IPsec Basics: A Primer
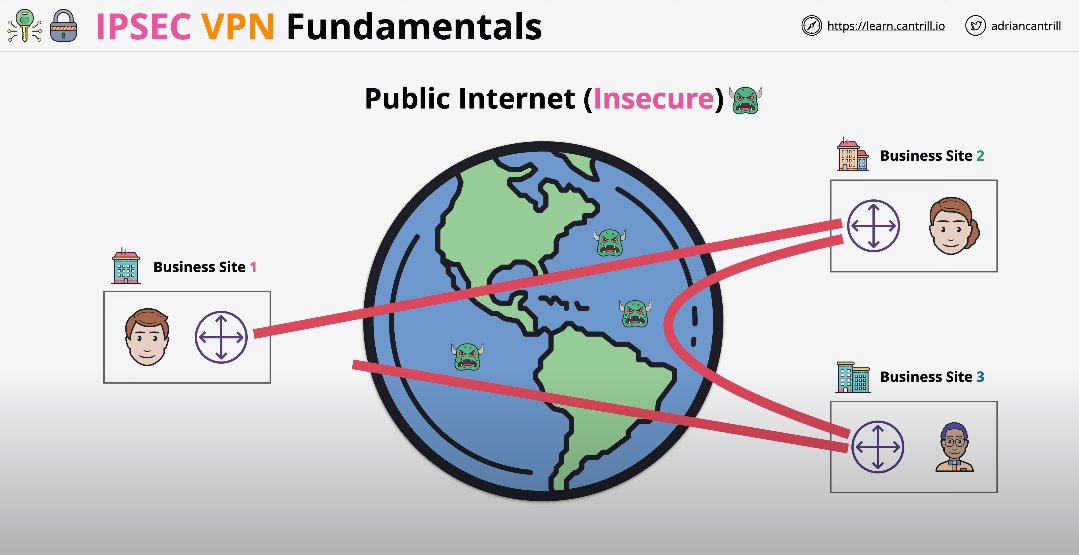
IPsec, short for Internet Protocol Security, is a protocol suite used to secure internet communication by authenticating and encrypting IP packets. It provides a secure channel for data transmission between two networked devices, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the data.IPsec operates at the network layer of the OSI model and can be implemented in both IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
Key Components of IPsec Architecture
1. Security Associations (SAs): IPsec uses SAs to establish and manage secure communication between two entities. SAs define the security parameters, such as encryption algorithms, integrity algorithms, and key exchange methods.
2. Authentication Header (AH): AH provides data integrity and authentication for IP packets. It ensures that the data has not been modified during transit and verifies the identity of the sender.
Benefits of Using IPsec for VPN Connections
1. Data Confidentiality: IPsec provides encryption techniques to ensure that the data transmitted over the VPN connection remains confidential. This prevents unauthorized access and eavesdropping on sensitive information.
2. Data Integrity: IPsec uses integrity algorithms to verify that the data has not been tampered with during transmission. This ensures that the received data is authentic and has not been modified or altered.
3. Data Authentication: IPsec provides authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of the communicating entities.
IPsec Modes Explained
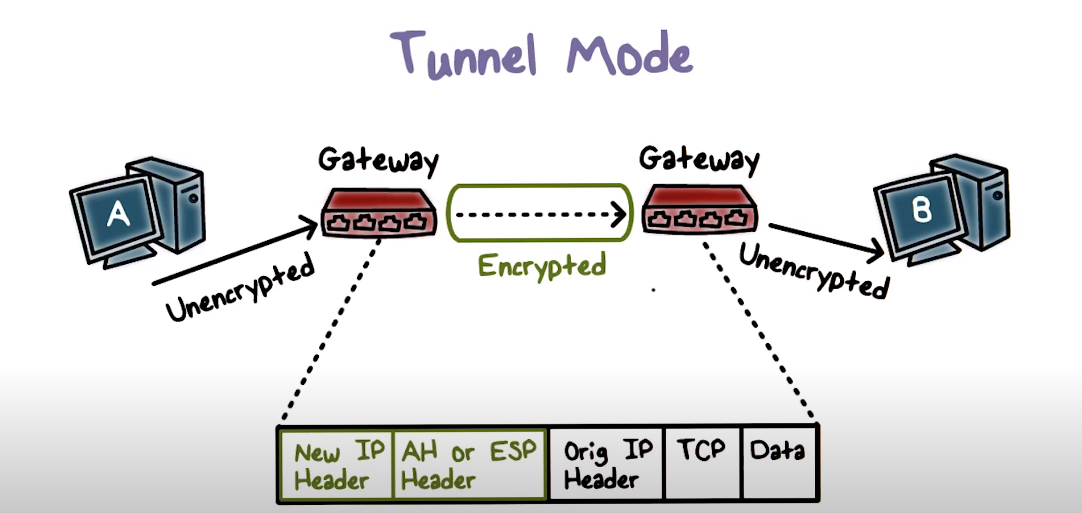
Tunnel Mode
Tunnel mode is one of the two modes of IPsec, the other being transport mode. In tunnel mode, the entire IP packet is encapsulated within another IP packet, adding an extra layer of security. This is commonly used when connecting two networks securely over the internet. In tunnel mode, the original IP packet is encrypted and then encapsulated within a new IP packet. The new IP packet has a different source and destination IP address, making it difficult for attackers to intercept or modify the original packet.
