The layer in the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model used to encrypt data is the Presentation Layer. The Presentation Layer is the sixth layer in the OSI model. It is responsible for the translation, encryption, and compression of data to ensure it is in a format that the application layer at the receiving end can understand.
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework to understand how different networking protocols and technologies work together to enable communication between devices. It consists of seven layers, each responsible for specific tasks in the data transmission process. Encryption, a crucial aspect of data security, is employed at a specific layer in the OSI model. In this article, we explore the layer responsible for data encryption and delve into the importance of encryption in securing data during its journey across networks.
Understanding the OSI Model
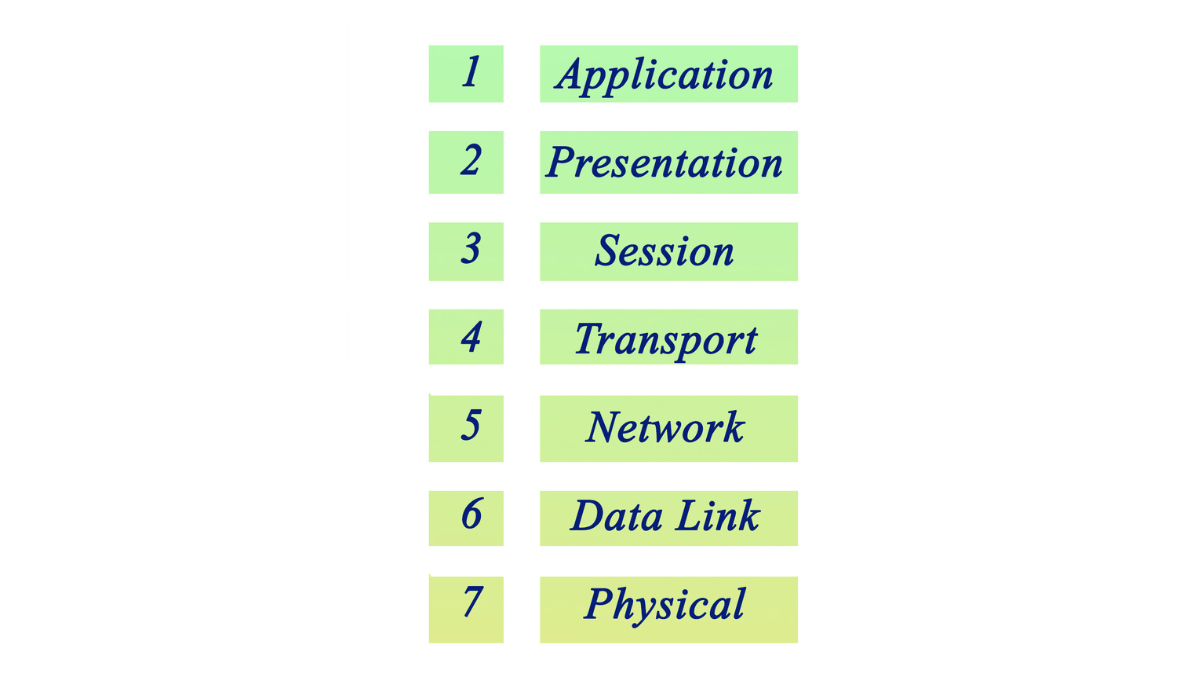
Before we dive into the layer responsible for data encryption, let’s briefly review the seven layers of the OSI model:
-
Physical Layer (Layer 1)
The Physical Layer deals with the physical connection between devices and the transmission of raw binary data over a physical medium, such as cables or wireless signals.
-
Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
The Data Link Layer is responsible for the reliable transmission of data frames between devices connected to the same network segment.
-
Network Layer (Layer 3)
The Network Layer handles the routing of data packets between different networks, ensuring they reach their intended destinations.
-
Transport Layer (Layer 4)
The Transport Layer manages end-to-end device communication, correcting errors and controlling flow.
-
Session Layer (Layer 5)
The Session Layer establishes, maintains, and terminates communication sessions between applications on different devices.
-
Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
The Presentation Layer is responsible for data translation, encryption, and compression to ensure system compatibility.
-
Application Layer (Layer 7)
The Application Layer is where user applications like web browsers and email clients interact with the network.
