Introduction

A Social Security Number (SSN) is a unique identifier assigned to individuals by the Social Security Administration (SSA) in the United States. It is an important piece of personal information used for various purposes, including employment, taxation, and government benefits.
Qualitative Vs Quantitative Data
Qualitative data refers to non-numerical data that is descriptive. It is often used to gain insights into people’s attitudes, beliefs, and opinions. Examples of qualitative data include interviews, surveys, and focus groups.
Quantitative data, on the other hand, refers to numerical data that can be measured and analyzed statistically. It is often used to quantify trends, patterns, and relationships. Examples of quantitative data include sales figures, test scores, and demographic information.
Qualitative data is descriptive and provides insights into attitudes, beliefs, and opinions. It is often collected through interviews, surveys, and focus groups. On the other hand, quantitative data is numerical and can be measured and analyzed statistically. It is used to quantify trends, patterns, and relationships and includes data such as sales figures, test scores, and demographic information. Both qualitative and quantitative data are important in research and can be used to gain a comprehensive understanding of a given topic.
Understanding Qualitative Data
Qualitative data is non-numerical and is used to capture subjective information such as opinions, attitudes, and experiences. It is often collected through open-ended questions, observations, and document analysis. Qualitative data is useful in providing rich and detailed insights into a particular phenomenon and can help researchers understand the context and complexity of a given situation. However, because it is subjective, it can be difficult to analyze and draw conclusions from. Therefore, it is often used in conjunction with quantitative data to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Understanding Quantitative Data
Quantitative data, on the other hand, is numerical data that can be measured and analyzed using statistical methods. It is objective and can provide precise and accurate information about a particular phenomenon. Quantitative data can be collected through surveys, experiments, and other methods that involve numerical measurements. One advantage of quantitative data is that it can be easily analyzed and interpreted using statistical software. This allows researchers to identify patterns and relationships between variables, and to draw conclusions based on empirical evidence. However, quantitative data may not provide the same level of detail and context as qualitative data, and may not capture the subjective experiences of individuals.
In summary, both qualitative and quantitative data have their strengths and weaknesses and can be used together to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular phenomenon. As a writing assistant, it is important to consider the type of data that is most appropriate for a given research question or topic and to use it effectively in your writing.
Is Social Security Number Categorical Data?
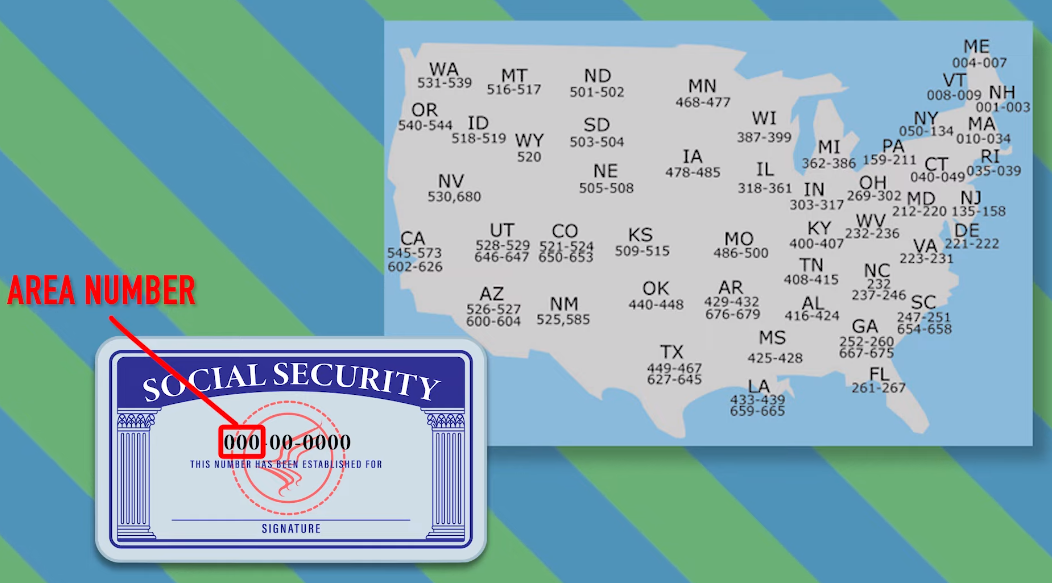
Yes, social security numbers (SSNs) are considered categorical data. Categorical data refers to data that can be sorted into categories or groups based on their characteristics. SSNs are assigned to individuals by the government and are used to identify and track individuals for various purposes such as taxation, employment, and social security benefits. SSNs are typically composed of nine digits and are unique to each individual, making them categorical data.
Categorizing SSNs: Qualitative Or Quantitative?
Categorizing SSNs as qualitative or quantitative depends on the context in which they are being analyzed. In terms of their numerical values, SSNs are quantitative data because they consist of a series of digits that can be measured and compared mathematically. However, in most cases, SSNs are treated as categorical data because they are used to sort individuals into distinct groups based on their unique identification numbers.
Therefore, it is more common to categorize SSNs as qualitative data, which refers to data that can be sorted into categories or groups based on their characteristics, rather than quantitative data, which refers to data that can be measured and expressed numerically.
The Duality Of SSNs: Qualitative And Quantitative Aspects

It is important to note the duality of SSNs as both qualitative and quantitative data. As a writing assistant, I can help you further explore this topic or assist in any writing tasks related to it. Just let me know how I can be of assistance.