Transport Mode
Transport mode is one of the two modes of IPsec, the other being tunnel mode. In transport mode, only the payload of the IP packet is encrypted, while the IP header remains intact. This mode is commonly used for end-to-end communication between two hosts, providing data confidentiality and integrity.
IPsec Mode: Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
In IPsec’s transport mode, the payload of the IP packet is encrypted while the IP header remains unencrypted. This mode ensures data confidentiality and integrity for end-to-end communication between two hosts. The specific protocol used for encryption in transport mode is called Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP).
ESP in Tunnel Mode
In IPsec’s tunnel mode, both the IP header and the payload of the IP packet are encrypted. This mode is commonly used to create secure virtual private network (VPN) connections between two networks. The Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol is also used for encryption in tunnel mode.
ESP in Transport Mode
In IPsec’s transport mode, only the payload of the IP packet is encrypted while the IP header remains intact. This mode is typically used for end-to-end communication between two hosts. The Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol is used for encryption in transport mode.
IPsec Mode: Authentication Header (AH)
In IPsec’s transport mode, the payload of the IP packet is encrypted while the IP header remains intact. This mode is commonly used for end-to-end communication between two hosts. The Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol is used for encryption in transport mode. Another mode used in IPsec is the Authentication Header (AH), which provides authentication and integrity protection for the entire IP packet.
AH in Tunnel Mode
In IPsec’s tunnel mode, the entire IP packet, including both the IP header and payload, is encapsulated and encrypted. The Authentication Header (AH) protocol can also be used in tunnel mode to provide authentication and integrity protection for the entire IP packet. This mode is commonly used for secure communication between two networks or gateways.
AH in Transport Mode
In IPsec’s transport mode, the Authentication Header (AH) protocol provides authentication and integrity protection for the IP payload, but not the IP header. This mode is commonly used for secure communication between two hosts.
Choosing the Right IPsec Mode
When choosing the right IPsec mode, it is important to consider the specific requirements of your network or communication needs. The tunnel mode of the Authentication Header (AH) protocol is commonly used for secure communication between networks or gateways, as it provides authentication and integrity protection for the entire IP packet. On the other hand, the transport mode of AH is typically used for secure communication between two hosts, as it only provides authentication and integrity protection for the IP payload, not the IP header.
Comparison of Tunnel Mode, Transport Mode, ESP, and AH
Tunnel Mode:
– Used for secure communication between networks or gateways.
– Provides authentication and integrity protection for the entire IP packet, including the IP header and payload.
– Suitable for scenarios where the entire IP packet needs to be protected.Transport Mode:
– Used for secure communication between two hosts.
– Provides authentication and integrity protection for the IP payload only, not the IP header.
– Suitable for scenarios where only the payload needs to be protected.
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload):
– A protocol used for providing confidentiality, authentication, and integrity protection for IP packets.
– Can be used in both tunnel mode and transport mode.
– In tunnel mode, it encapsulates the entire IP packet, while in transport mode, it only encapsulates the payload.
AH (Authentication Header):
– A protocol used for providing authentication and integrity protection for IP packets.
– Can be used in both tunnel mode and transport mode.
– In tunnel mode, it protects the entire IP packet, while in transport mode, it protects the payload.
In summary, the tunnel mode of AH is commonly used for secure communication between networks or gateways, providing authentication and integrity protection for the entire IP packet.
Appropriate IPsec Mode Based on Requirements
Determining the appropriate IPsec mode based on requirements:
1. If secure communication between networks or gateways is required, the tunnel mode of AH is commonly used. It provides authentication and integrity protection for the entire IP packet.
2. If only the payload needs to be protected, the transport mode of AH can be used. It provides authentication and integrity protection for the payload.
Consider the specific requirements and choose the mode that best suits the desired level of security and protection for the IP packets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary purpose of IPsec modes?
The primary purpose of IPsec modes is to provide secure communication between networks or gateways by offering authentication and integrity protection for IP packets. The two modes, tunnel mode and transport mode, offer different levels of security and protection depending on the specific needs of the communication.
How does Tunnel Mode differ from Transport Mode?
Tunnel Mode and Transport Mode in IPsec differ in terms of the scope of protection they provide. Tunnel Mode encapsulates the entire IP packet within a new IP packet, adding IP header. This mode is typically used for secure communication between networks or gateways. It provides a higher level of security as the original IP packet is protected and hidden from the underlying network.
Which IPsec mode provides encryption for both the header and data?
The IPsec mode that provides encryption for both the header and data is Tunnel Mode.
Are ESP and AH mutually exclusive or can they be used together?
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) and AH (Authentication Header) are two different protocols used in IPsec. They can be used together in IPsec to provide both encryption and authentication for IP packets. They are not mutually exclusive and can be used in combination to enhance the security of IP communication.
Conclusion
Based on the requirements provided, it is recommended to use the tunnel mode of AH for secure communication between networks or gateways. This mode provides authentication and integrity protection for the entire IP packet. If only the payload needs to be protected, the transport mode of AH can be considered, as it provides authentication and integrity protection for the payload. The choice between the two modes should be based on the desired level of security and protection for the IP packets.