The Encryption Layer: Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
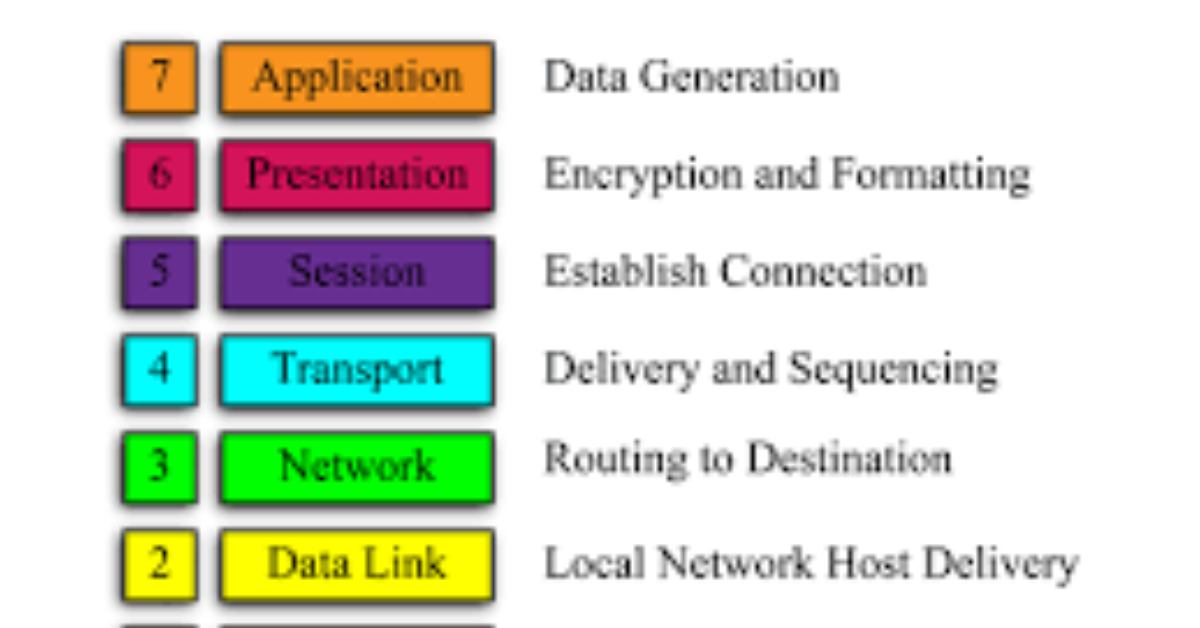
The Presentation Layer (Layer 6) is designated for data encryption among the seven OSI model layers. This layer handles the translation and encryption of data before it is transmitted to the destination. Encrypting data at this layer ensures sensitive information remains secure across various networks and devices.
How does it work?
Encryption at the Presentation Layer involves transforming the data into an encrypted format using algorithms and cryptographic keys. This process ensures that unauthorized entities cannot interpret the data even if they manage to intercept it while traversing the network. Once the encrypted data reaches its destination, the Presentation Layer on the receiving end decrypts it back into its original format so the application can process it.
By incorporating encryption at the Presentation Layer, network communications can remain secure and safeguarded against potential eavesdropping and unauthorized access. It adds a layer of protection to sensitive data and plays a vital role in overall data security within a networked environment. However, it’s essential to note that encryption at the Presentation Layer is just one aspect of a comprehensive data security strategy, and other layers in the OSI model also contribute to creating a robust and secure network infrastructure.
The Importance of Data Encryption
Data encryption is paramount in today’s digital world, where cyber threats are ever-evolving. Here are some key reasons why encryption is crucial:
- Data Privacy and Confidentiality
Encryption ensures data privacy and confidentiality by making it inaccessible to unauthorized individuals, even if they manage to gain access to the data.
- Protection Against Data Breaches
Encrypted data remains secure in the event of a data breach, reducing the risk of data loss and potential damage to an organization’s reputation.
- Compliance with Regulations
Many industries and jurisdictions require data encryption to comply with data protection and privacy regulations.
Encryption provides a secure means of transmitting sensitive data over unsecured networks like the Internet.
- Safeguarding Intellectual Property
Encrypting intellectual property and sensitive business information prevents unauthorized access and theft.
Key Takeaways
- The Presentation Layer (Layer 6) in the OSI model is responsible for data encryption during transmission, ensuring data security and confidentiality.
- Encryption involves converting data into ciphertext using cryptographic algorithms, making it unreadable to unauthorized users without the decryption key.
- Data encryption is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information, preventing breaches, and complying with data protection regulations.
- By encrypting data, organizations can protect intellectual property, secure data transmission, and maintain the privacy of user information.
- Embracing encryption is essential in the digital age to mitigate cyber threats and preserve the integrity of valuable data.
FAQs
How does encryption protect data during transmission?

Encryption converts data into an unreadable format (ciphertext), ensuring that the information remains secure and confidential even if intercepted.
What is the role of the Presentation Layer (Layer 6) in data encryption?
The Presentation Layer handles data encryption and translation to ensure compatibility between different systems and devices.
Can encrypted data be decrypted without the proper key?
No, encrypted data can only be decrypted with the correct decryption key, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to access the original information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the layer in the OSI model used to encrypt data is the Presentation Layer (Layer 6). Data encryption is vital to data security, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected and confidential during transmission. Organizations and individuals can use encryption at this layer to safeguard their data from potential cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Data security is an ongoing challenge in the digital age, and encryption plays a crucial role in mitigating risks and preserving the integrity of valuable information. As technology advances, the importance of data encryption will only grow, making it an essential practice for individuals and organizations.
