Introduction
Google Drive is one of the most popular cloud storage services out there, but when it comes to data privacy and security, users should be wary. While Google claims that all files uploaded to its servers are encrypted using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), this encryption only applies while the data is in transit or being stored on Google’s servers. It does not include end-to-end encryption, which means that if someone gains access to a user’s account, they can view any unencrypted files.
This lack of end-to-end encryption raises concerns about data security for businesses and individuals alike. If sensitive information such as financial records or personal details falls into the wrong hands, it can result in financial losses or identity theft. This is why it’s important for users to take additional steps to secure their data by enabling two-factor authentication and regularly updating their passwords.
Understanding Encryption
What Is Encryption?

Encryption is a process of encoding messages, files, or any other form of digital data so that it can only be read by authorized parties. It is an essential security measure that protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensures privacy. Encryption works by transforming the original message into an unreadable format using mathematical algorithms and a secret key.
Types Of Encryption
There are many types of encryption, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The most popular forms of encryption are symmetric-key encryption, public-key encryption, and hashing.
Symmetric-key encryption involves using the same key to both encrypt and decrypt data. This type of encryption is fast, but it can be less secure than other methods because if someone gets hold of the key they can easily read the encrypted data.
Public-key encryption uses two keys: a private key that only the owner knows and a public key that anyone can use to encrypt messages or files for the owner. This method is more secure than symmetric-key encryption because even if someone intercepts an encrypted message, they would not have access to the private key needed to decrypt it.
Hashing is another form of encryption which creates a unique digital “fingerprint” for a piece of data by running it through an algorithm that generates a fixed-length string of characters known as a hash value. While hashing cannot be used for decryption purposes like traditional forms of cryptography, it has useful applications in verifying file integrity (ensuring that no one has tampered with or modified your files) and password storage (by storing hashed versions instead of plain-text passwords).
Google Drive’s Encryption Methods
Google Drive’s Encryption Protocols
Google claims that all files stored on its Drive platform are encrypted at rest using standard AES 128-bit encryption. This means that the data is scrambled and unreadable without proper decryption keys. Additionally, all files uploaded or downloaded over Google servers are also encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols to prevent interception or eavesdropping.
Client-Side Encryption And Server-Side Encryption
Client-side encryption involves encrypting data on the client’s device before it is transmitted to a server. This method ensures that only the client has access to the decryption key, making it difficult for anyone else to access the data. In contrast, server-side encryption involves encrypting data after it has been uploaded to a server. The decryption key is stored on the server, meaning anyone with access to the server can potentially decrypt and view the data.
Google Drive uses server-side encryption by default, which means that although your files are encrypted while in transit and at rest on their servers, Google still holds the keys necessary for decrypting them if required by law enforcement or government authorities.
Security Features Of Google Drive’s Encryption
All data stored on Google Drive is encrypted in transit using SSL/TLS protocols, which ensures that your files are protected while they’re being uploaded or downloaded to and from the cloud storage.
Google Drive uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption to secure your files at rest. This means that each file is encrypted with a unique key that only you have access to, making it nearly impossible for anyone else to decrypt or access your files without authorization.
Furthermore, Google provides additional security measures such as multi-factor authentication and account recovery options in case you ever lose access to your account. With these features in place, users can be confident that their sensitive information is being stored securely on the cloud platform.
How Secure Is Google Drive?
While Google has stated that they use encryption technology to protect user data on their servers, it is important for users to also take necessary precautions such as using strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication. Additionally, regular monitoring and updates of security settings can help reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
One of the primary concerns with Google Drive is the potential security breach that could result in unauthorized access to sensitive data. While Google claims to encrypt all user data stored on its servers, there is still a risk that hackers or malicious insiders can gain access.
Another concern when using Google Drive is the privacy of your information. Although Google states that it does not sell or share user data, it does use automated systems to analyze content for advertising purposes. This means that anything you store on Google Drive, including personal files and documents, may be scanned by these systems and used to target you with personalized ads.
Another vulnerability of using Google Drive is the risk of human error or accidental deletion of important files. While there are measures in place to help recover deleted files from the trash folder within 30 days, it’s important for users to regularly back up their data elsewhere as an extra precaution against loss or corruption.
Third-Party Access To Google Drive Data
Third-party apps and services can provide additional functionality, but they can also pose a security risk by accessing sensitive information.
While Google Drive itself is encrypted, third-party applications that have been granted permission to access the user’s data may not have the same level of encryption. This means that sensitive files and information could potentially be accessed by unauthorized parties.
Additionally, it can be difficult for users to determine which third-party applications have access to their Google Drive data. With so many apps available in the marketplace, it can be hard to keep track of who has permission to view or edit your files. Users should regularly review their connected apps list and revoke permissions from any apps they no longer use or trust.
To mitigate these concerns, users should only grant access to trusted third-party applications that are known for their strong security practices. It is also important for users to enable two-factor authentication on their account and use a unique password for each application they connect with Google Drive.
Impact Of Encryption On Google Drive Performance
Encryption And Its Impact On Google Drive Performance
Encryption offers numerous benefits, including enhanced security and privacy, but it can also impact the performance of certain applications like Google Drive. When we talk about encryption in Google Drive, we refer to its capability to encrypt data both in transit and at rest using industry-standard protocols such as TLS and AES.