Factors Influencing The Classification Of SSNs
Several factors can influence the classification of SSNs. One factor is the purpose for which the SSN is being used. For example, if the SSN is being used for research purposes, it may be classified differently than if it is being used for administrative purposes. Another factor is the context in which the SSN is being used. For example, if the SSN is being used in a medical context, it may be classified differently than if it is being used in a financial context.
The characteristics of the individuals or groups associated with the SSN can also influence its classification. For example, if the SSN is associated with a vulnerable population, such as children or the elderly, it may be classified differently than if it is associated with a general population.
Best Practices For SSN Data Analysis
When analyzing SSN data, it is important to follow best practices to protect the privacy and security of individuals. Here are some tips:
- Minimize the collection of SSNs: Only collect SSNs when necessary and limit access to those who need it.
- Use encryption: When storing SSNs, use encryption to protect against unauthorized access.
- Use de-identification techniques: If possible, remove SSNs from data sets or use de-identification techniques to mask them.
- Implement access controls: Limit access to SSN data to only those who need it for their job duties.
- Train employees: Educate employees on the importance of protecting SSN data and the proper handling of sensitive information.
By following these best practices, you can help ensure the privacy and security of SSN data.
Conclusion
In conclusion, protecting your Social Security Number (SSN) is crucial to safeguarding your personal and financial information. We discussed various ways to protect your SSN, such as avoiding sharing it unnecessarily, using secure websites for online transactions, and regularly checking your credit report. It is also essential to be aware of potential scams and phishing attempts that may try to obtain your SSN. By following these tips, you can minimize the risk of identity theft and financial harm. SSNs are generally considered to be qualitative data because they are not numerical values that can be measured or counted. Instead, they are unique identifiers that are used to distinguish one individual from another. However, in some cases, SSNs may be treated as quantitative data if they are used for statistical analysis or other numerical calculations. Ultimately, the classification of SSNs as qualitative or quantitative data may depend on the specific context in which they are being used.
Understanding the duality of SSNs as both qualitative and quantitative data is important in data analysis because it can impact the methods and techniques used to analyze and interpret the data. If SSNs are treated solely as qualitative data, certain statistical analyses may not be appropriate or accurate. On the other hand, if SSNs are treated solely as quantitative data, important contextual information about individuals may be lost. It is also important to consider the ethical and legal implications of using SSNs in data analysis. SSNs are considered sensitive personal information and must be protected to prevent identity theft and other forms of fraud. Therefore, data analysts must be mindful of the risks associated with using SSNs in their analyses and take appropriate measures to safeguard the data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A. Is A Social Security Number Considered Personal Data?
Yes, a Social Security Number (SSN) is considered personal data as it is a unique identifier assigned to individuals by the government and is used to track their earnings and benefits. It is considered highly sensitive information as it can be used for identity theft and other fraudulent activities. It is important to protect SSN data and handle it with care.
B. Can SSNs Be Used For Statistical Analysis?
Yes, SSNs can be used for statistical analysis, but only in a de-identified or anonymized form. This means that the SSN is removed or replaced with a unique identifier that cannot be traced back to an individual. This is important to protect the privacy of individuals and comply with data protection laws. It is also important to ensure that any analysis using SSN data is conducted in a secure environment and with appropriate safeguards in place to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure of the data.
C. How Are SSNs Used In Identity Verification?
SSNs are commonly used in identity verification as a way to confirm an individual’s identity. For example, when applying for a loan or credit card, the lender may ask for the applicant’s SSN to verify their identity and check their credit history. Similarly, when applying for a job, the employer may ask for the applicant’s SSN to conduct a background check and verify their employment eligibility. However, it is important to note that the use of SSNs for identity verification should be done carefully and securely to prevent identity theft or fraud.
D. Are There Alternative Identification Systems To SSNs?
Yes, there are alternative identification systems to SSNs. Some organizations may use employee or customer identification numbers instead of SSNs. Additionally, some countries have national identification systems that are used for various purposes, such as healthcare and voting. However, the use of any identification system should still be done with caution and proper security measures to protect personal information.
E. What Are The Potential Risks Of Sharing SSNs?
Sharing SSNs can pose several potential risks, including identity theft, fraud, and financial harm. If a person’s SSN falls into the wrong hands, it can be used to open fraudulent accounts, obtain loans, and even file false tax returns. It can also be used to access sensitive information, such as medical records and credit history. Additionally, if a company or organization experiences a data breach and SSNs are compromised, it can have significant consequences for those affected, including damage to their credit score and financial stability.
F. How Can Individuals Protect Their SSN Data From Identity Theft?
There are several steps individuals can take to protect their SSN data from identity theft:
- Keep your SSN private: Only share your SSN when it is necessary, such as when applying for credit or employment.
- Secure your documents: Store your SSN card and other sensitive documents in a secure location, such as a locked safe or filing cabinet.
- Monitor your accounts: Regularly review your bank and credit card statements for any unauthorized charges or activity.
- Use strong passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for all of your online accounts, and never use the same password for multiple accounts.
- Be cautious online: Be wary of unsolicited emails or phone calls asking for your SSN or other personal information.
- Freeze your credit: Consider placing a credit freeze on your accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Check your credit report: Check your credit report regularly for any suspicious activity or accounts opened in your name.
By taking these steps, individuals can help protect their SSN data from identity theft and minimize the risk of financial and personal harm.
