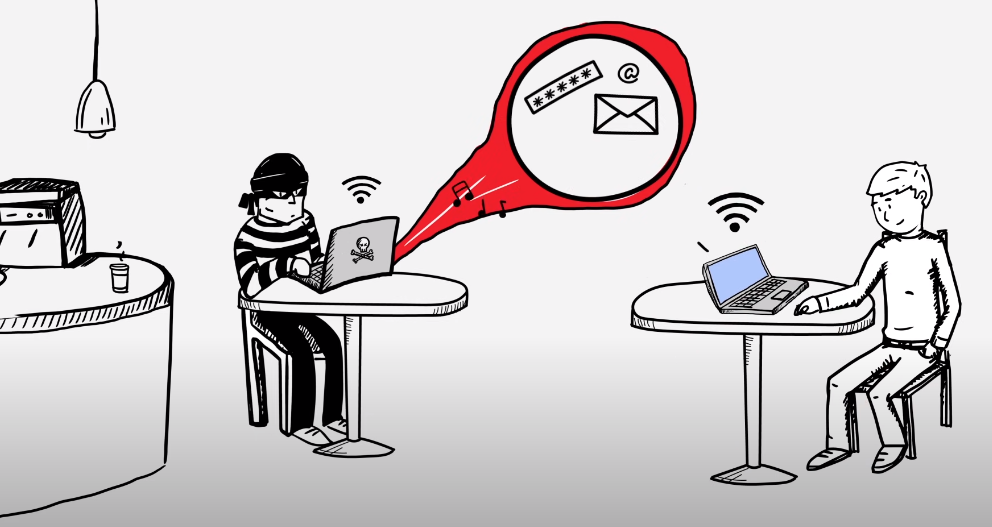

When connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, avoid open, unsecured networks. Instead, use virtual private networks (VPNs) to encrypt your internet connection and protect your data from potential eavesdropping.
Conclusion:
Understanding and addressing cellphone vulnerabilities is necessary. where our mobile devices store a wealth of personal and sensitive information. From operating system vulnerabilities to the risks posed by outdated software, malware, and phishing attacks, users must be vigilant in protecting their smartphones. Device encryption emerges as a crucial line of defense, ensuring that even in the face of loss or theft, our personal data remains shielded from prying eyes.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is device encryption available on all cell phones?
Not all cell phones support device encryption. It’s essential to check if your device is compatible. Most modern smartphones offer this feature, but it’s always wise to verify.
How do I enable device encryption on my cellphone?
To enable device encryption, go to your device’s settings, find “Security” or “Privacy,” and look for the encryption option. Follow the on-screen instructions, and your phone will begin the encryption process.
FAQ 6: Does device encryption affect my phone’s performance?
Answer: Device encryption can have a minor impact on your phone’s performance, but it’s usually negligible on modern smartphones. The added security outweighs any performance concerns.
What if I forget my lock screen password or lose my decryption key?
If you forget your password or lose your decryption key, recovering your data can be challenging. It’s crucial to keep a backup of your data and store your encryption key securely to avoid such situations.