However, this encryption process takes up significant computing resources and can result in slower upload/download speeds for large files. Moreover, some users have reported issues with syncing their files due to encryption-related errors. As a result, many people choose not to enable full-disk encryption or selectively encrypt only sensitive files when using Google Drive.
Factors Affecting Google Drive’s Encryption Speed And Processing Time
One major factor is the size of the files being encrypted or decrypted. Larger files tend to take longer to encrypt or decrypt compared to smaller ones. Another factor affecting Google Drive’s encryption speed and the processing time is the device used for accessing your account. Older devices with slow processors may experience slower encryption times than newer devices with faster processors. Additionally, network bandwidth can also have an impact on encryption speed since it affects how quickly data can be transferred between devices.
Balancing Data Security And Performance On Google Drive
Balancing data security and performance on Google Drive requires careful consideration of the types of files being stored and how they are accessed by different users. Users must be aware of the risks associated with storing sensitive or confidential information on Google Drive and take steps to protect their files accordingly. This includes using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, restricting file-sharing permissions, and regularly monitoring account activity.
Alternative Cloud Storage Options
Comparing Google Drive With Other Cloud Storage Providers
Google Drive uses a combination of AES-128 and RSA-2048 encryption for file transfers and at rest data. While this may sound secure, there is still a risk of unauthorized access by Google employees since they have access to user data.
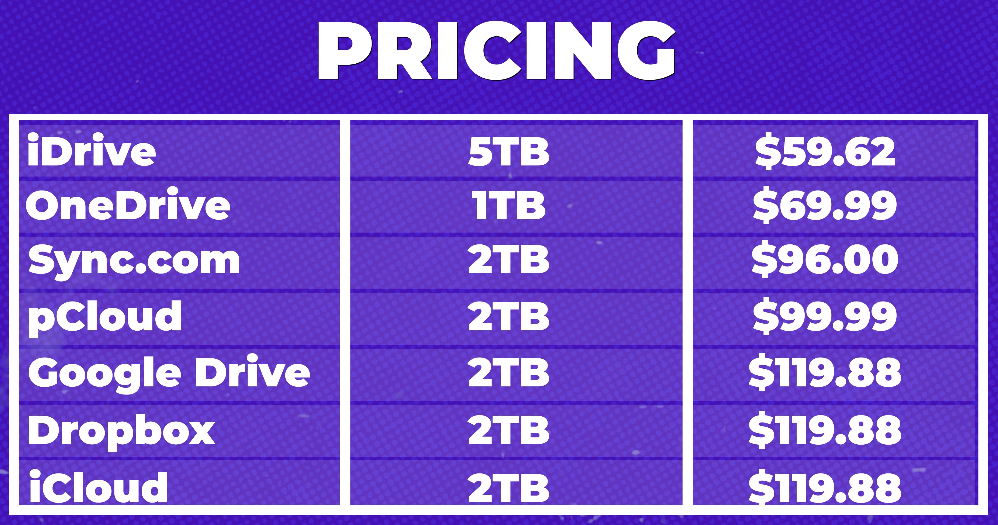
Other cloud storage providers like Sync.com use end-to-end encryption where only the user has access to their files through their private key. This ensures that no one else can view or tamper with their files, including the provider’s employees. Another advantage that Sync.com has over Google Drive is that all files are stored on Canadian servers which are protected under Canada’s privacy laws.
Encryption Policies And Standards Of Other Cloud Storage Providers
Other major cloud storage providers such as Dropbox and Microsoft OneDrive also use encryption to protect user data. Dropbox uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols for data transmission and stores files with AES-256 bit encryption in its servers. Meanwhile, OneDrive utilizes BitLocker drive encryption for all user files stored in its servers.
It is important to note that while these companies use encryption techniques to protect user data, they do retain certain access rights over your information according to their terms of services.
Choosing The Best Cloud Storage Provider For Your Data Security Needs
If privacy is a top priority for you, then Google Drive may not be the best option. Instead, consider using cloud providers that use client-side encryption such as Sync.com or pCloud. With client-side encryption, only you hold the key to decrypt your data meaning that even if someone gains access to the server where your files are stored they won’t be able to view them without having access to your decryption key.
Other important factors when choosing a cloud storage provider include whether they offer two-factor authentication and if they have a history of data breaches or security vulnerabilities.
FAQs
Can I Use Third-Party Encryption Tools To Secure My Google Drive Data?
Using third-party encryption tools can be an excellent way to enhance the security of your Google Drive data. By using a third-party encryption tool, you can add another layer of protection that ensures your files remain secure even in the event of a breach.
How Can I Protect My Google Drive Data From Data Breaches?
To protect your data from unauthorized access, make sure you use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication in your Google account.
In addition to securing your account with strong passwords and two-factor authentication, it’s also important to regularly review and manage the permissions granted to different users or applications that have access to your Google Drive files. You should only grant permission to trusted individuals or organizations that have a need for the information stored in your drive.
Does Google Drive’S Encryption Impact Its Performance?
Google Drive uses industry-standard AES-256-bit encryption to secure user data both when it’s at rest (stored on servers) and when it’s in transit between devices or networks. While this level of security does require more computing power than unencrypted files would need, Google has optimized its platform to ensure there’s no noticeable difference in speed or responsiveness when working with encrypted files versus unencrypted ones.
Conclusion
While Google Drive encryption may provide some level of security for users’ data, it is not foolproof. The fact that Google has access to the encryption keys means that their employees could potentially access users’ files. Additionally, there are ways for hackers to bypass the encryption and gain access to sensitive information.
